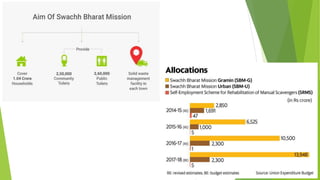
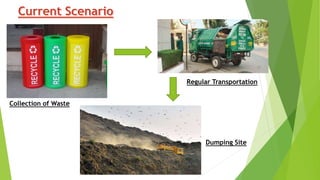
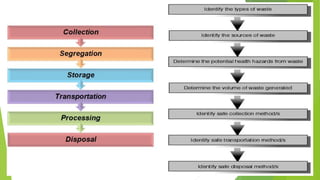
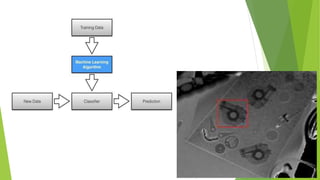
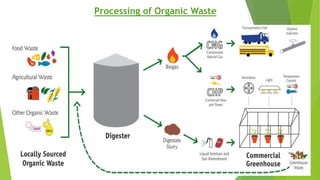
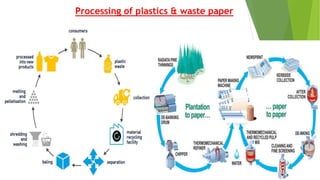
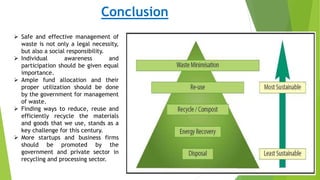
The document discusses India's municipal solid waste problem. It notes that only 29% of collected waste is treated. Most cattle in India ingest plastics from waste. It proposes using IoT, AI, computer vision, and other technologies to better monitor, segregate, store, transport, and process waste. The government of India has initiatives like Swachh Bharat Abhiyan but more funding and individual participation is still needed. Startups are working on waste management but it remains a key challenge. The conclusion emphasizes the social responsibility to safely and effectively manage waste.