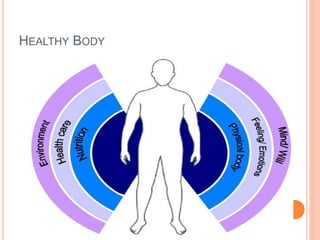
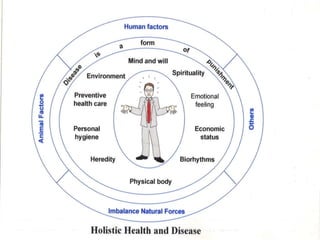
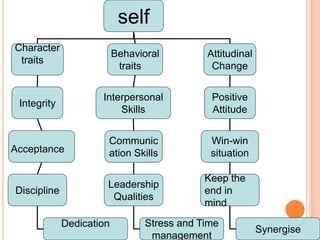
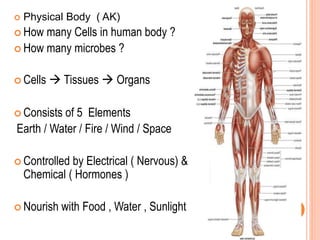
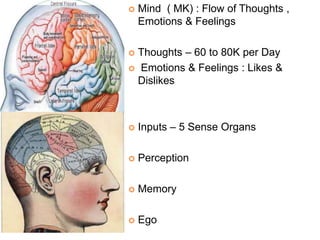
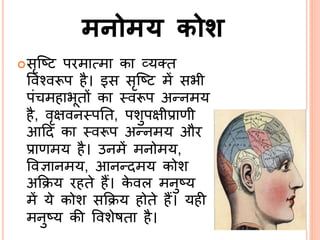
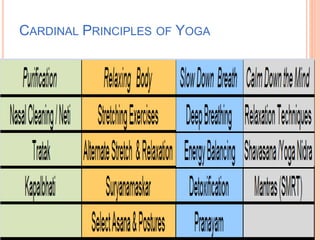
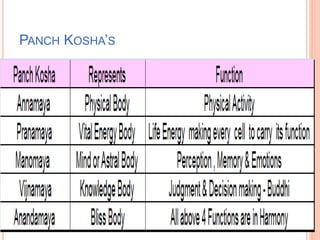
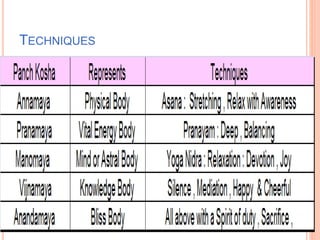
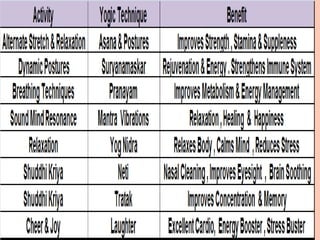
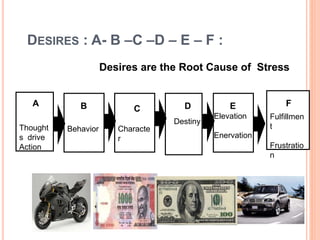
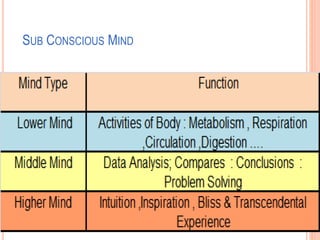
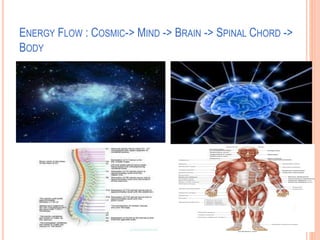
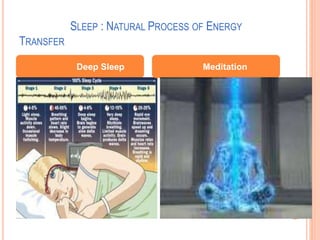
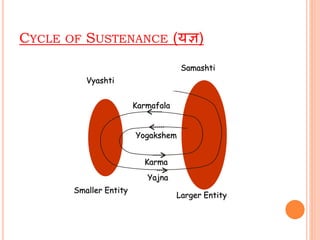
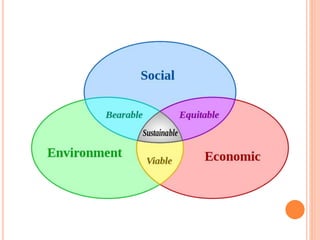
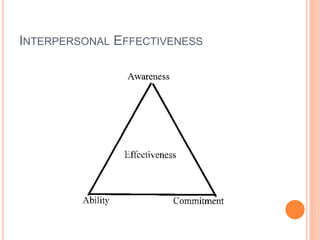
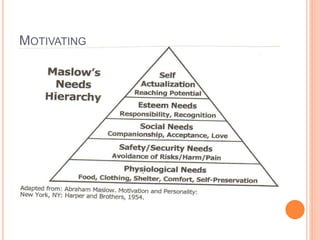
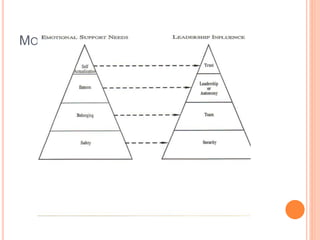
The document discusses the concept of self from the perspective of Indian philosophy. It explains that according to this view, the self has three aspects - a physical body composed of the five elements, an energy body governed by prana or life force, and a mind that processes thoughts, emotions and feelings. Developing all three aspects through practices like yoga, pranayama and meditation is important for cultivating a healthy self.