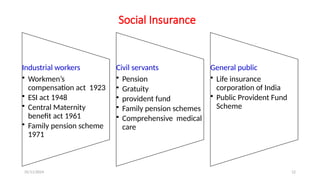
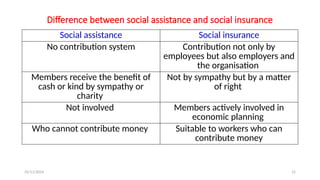
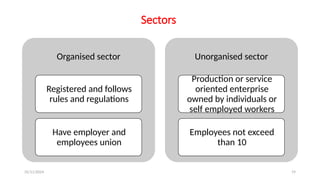
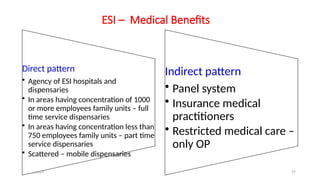
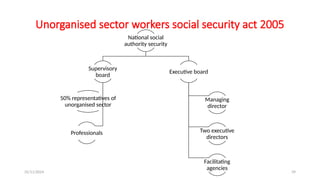
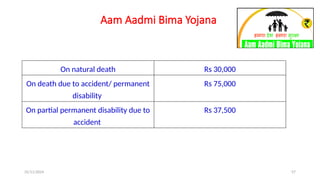
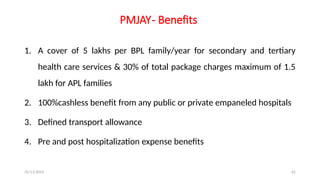
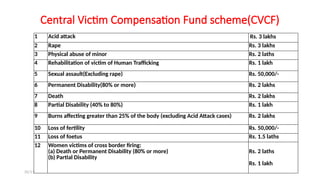
The document discusses various social security measures aimed at providing protection to different segments of society, including industrial workers, civil servants, and the general public. It covers aspects such as social insurance and assistance, outlining key benefits and schemes like maternity benefits, health insurance, and pension plans. Additionally, it highlights the differences between social insurance and assistance, as well as specific programs targeted at unorganized sector workers and rural populations.