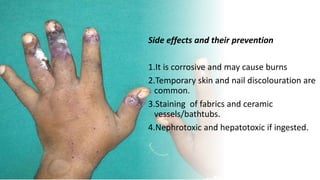
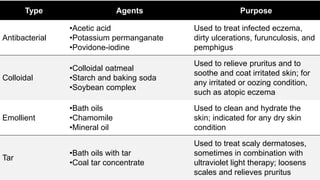
This document discusses various soaks and baths used in dermatology. It describes Condy's soaks using potassium permanganate which acts as an astringent, oxidizing agent, and anti-inflammatory. Acetic acid soaks are also described, noting their mechanisms of action include enhancing lipid solubility and lowering pH. Other soaks mentioned include hydrogen peroxide, PUVA, saline, aluminum subacetate, and EUSOL. Bath types discussed are antibacterial, colloidal, emollient, and tar baths. Common conditions treated include infected wounds, eczema, ulcers, and scaly dermatoses. Precautions and side effects are also provided.