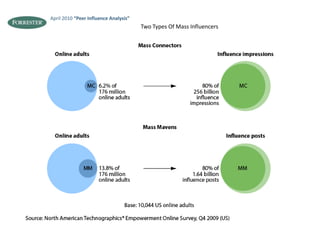
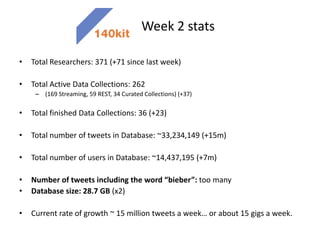
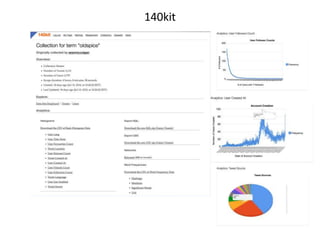
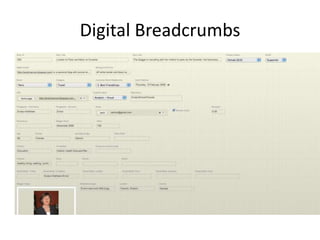
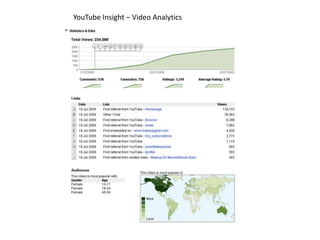
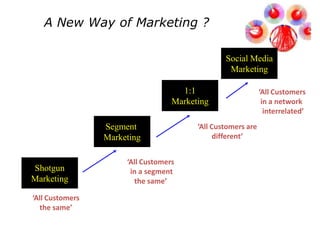
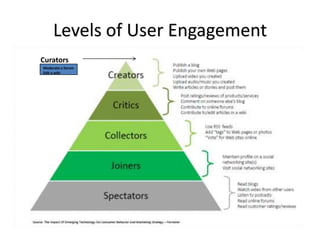
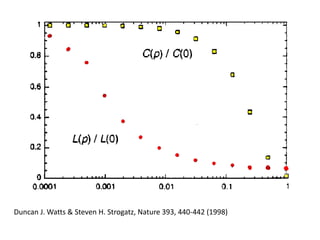
The document discusses what a small-world network is and provides context around the term. It references a 1967 psychology today article by Suresh Sood and Michael Light that may have originally coined the term. It also mentions that in 1991, the concept was popularized by studying social networks and the phenomenon of six degrees of separation. The small-world phenomenon shows that most people are connected through short chains of acquaintances.




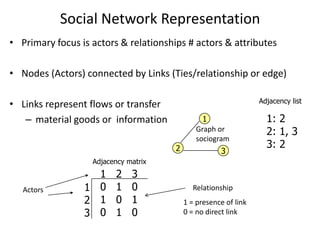
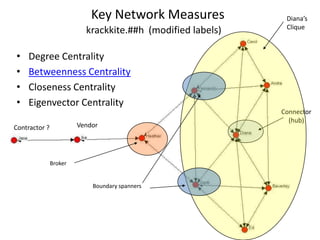





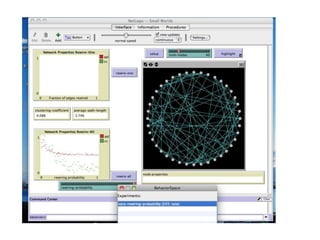




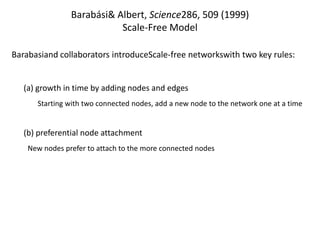
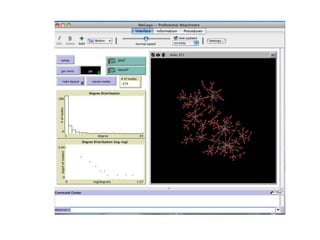
![Duncan Watts - The “New” Science of Networks Annu. Rev. Sociol. 2004. 30:243–70Goal to make “substantial progress on a number of previously intractable problems, reformulating old ideas, introducing new techniques, and uncovering connections between what had seemed to be quite different problems” [Examples of intractable problems - analysis of large-scale, complex networks, the study of the evolution and transformation of complex networks over time, the study of how information, innovations, disease, cultural fads flow/move through complex networks. Old ideas - affiliation networks, the small-world problem and community structure. New techniques - discrete mathematics, the power law, cellular automata and agent-based modelling. Cross-disciplinary connections - similarities in network structure at different levels of scale, from a protein to a human organization to an ecosystem. ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smallworldprezzoetalii-100808193746-phpapp01/85/Small-Worlds-Social-Graphs-Social-Media-31-320.jpg)