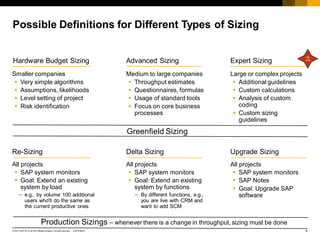
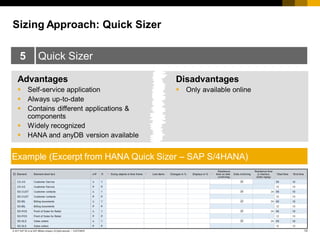
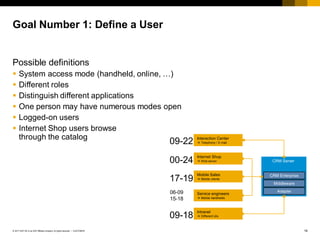
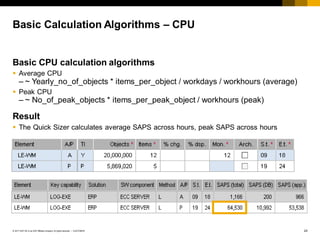
The document provides an introduction to sizing methods and tools for SAP systems. It discusses different sizing approaches including initial calculation methods, T-shirt sizing, formulas, questionnaires, and quick sizers. It also covers factors that influence sizing such as hardware, software, customizing, data volume, and user behavior. Finally, it discusses sizing based on users or throughput and risks involved in the sizing process.