Embed presentation
Download to read offline










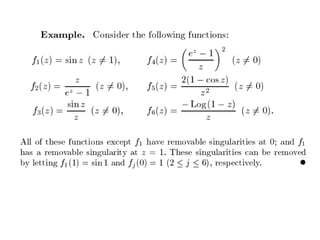






A regular point for a complex-valued function is where the function is analytic, while a singular point is where it is not, but at least one nearby point is analytic. An isolated singular point is one where the function is analytic in a deleted neighborhood around it, whereas a non-isolated singularity has singularities in every deleted neighborhood. Examples include the function 1/z, which has an isolated singularity at z = 0 and at every integer point.