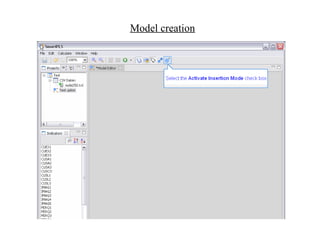
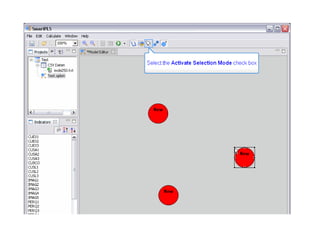
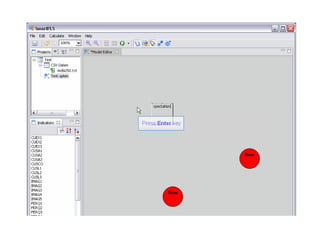
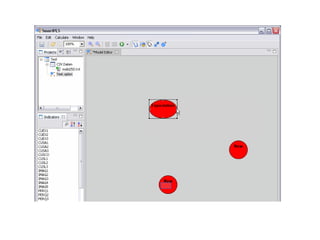
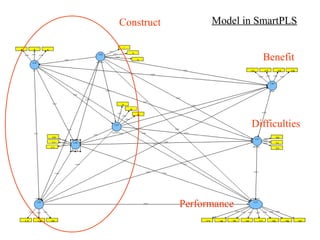
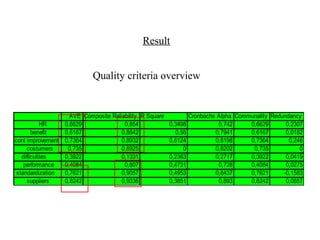
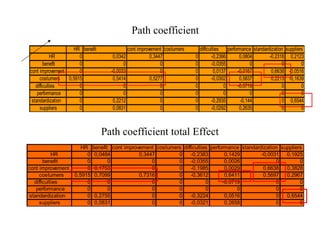
The document provides comprehensive resources on structural equation modeling and path analysis using SmartPLS software. It includes an overview of software features, examples of model design, and detailed explanations of statistical concepts like correlation, latent variables, and reliability metrics. Additionally, it presents tutorials, data input guidance, and quality criteria for analyzing results.