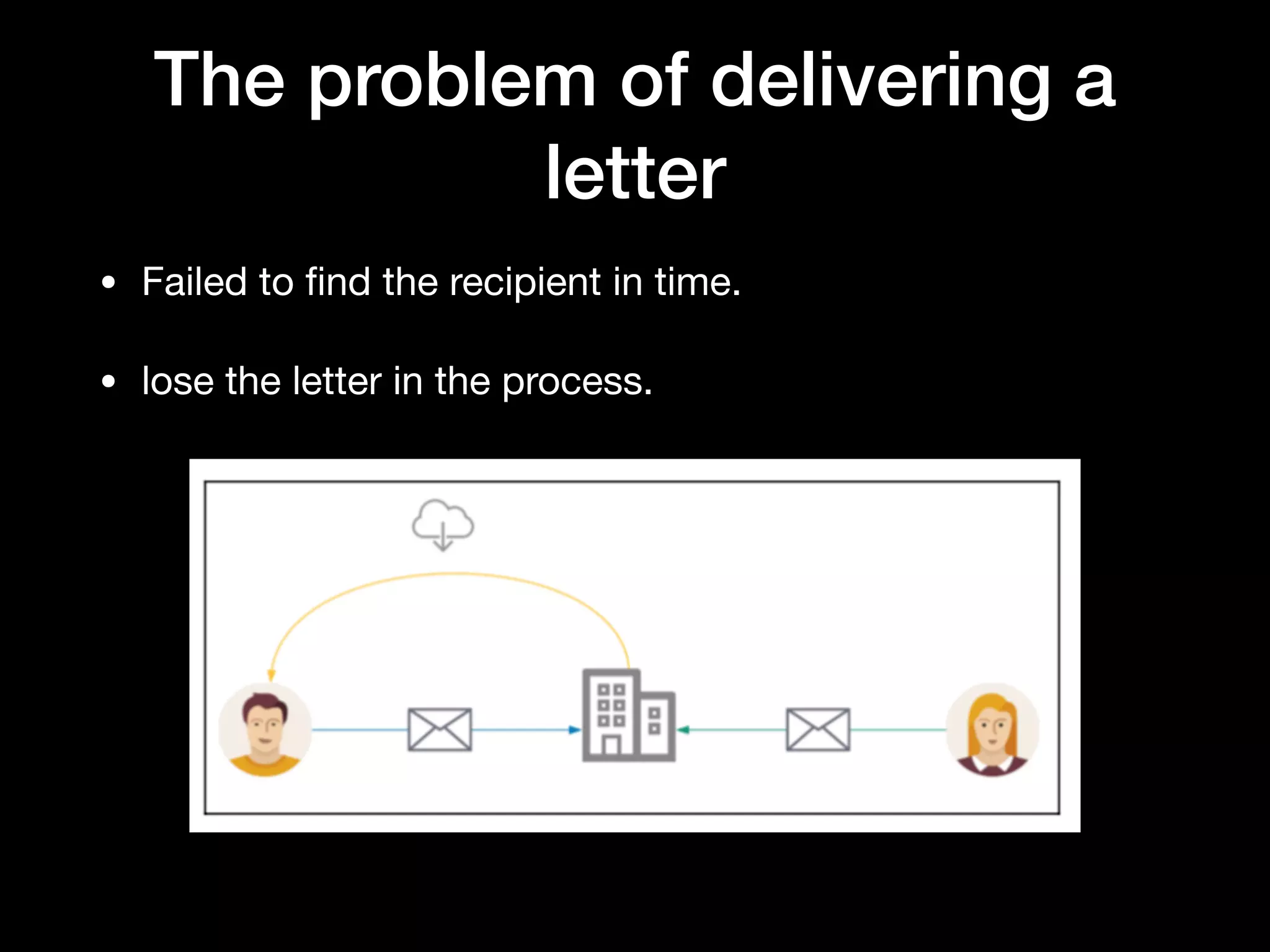
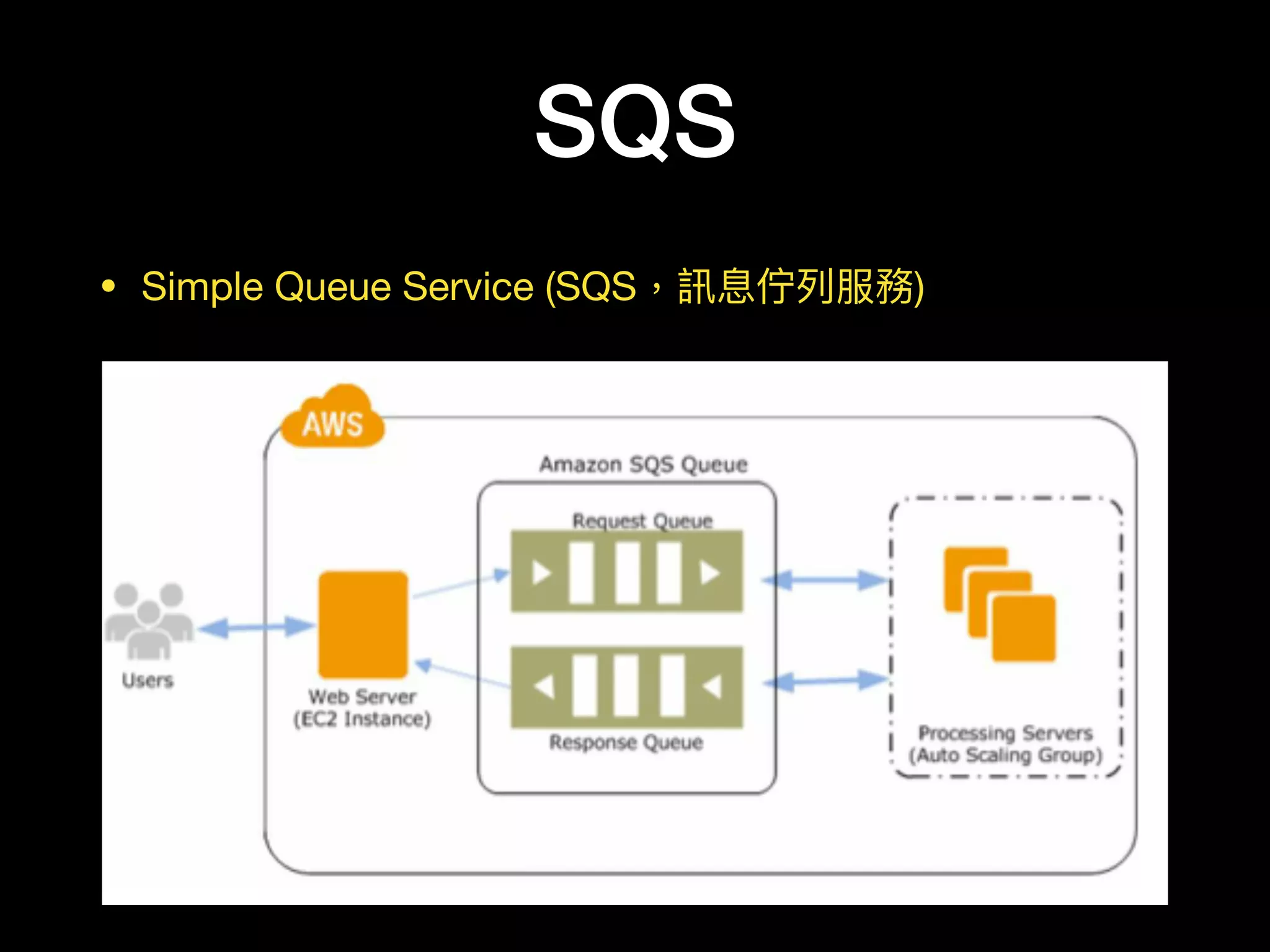
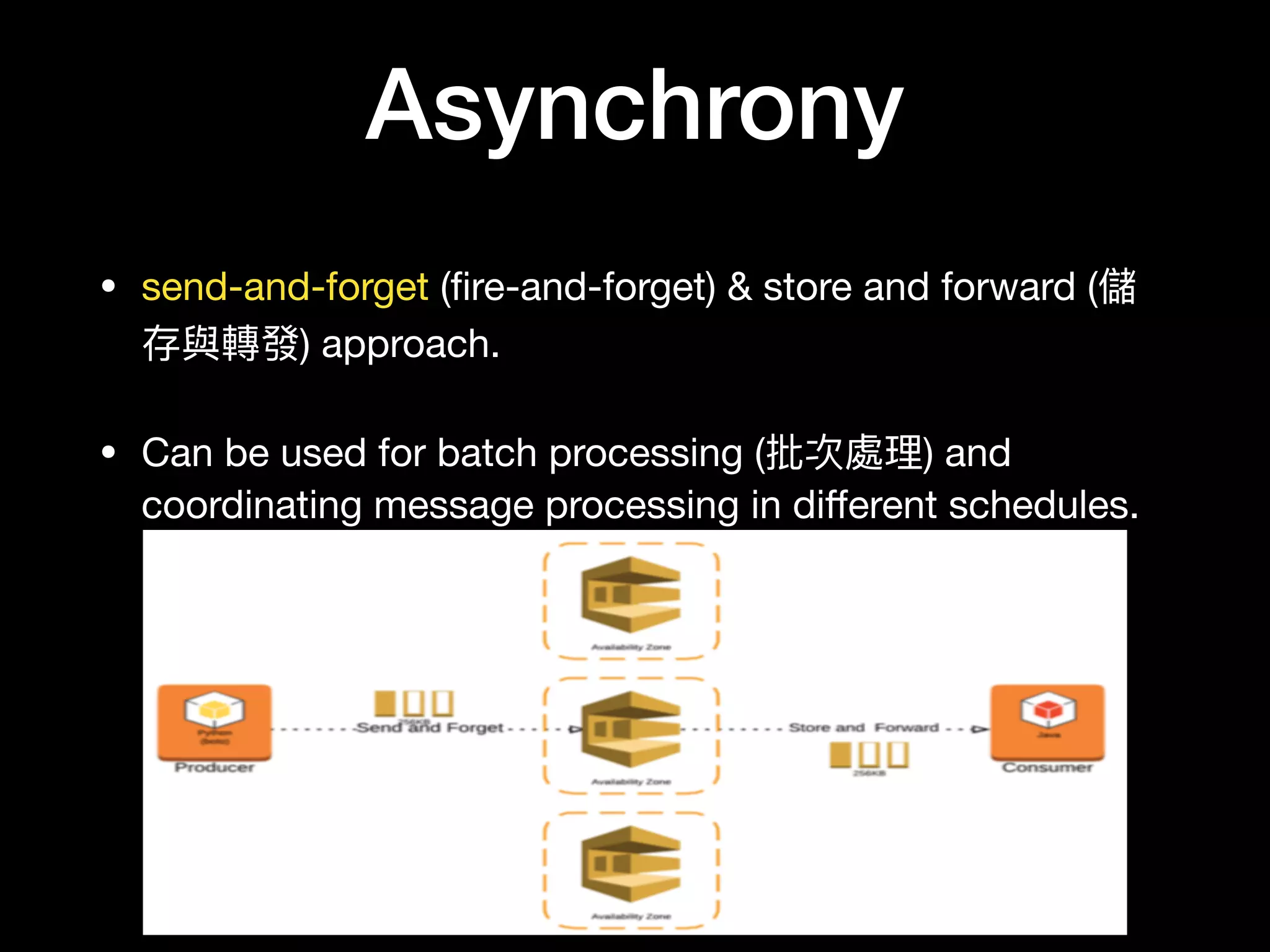
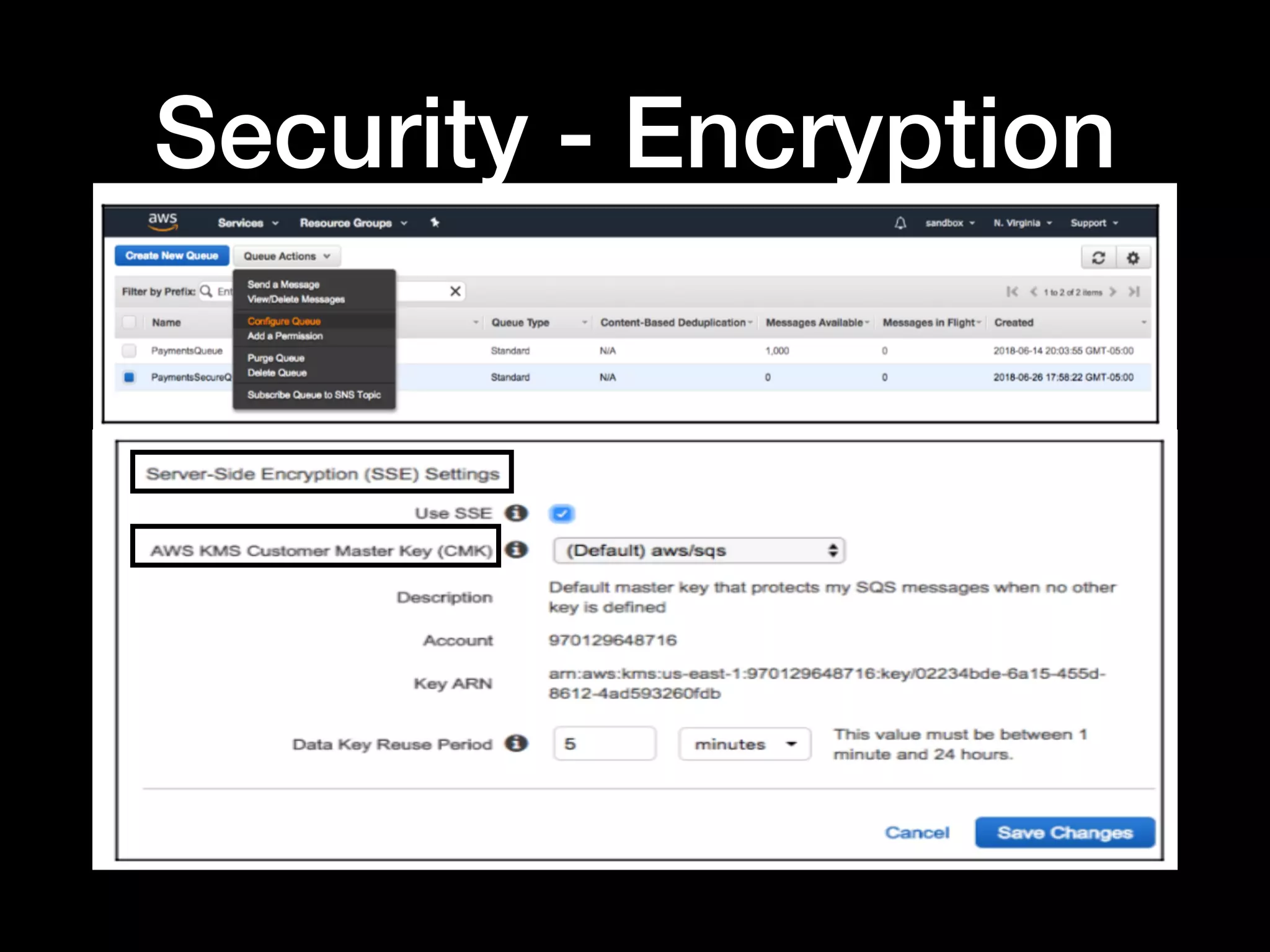
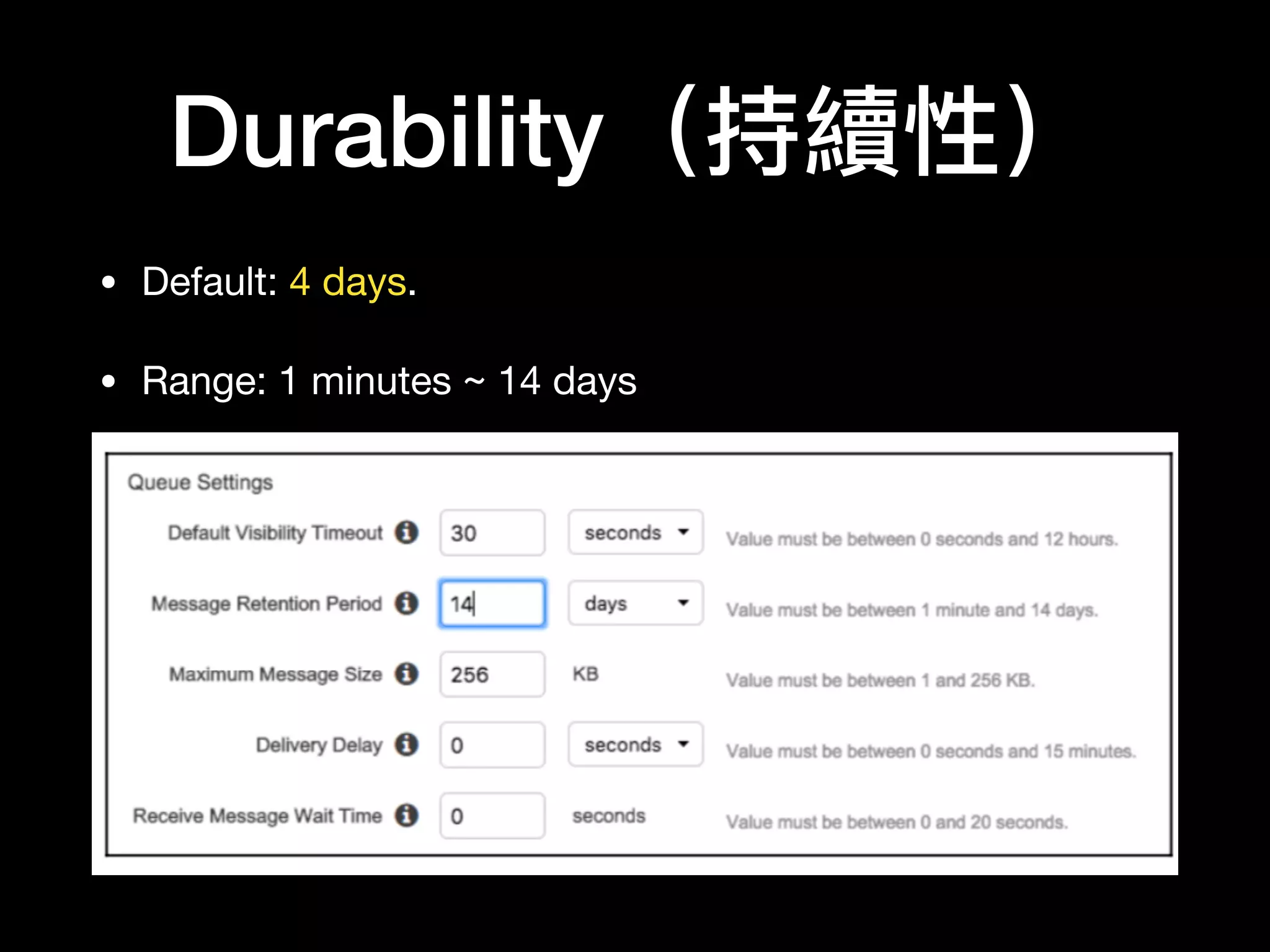
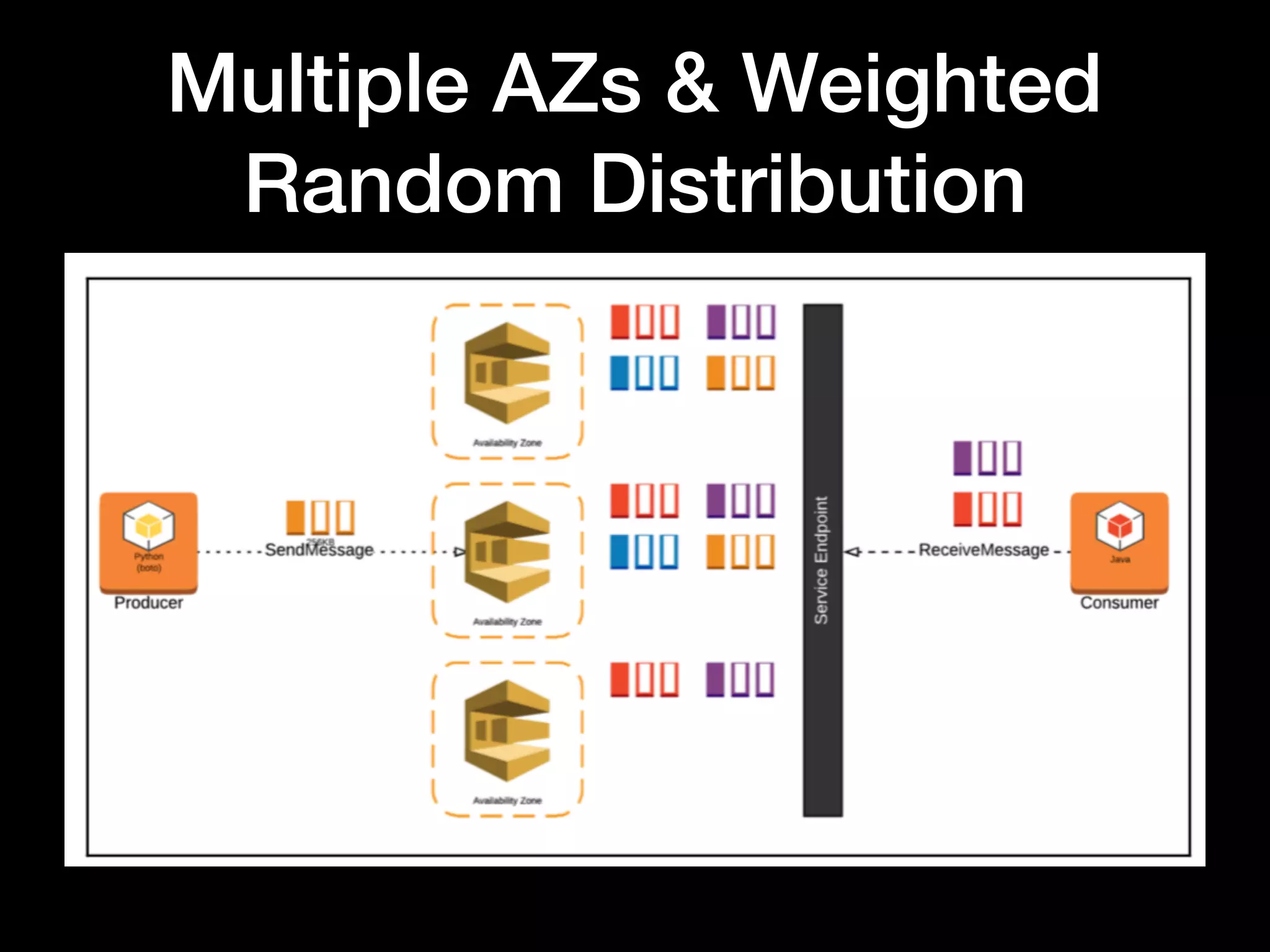
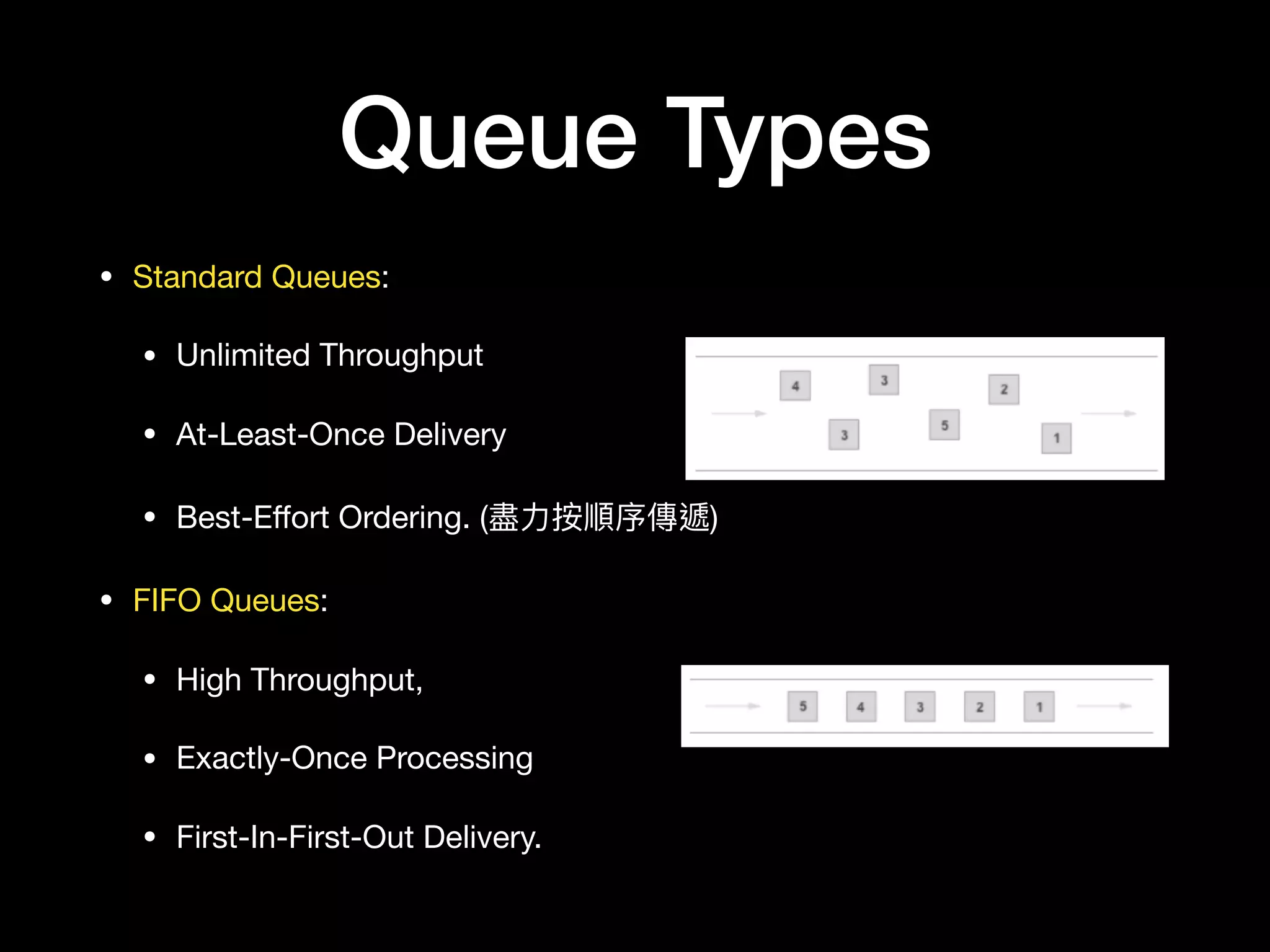
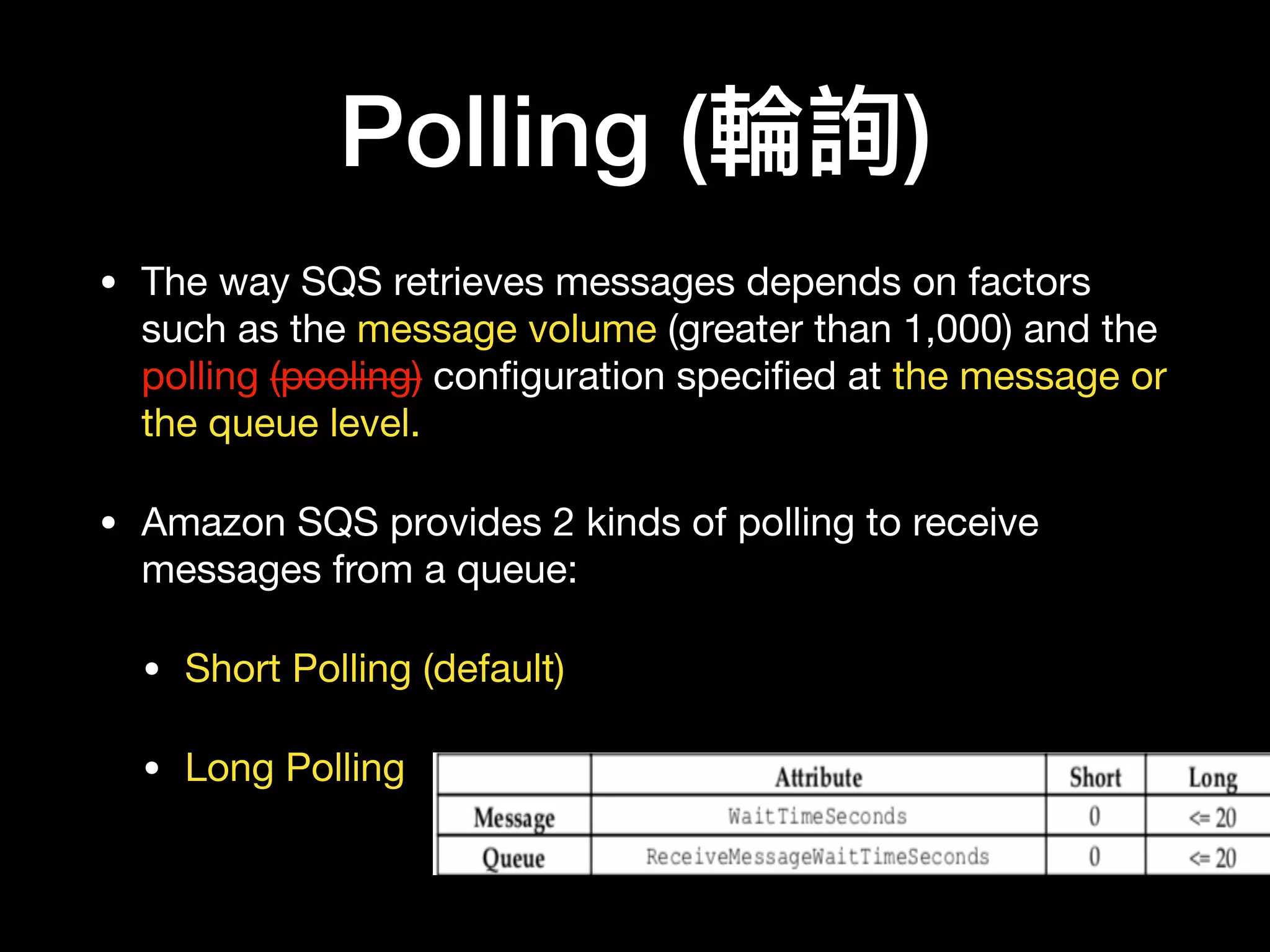
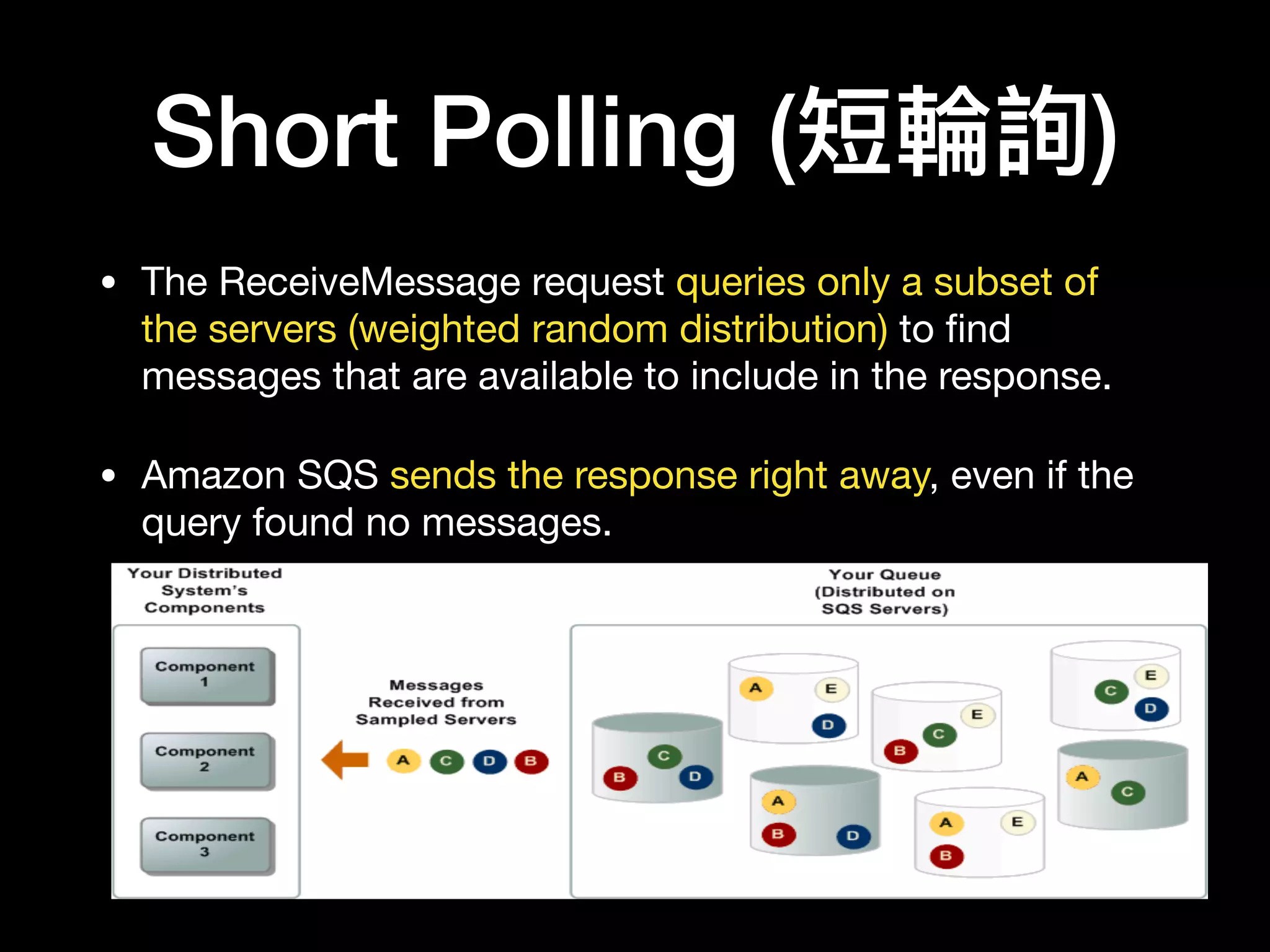
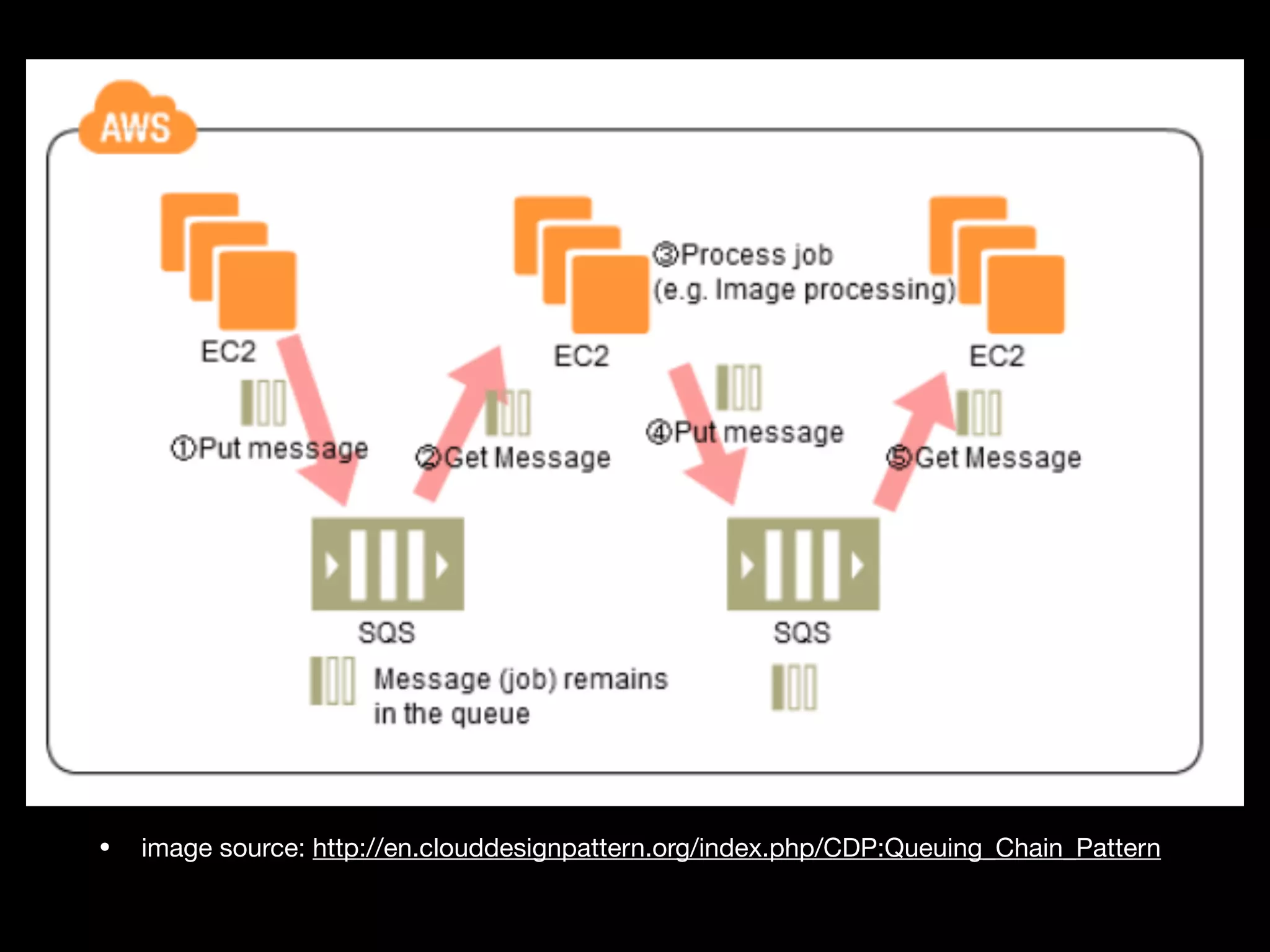
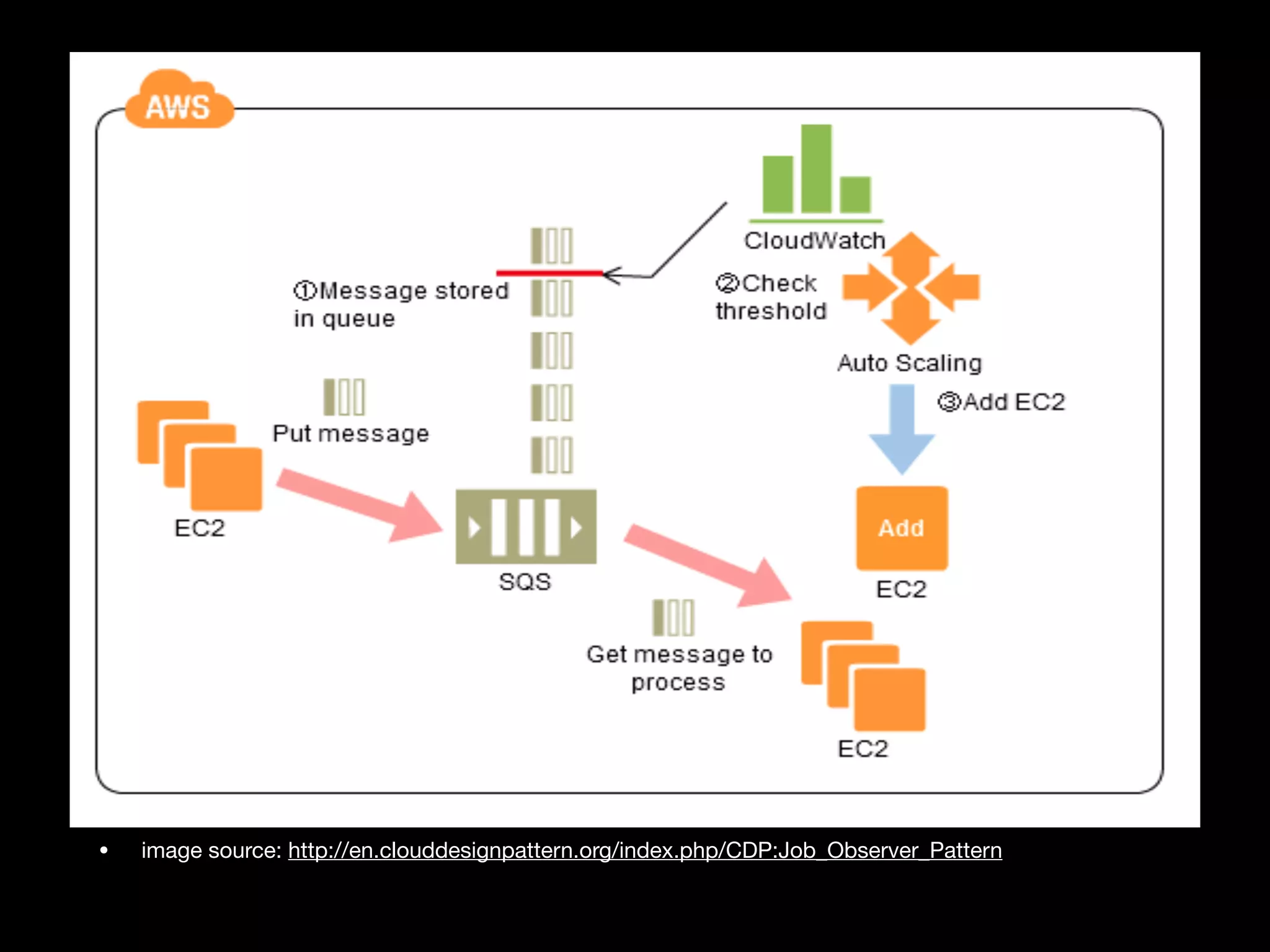
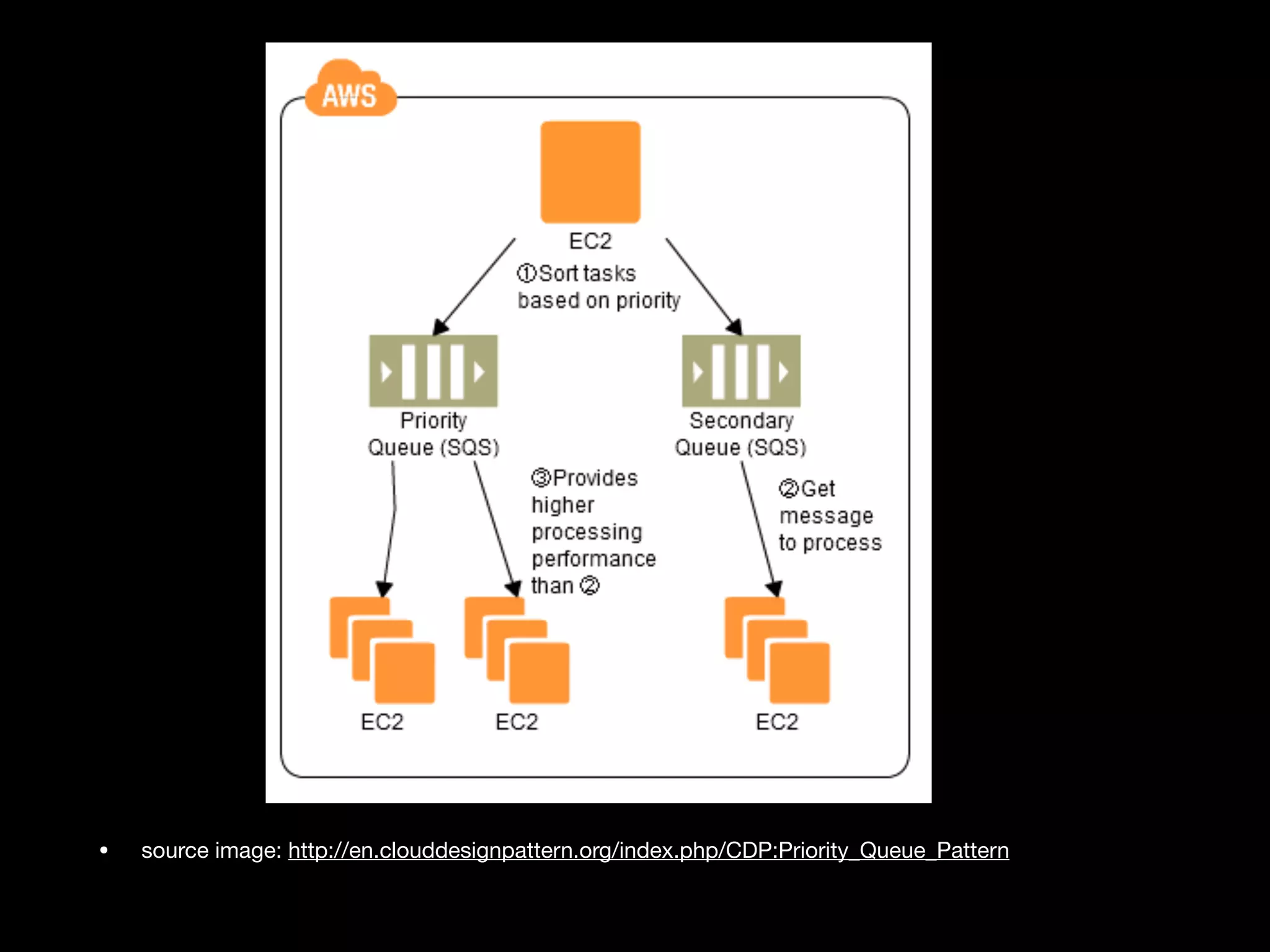
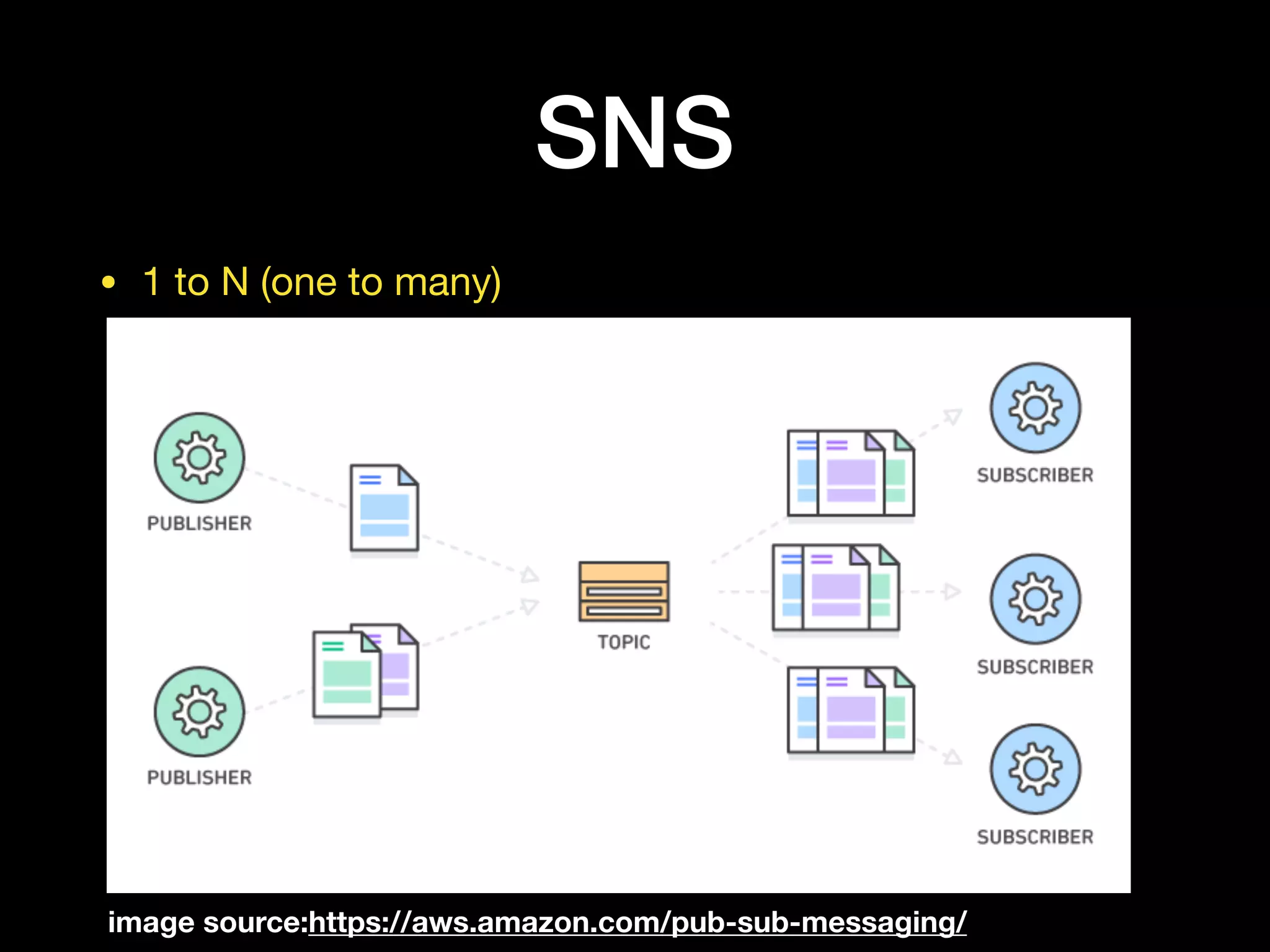
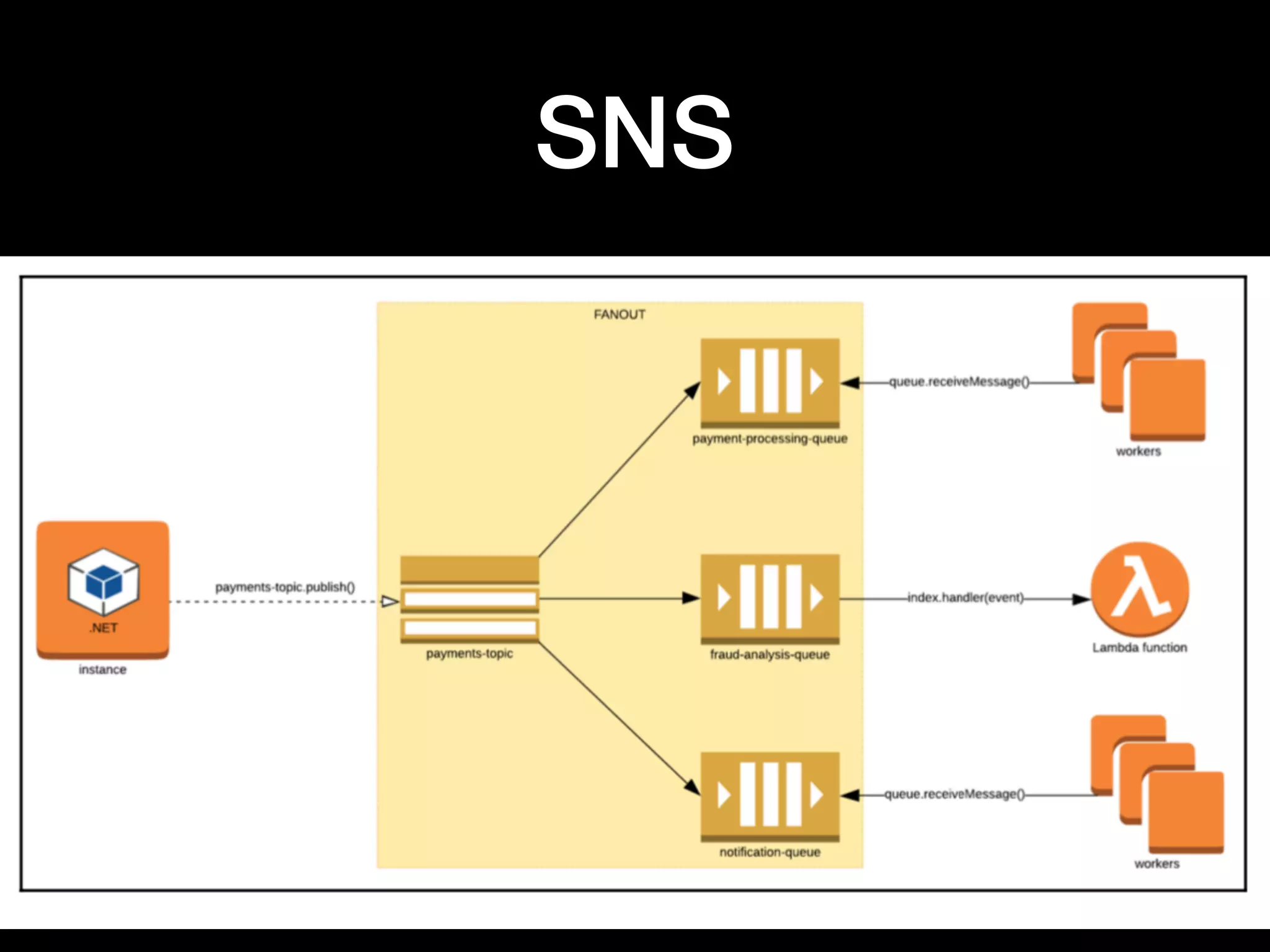
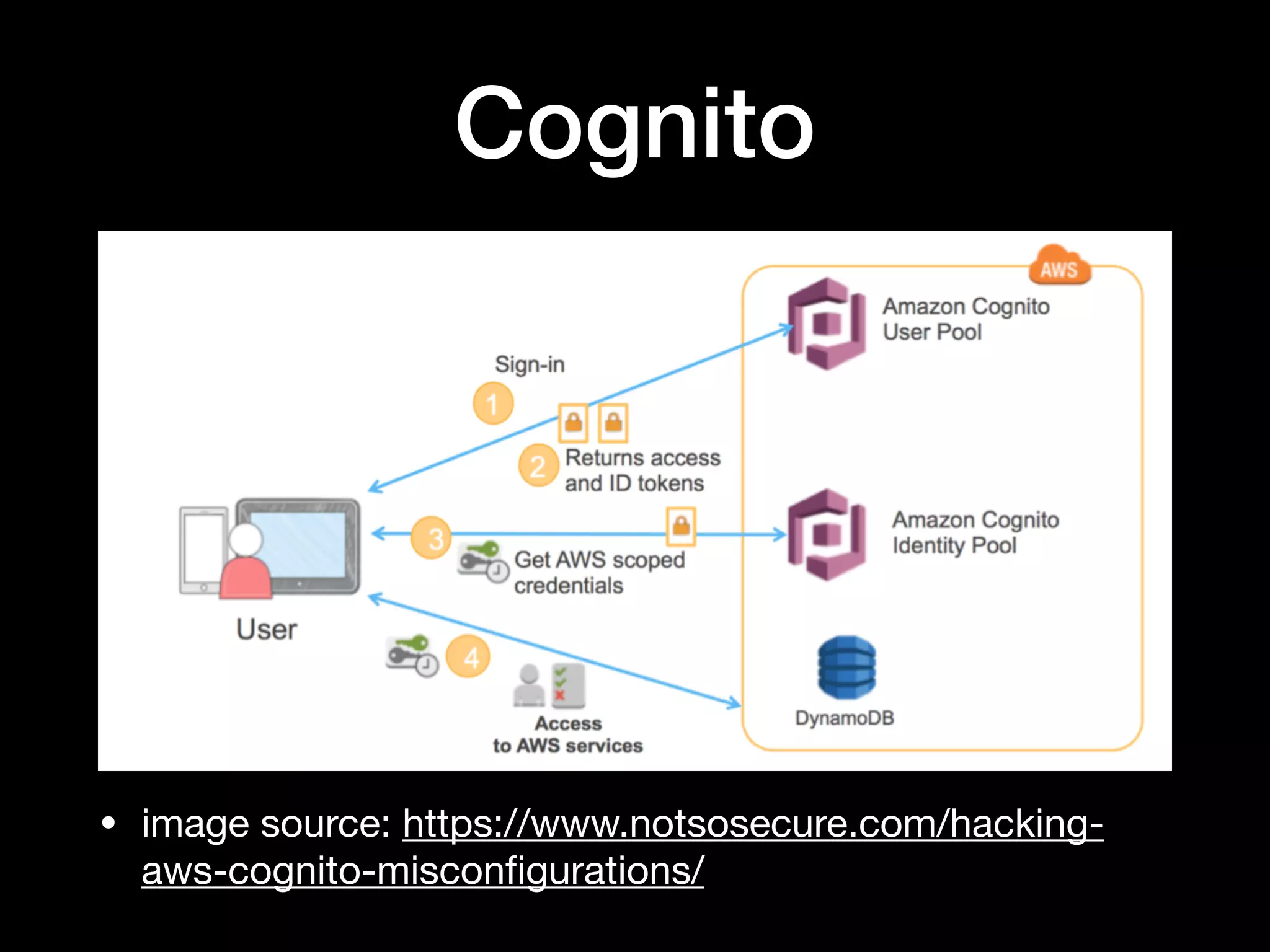
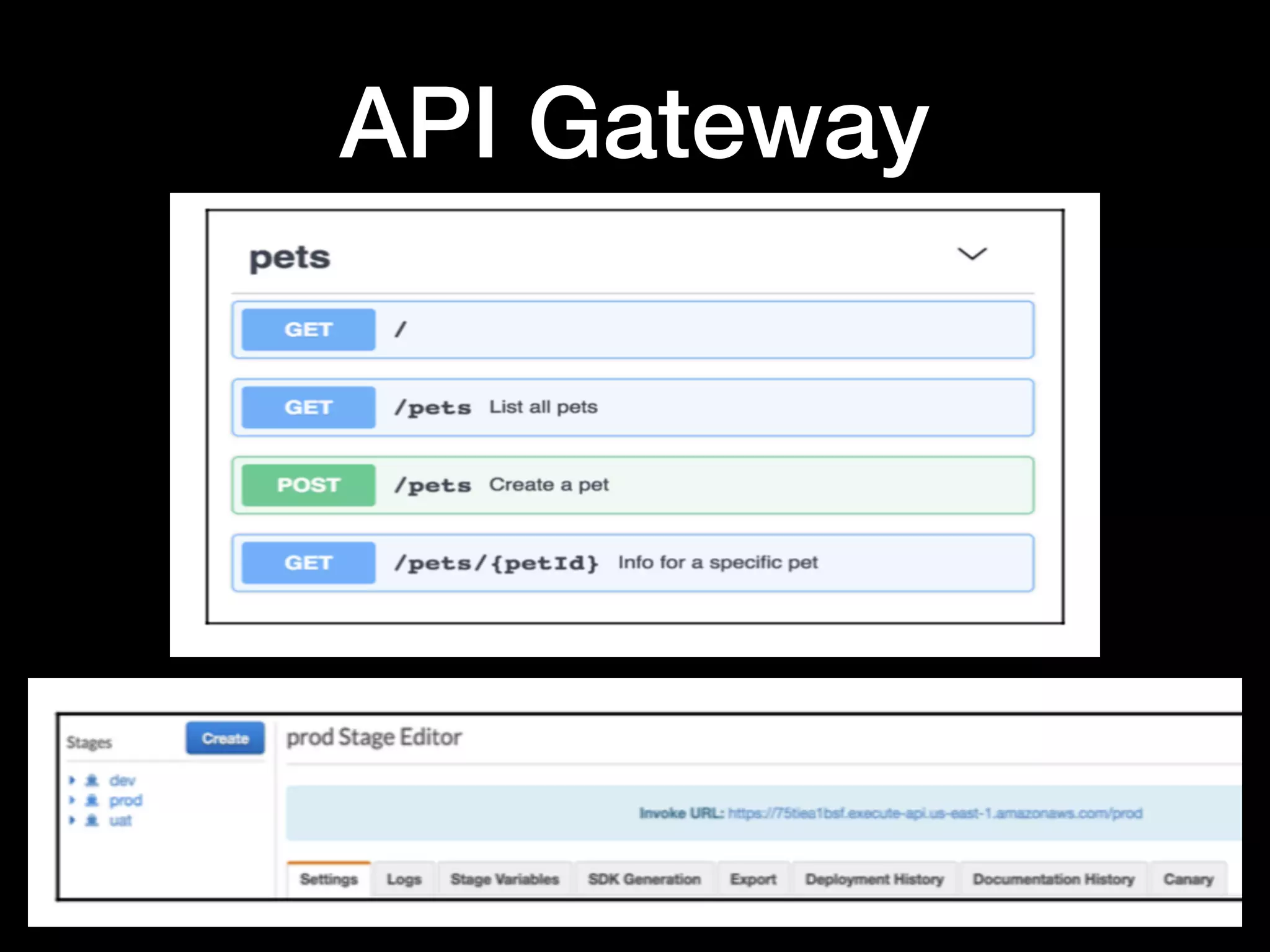
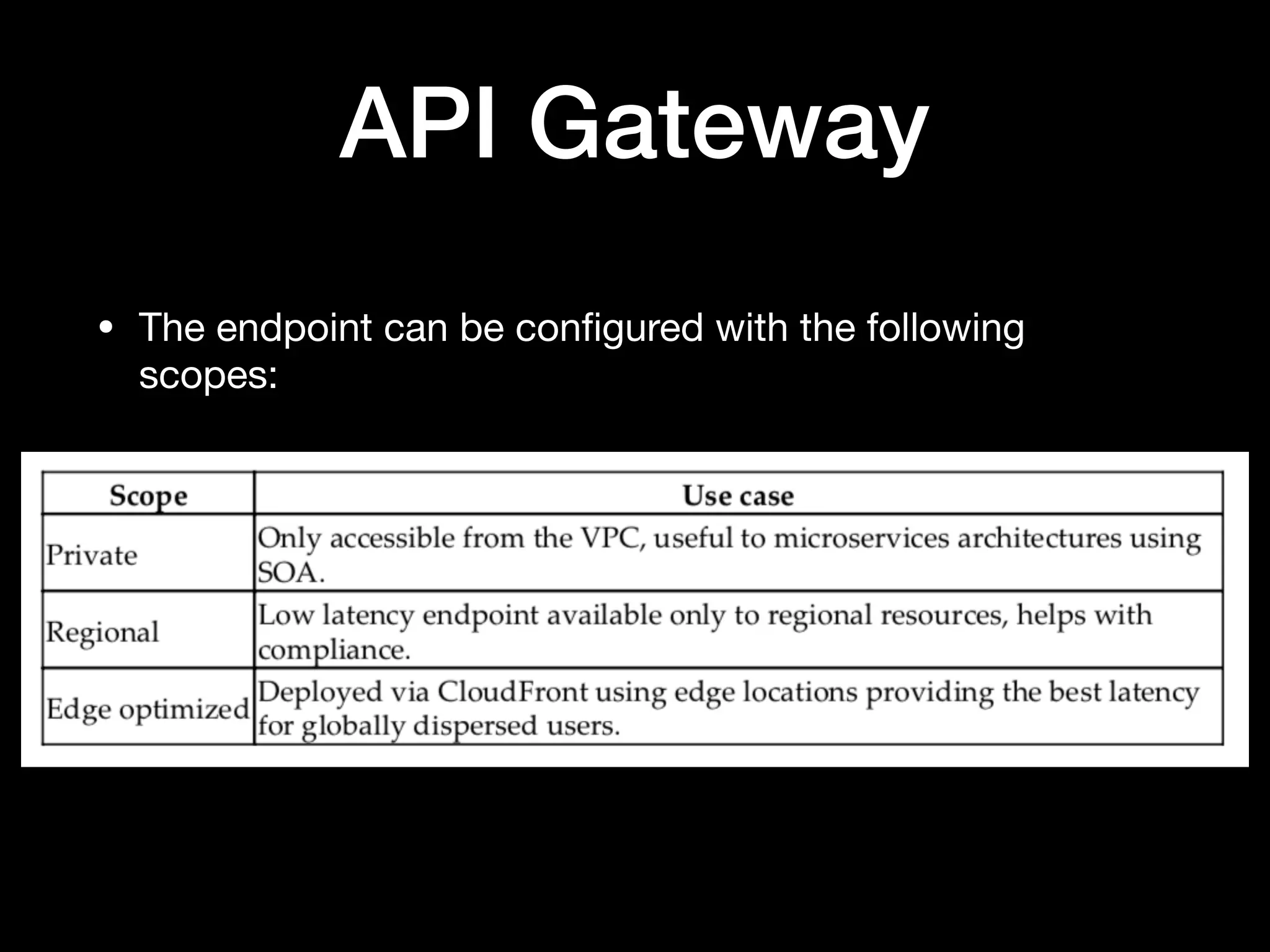
This document provides an overview of several AWS application services including SQS, SNS, Cognito, API Gateway, and WebSockets. It describes how SQS uses queues to asynchronously and reliably deliver messages between distributed components. SNS is a pub/sub messaging service that decouples systems using an event-driven model. Cognito provides authentication, authorization, and user management for web and mobile apps. API Gateway acts as a facade and endpoint for RESTful APIs. WebSockets in AWS can enable real-time communication using services like IoT and AppSync.