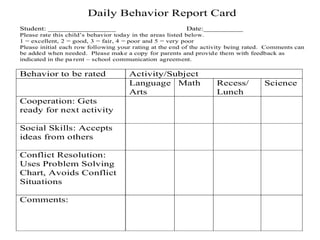
The document discusses strategies for supporting children with special needs in developing social skills, emphasizing the significance of social competence for positive peer relationships and overall well-being. It outlines practical methods like social narratives, direct teaching, and modeling to enhance pro-social behaviors such as cooperation, empathy, and self-control. The guide also advocates for collaboration with educators and tailoring intervention plans to suit individual children's experiences and needs.