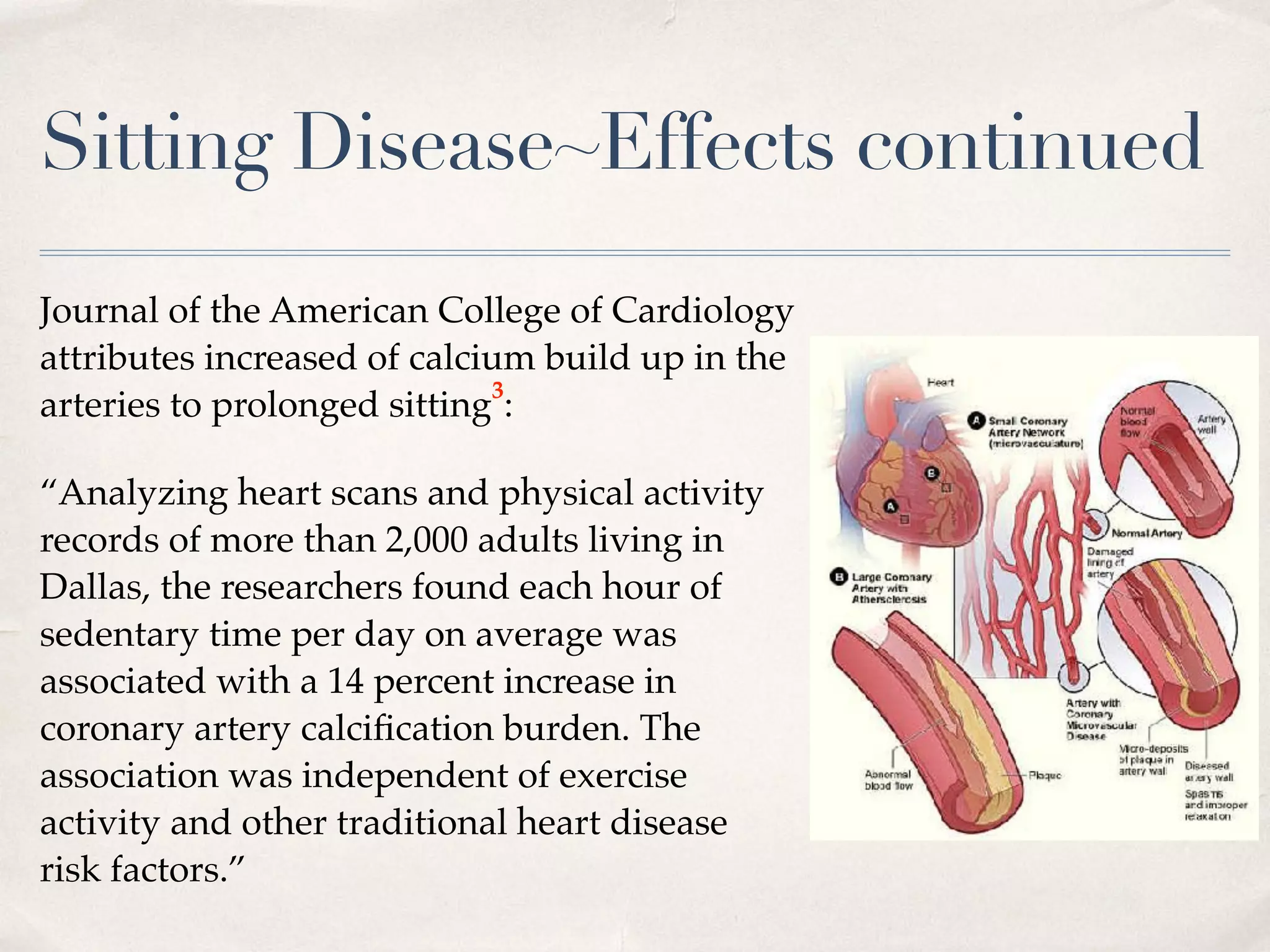
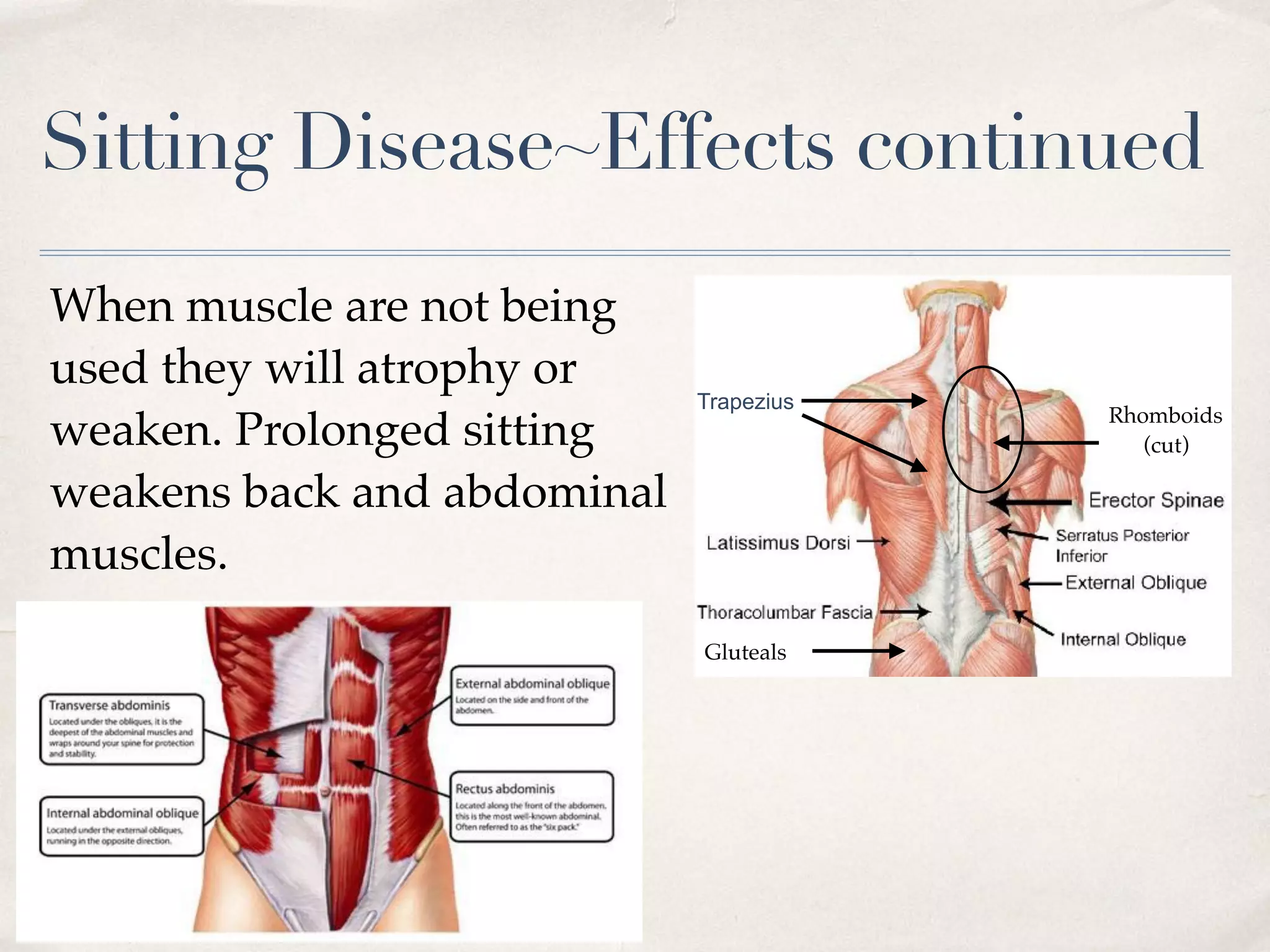
Sitting disease refers to the health risks associated with prolonged sitting, defined as sitting for more than 8-12 hours daily, which can lead to increased risks of heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Research indicates that extended periods of sitting correlate with harmful physiological effects, including poor insulin response and reduced blood flow to the brain, contributing to cognitive impairments. To mitigate these risks, strategies like the 20-8-2 rule, standing desks, and incorporating movement into meetings are recommended.