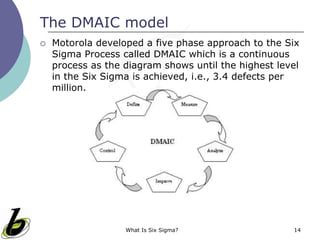
Kaizen and Six Sigma are continuous improvement methodologies. Kaizen focuses on gradual, continuous improvement involving all employees. Six Sigma aims to reduce defects to 3.4 per million opportunities through statistical analysis. It was developed by Motorola and focuses on the DMAIC cycle of Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. Six Sigma uses tools like control charts, design of experiments, and failure mode and effects analysis.