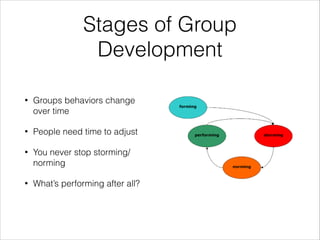
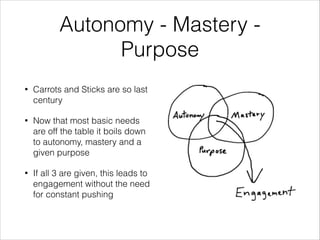
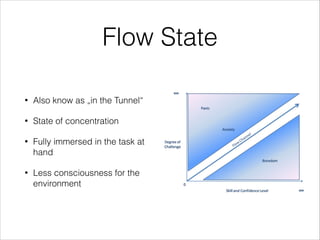
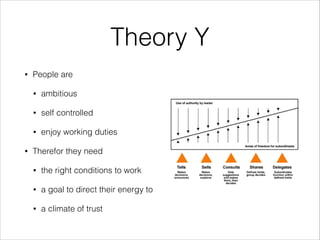
The document emphasizes that success in senior developer or team lead roles hinges on effective teamwork and motivation rather than solely on technical skills. It discusses various psychological and communication theories, such as Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and non-violent communication, to promote understanding and collaboration within teams. Practical applications and strategies for fostering a supportive work environment and enhancing group dynamics are also outlined.