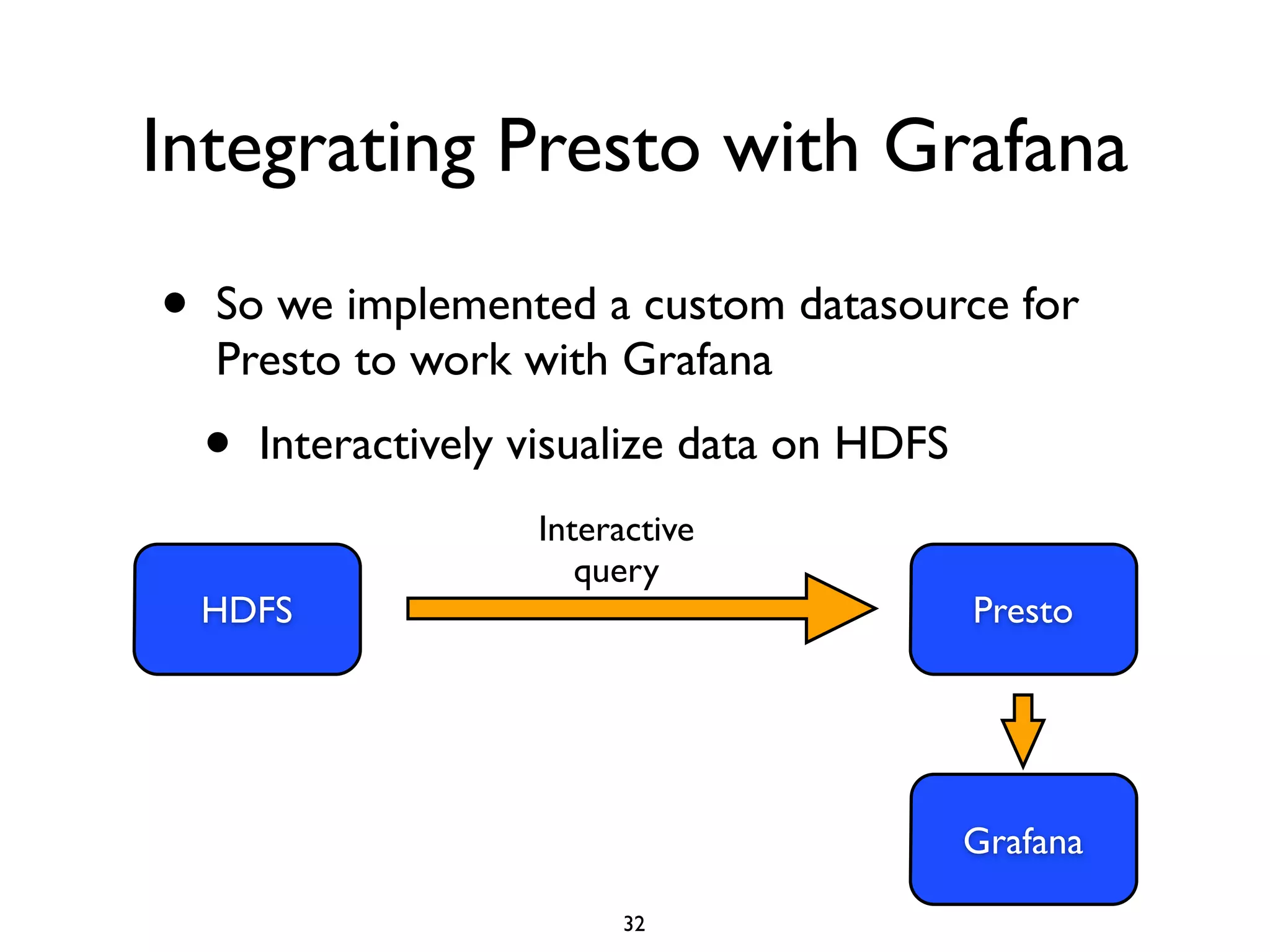
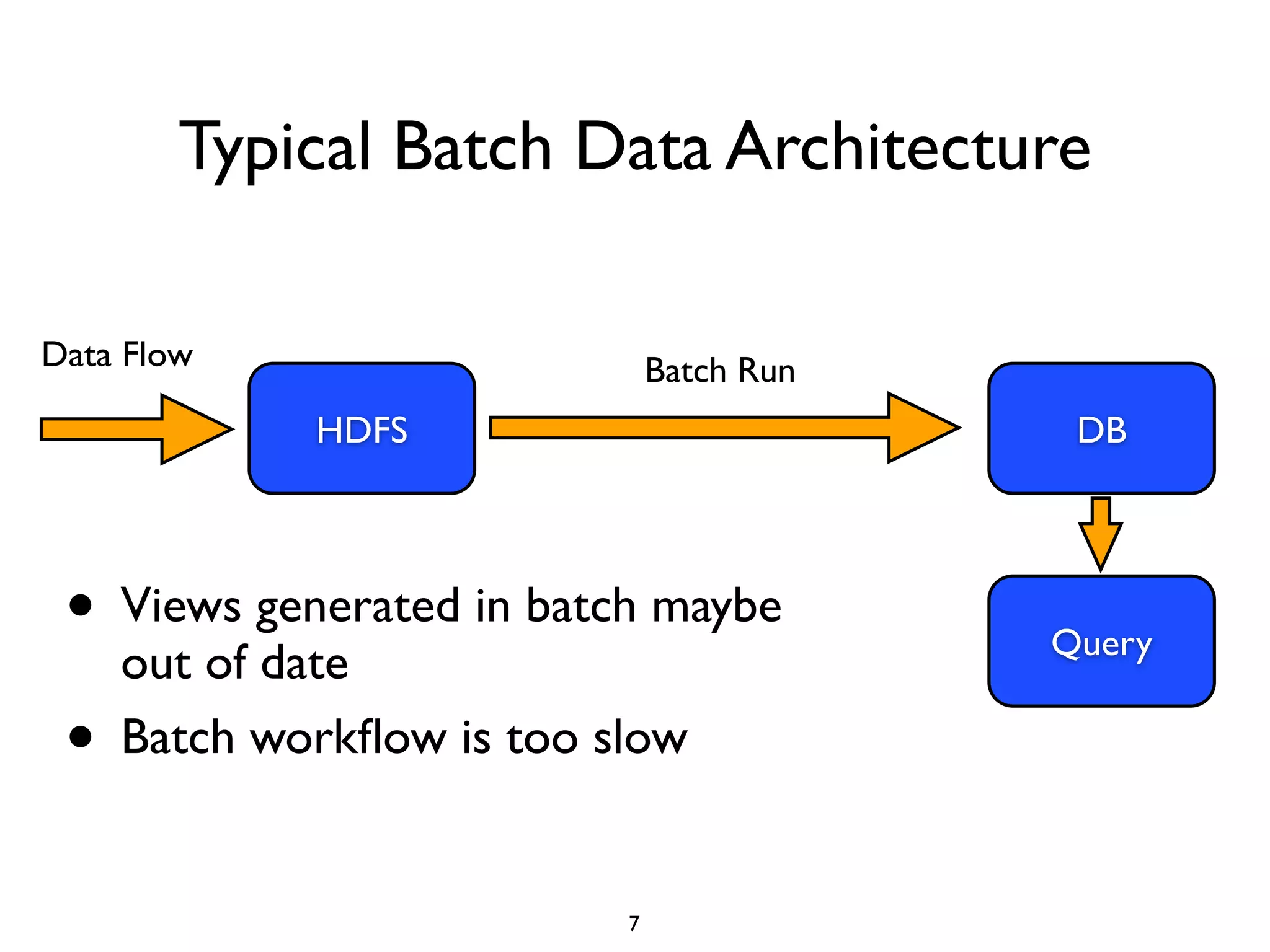
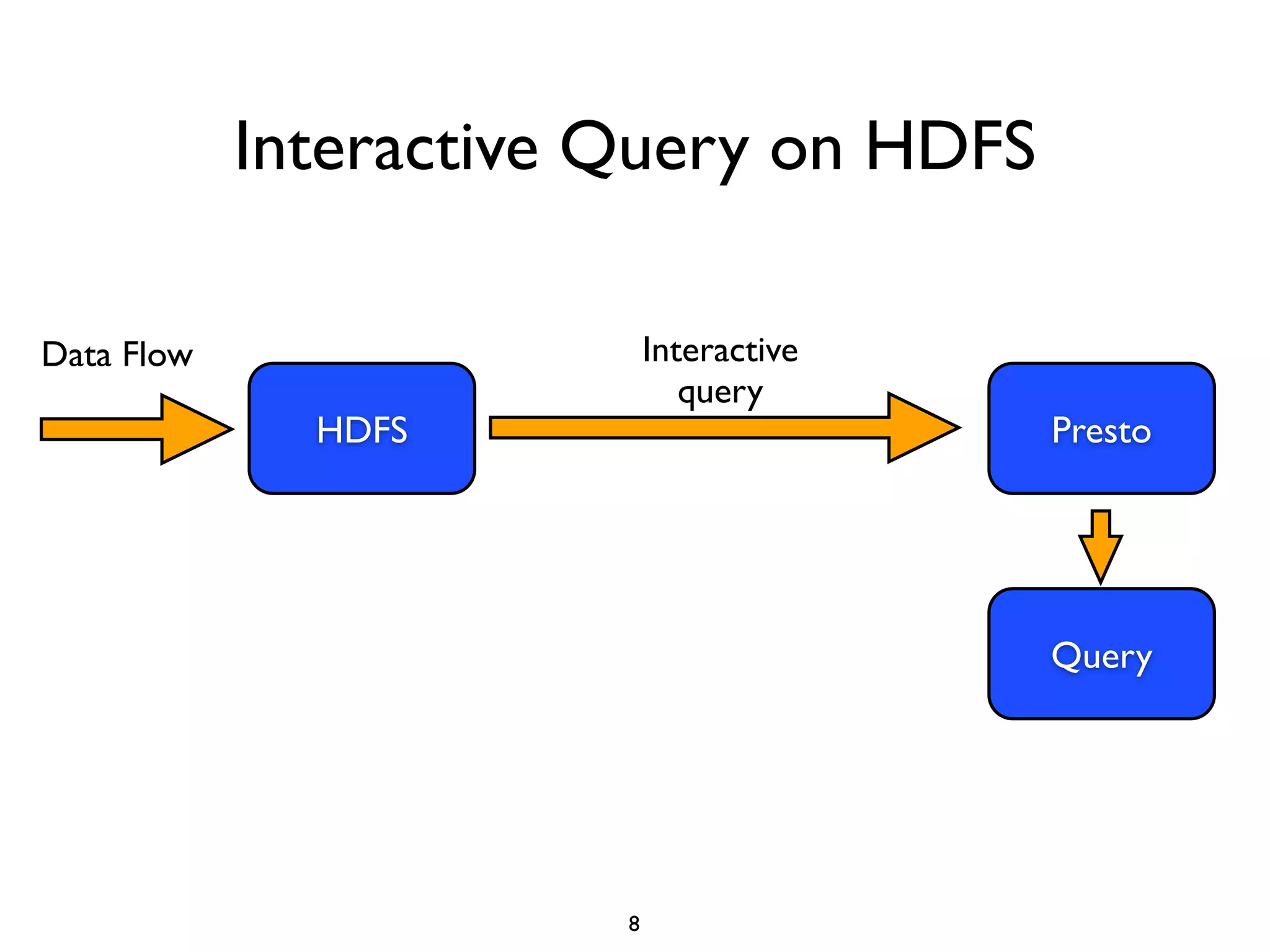
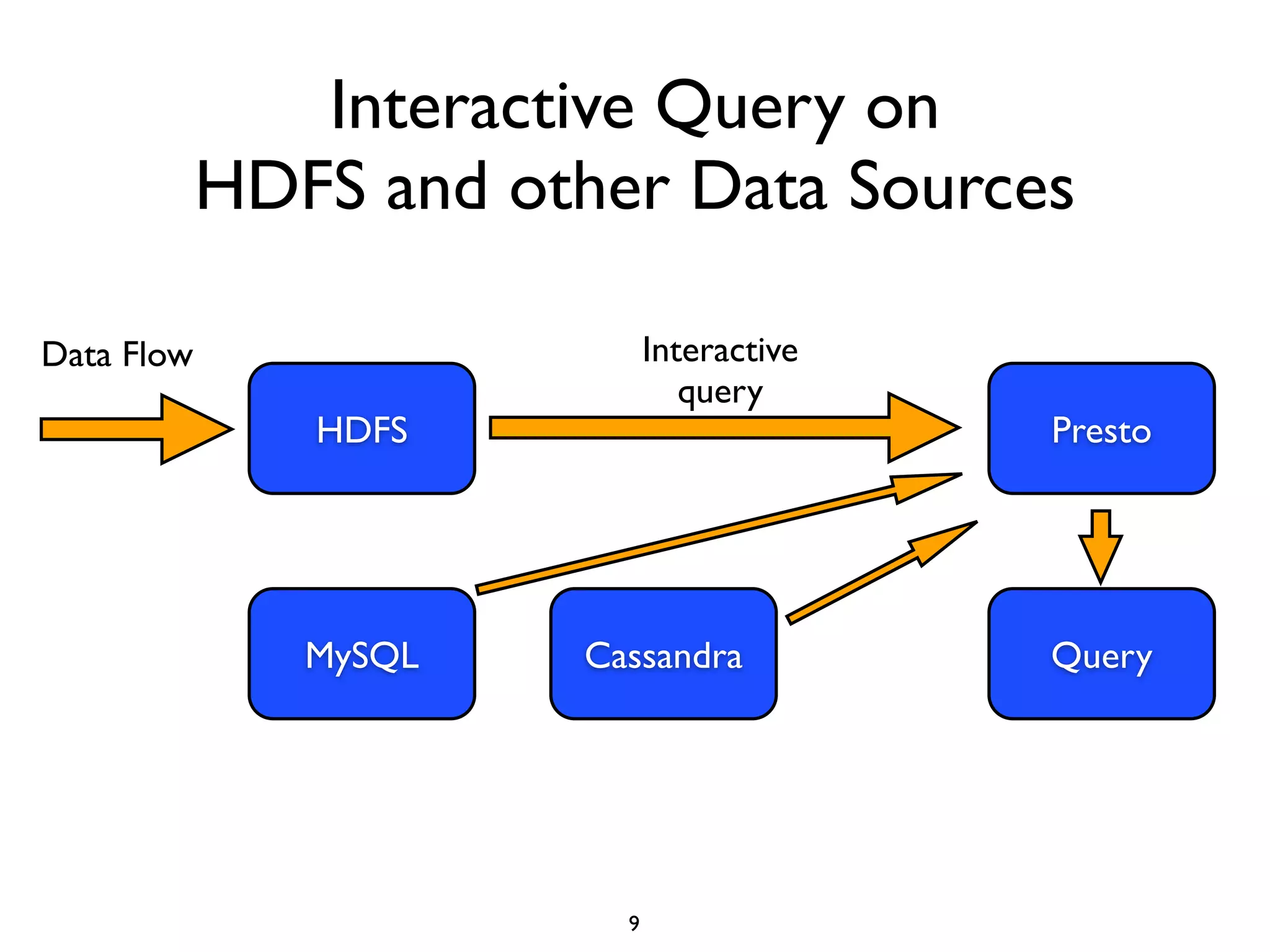
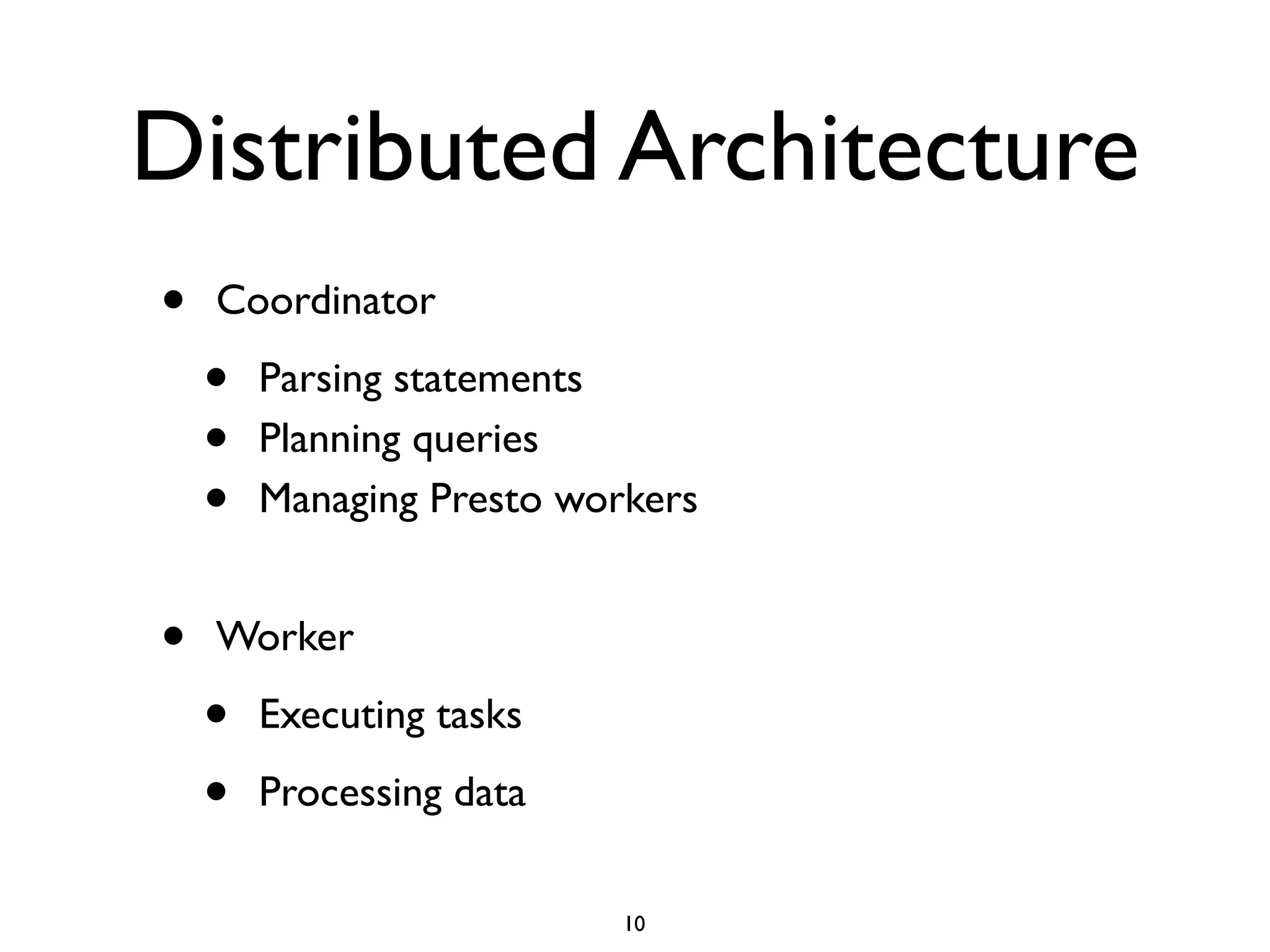
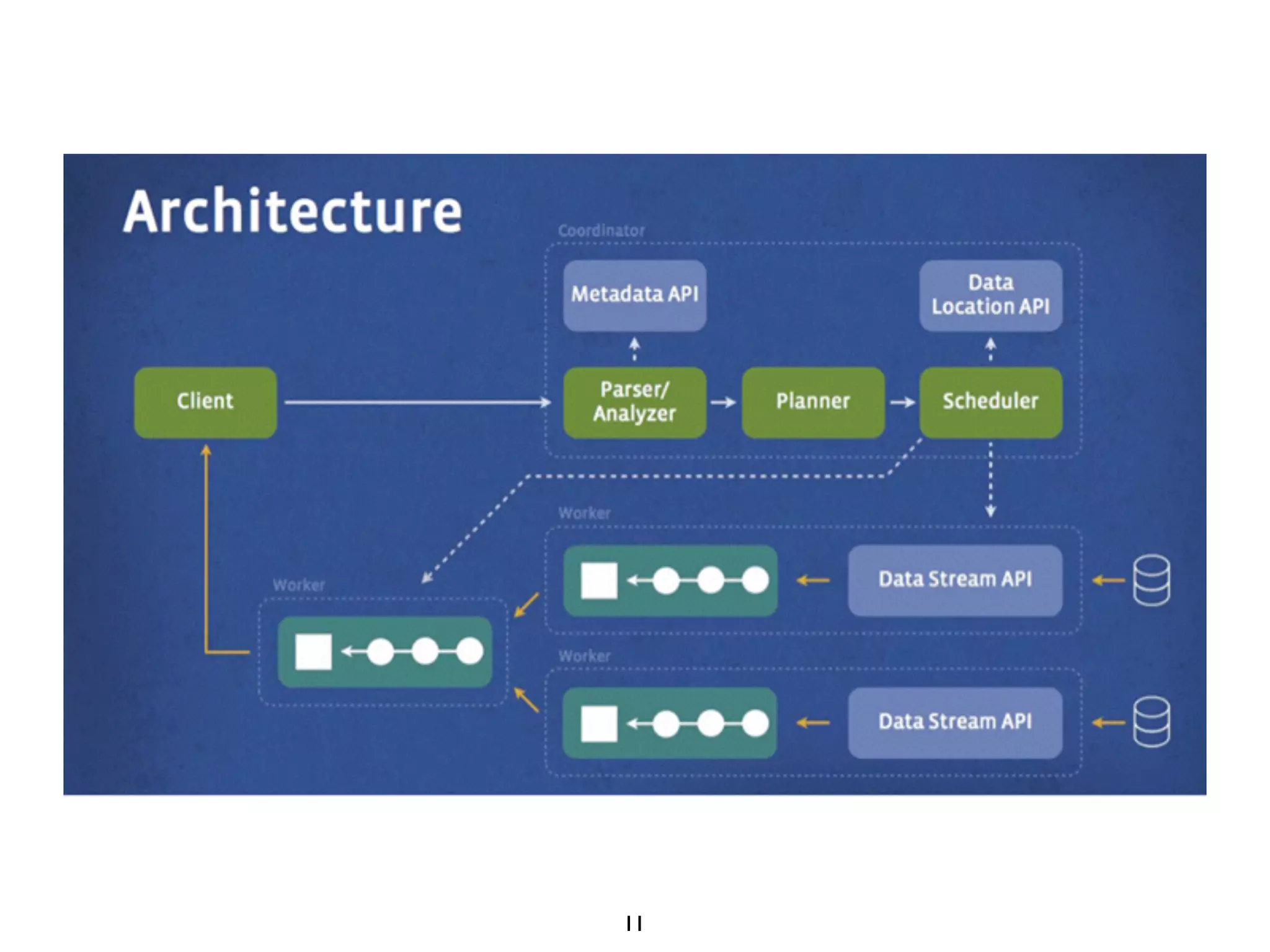
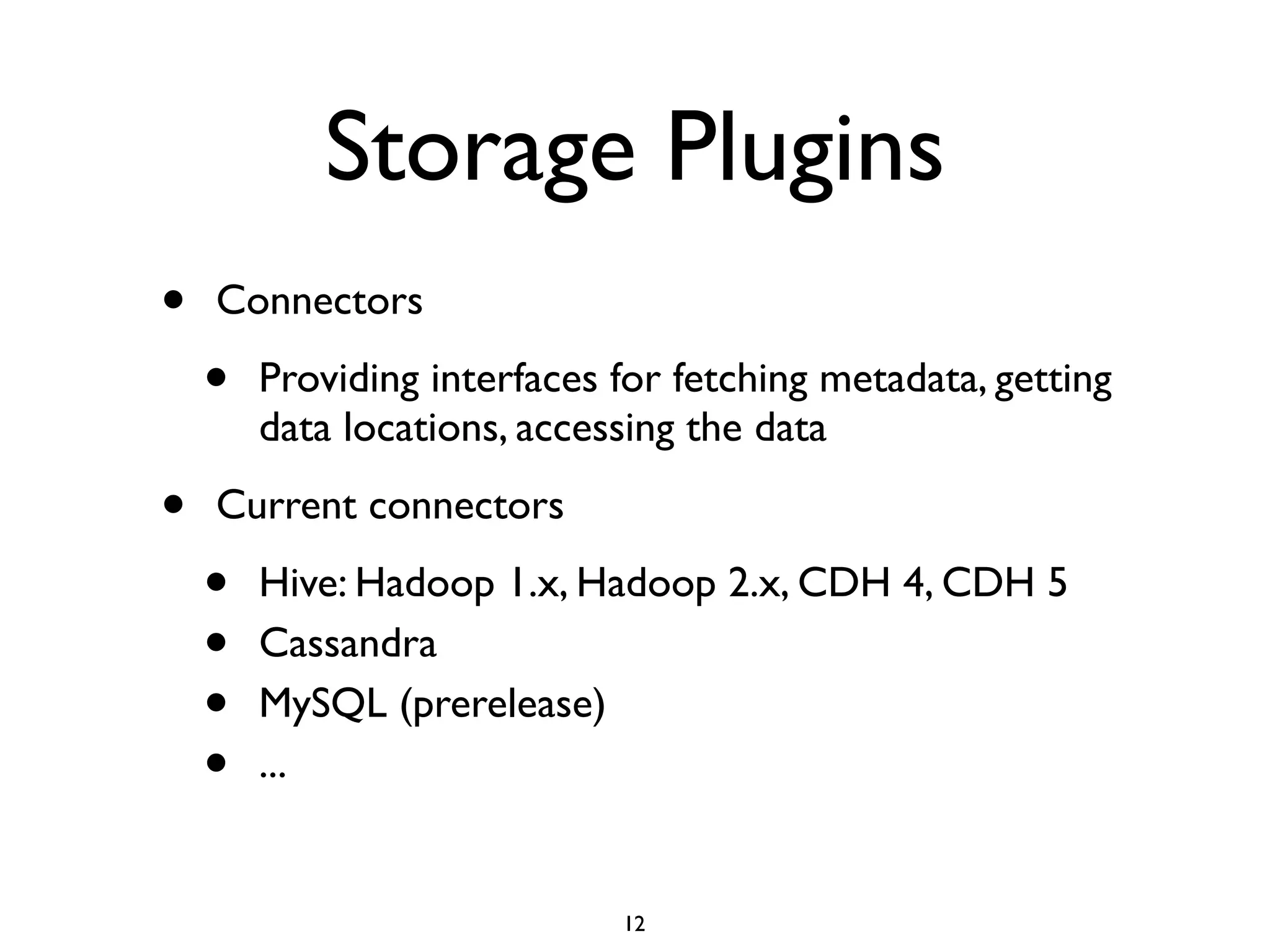
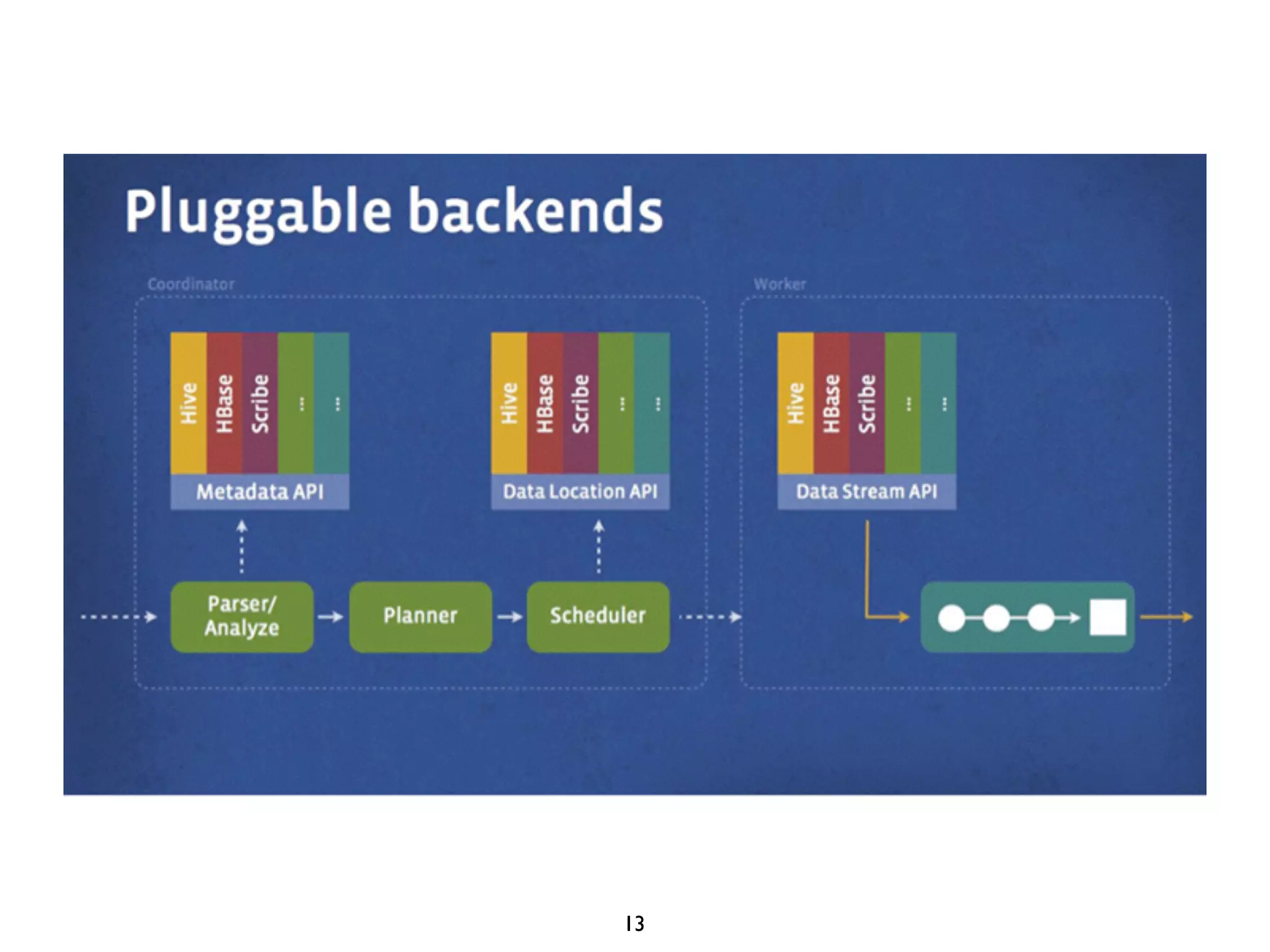
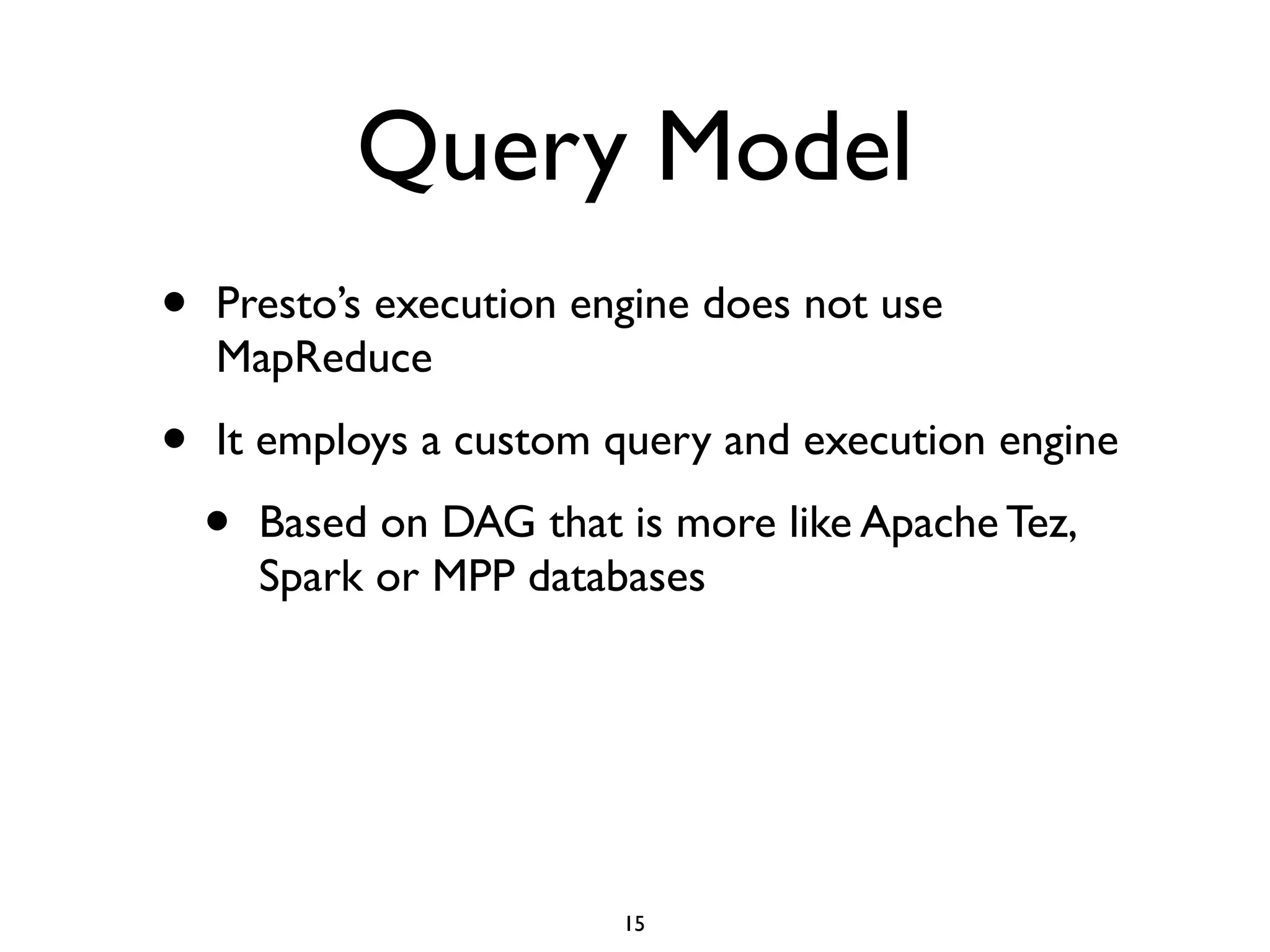
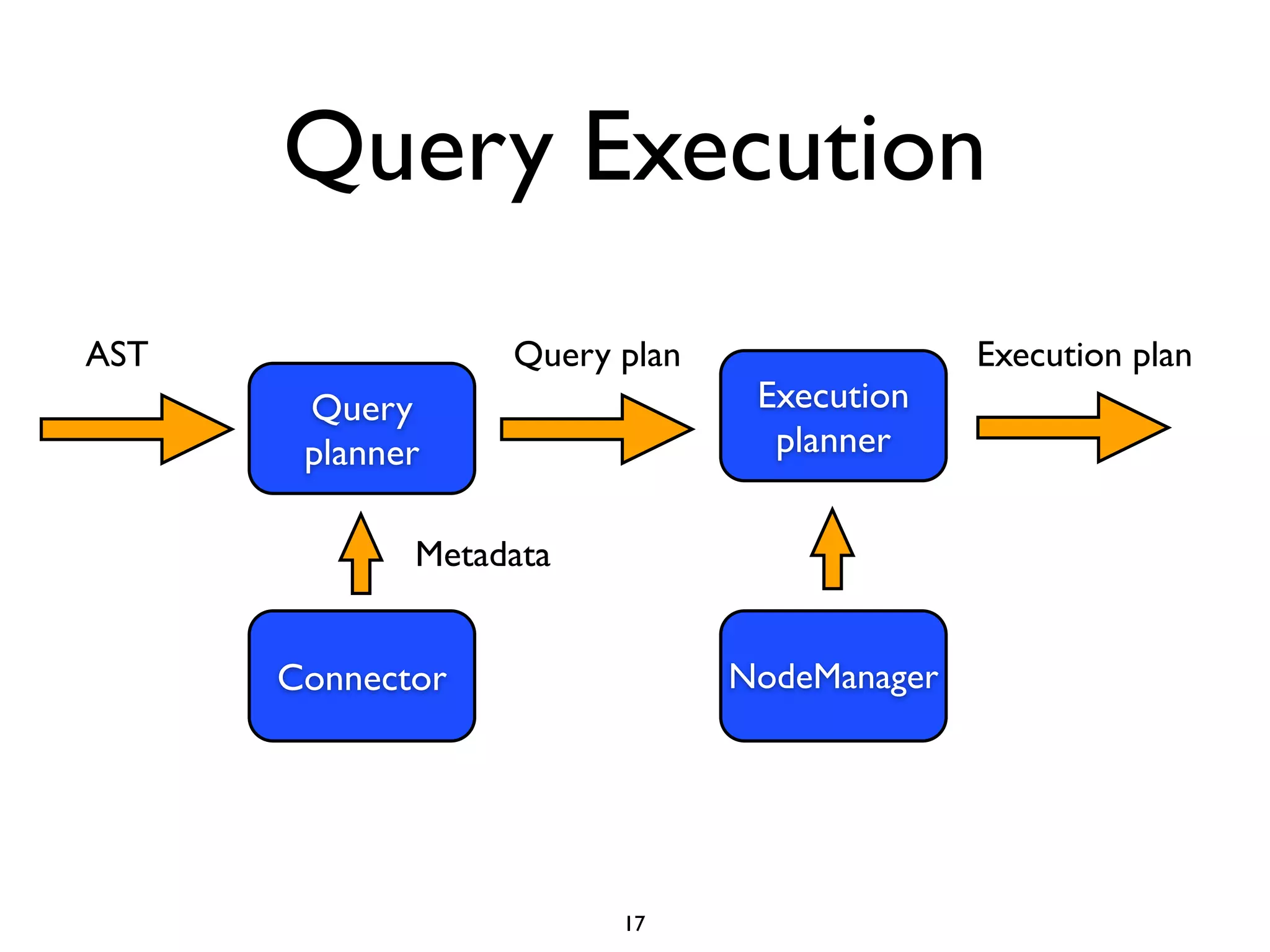
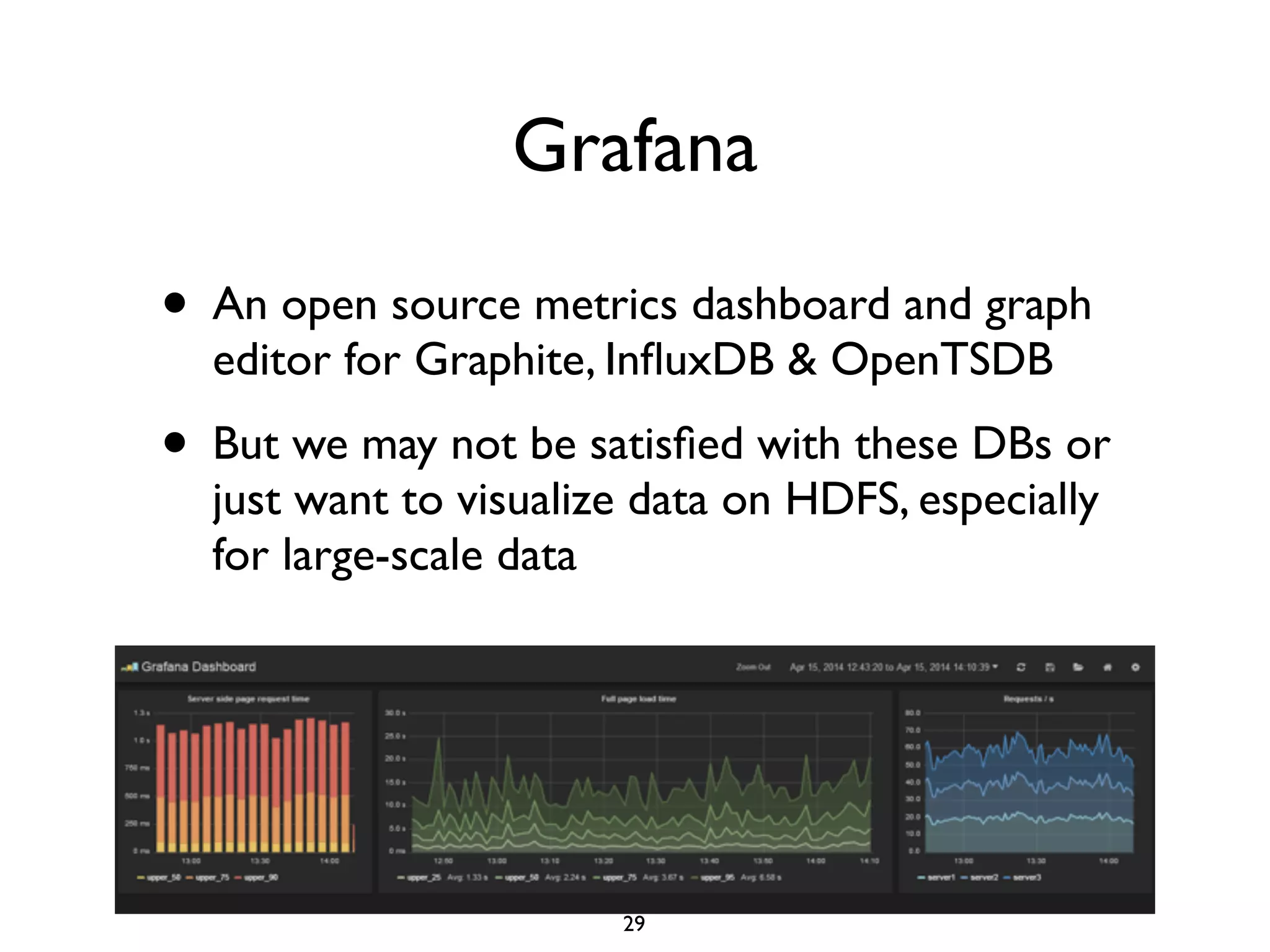
This document discusses using Presto to enable interactive analytic queries over large datasets on Hadoop. Presto is a distributed SQL query engine that is optimized for fast, ad-hoc queries against data stored in various data sources like HDFS, Cassandra and MySQL. It uses a coordinator and worker architecture to parallelize query execution across clusters. The document demonstrates how to deploy and configure Presto, and provides a demo of integrating Presto with Grafana for interactive data visualization.














![Integrating Presto with Grafana
• Presto also supports many common aggregation
functions
• avg(x) → double
• count(x) → bigint
• max(x) → [same as input]
• min(x) → [same as input]
• sum(x) → [same as input]
• …..
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-140913095001-phpapp02/75/Speed-up-Interactive-Analytic-Queries-over-Existing-Big-Data-on-Hadoop-with-Presto-31-2048.jpg)