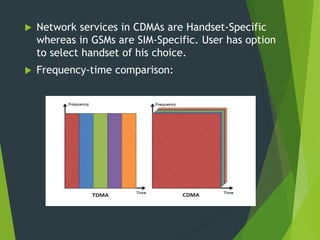
The document provides an overview of SMS and MMS technologies, explaining their definitions, functionalities, and protocols. SMS allows for text messaging using GSM and CDMA technologies, while MMS enables multimedia communications, including images and video. It also outlines the advantages and disadvantages of both services, illustrating their respective limitations and capabilities.