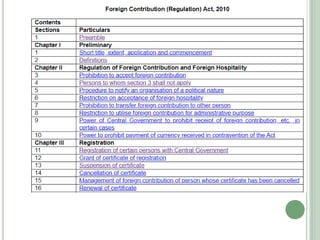
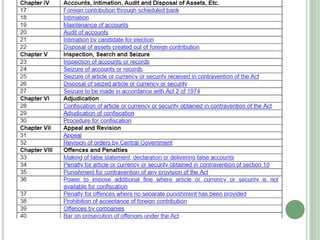
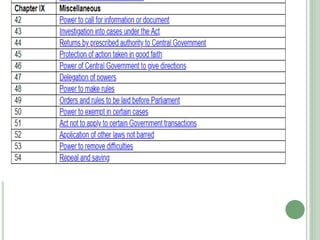
This document discusses the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA) of 2010 in India. The key points are:
1) The FCRA regulates acceptance and use of foreign contributions by NGOs, individuals, and other organizations in India. It aims to ensure foreign funds are used for their intended purposes and not for any detrimental activities.
2) Under the FCRA, foreign contribution is defined as donations, goods, or securities from foreign sources above a specified value. Income from such contributions is also considered foreign contribution.
3) NGOs, trusts, societies, companies, and individuals must be registered under the FCRA to legally accept foreign contributions. The registration process involves submitting documents