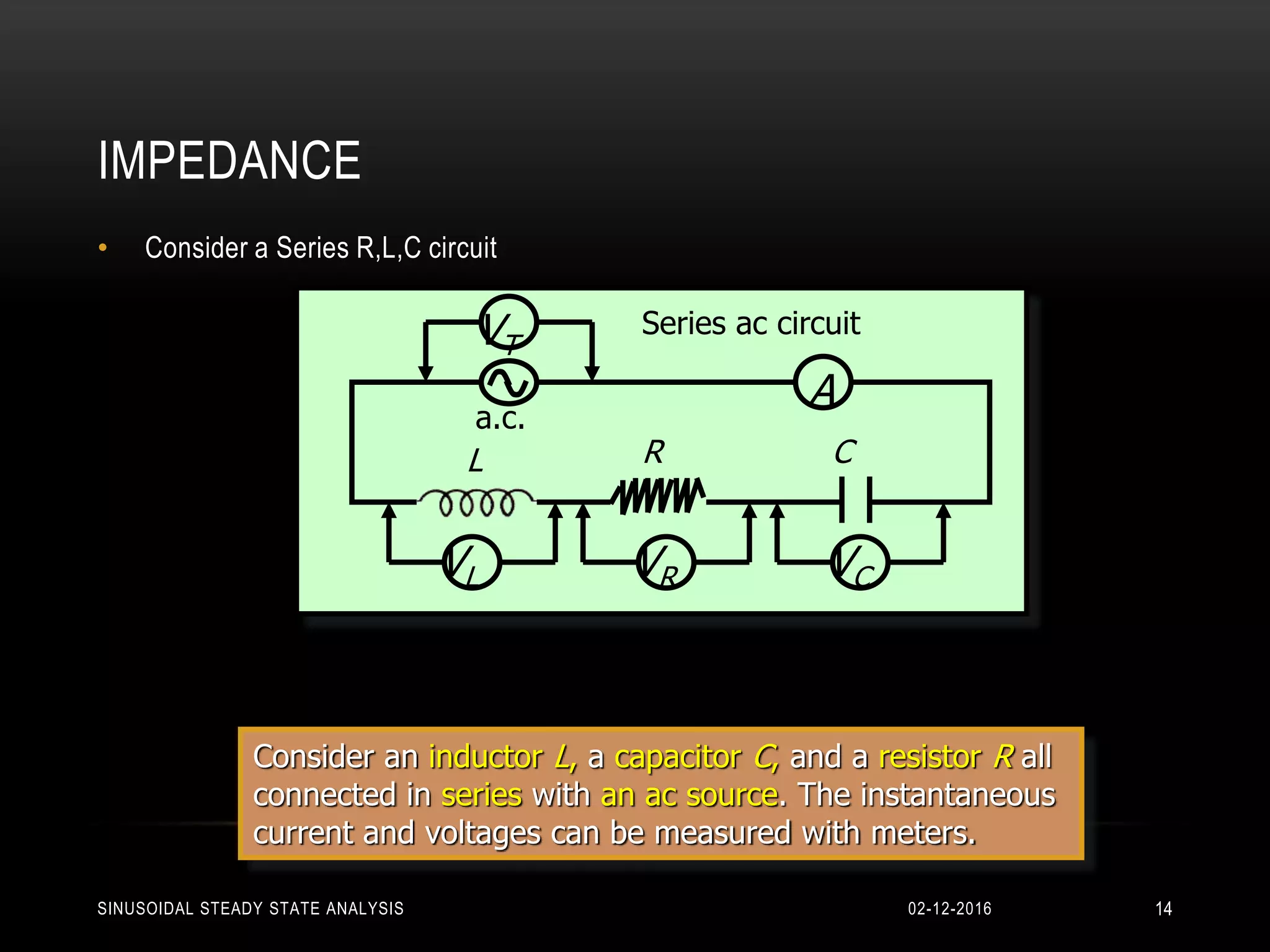
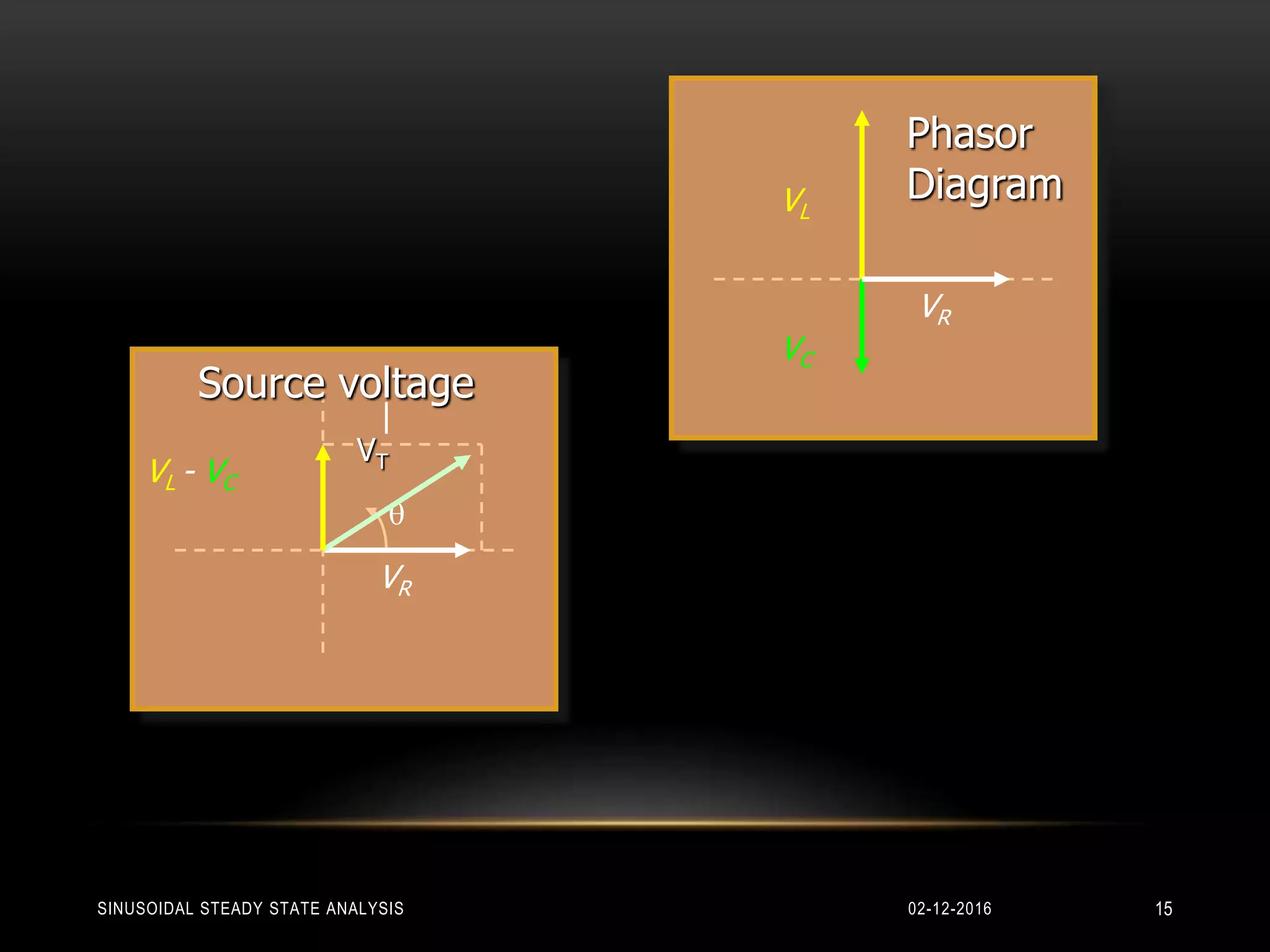
This document discusses sinusoidal steady state analysis and phasors. It introduces representing sine waves with phase using phasors, which characterize a sinusoidal voltage or current using just amplitude and phase angle. Circuits containing resistors, inductors and capacitors are examined, showing their phasor relationships: voltage and current are in phase for resistors, voltage lags current by 90 degrees for inductors and leads current by 90 degrees for capacitors. Impedance is defined as the total opposition to AC current, consisting of resistance and reactance. Phasor diagrams provide a graphical method to solve circuit problems by showing the relationship between phasor voltages and currents.