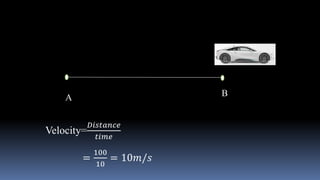
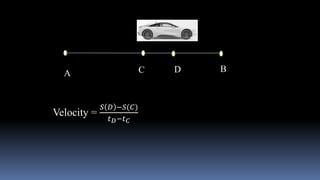
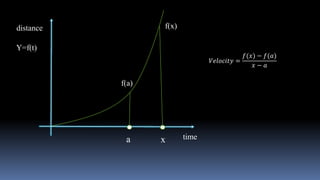
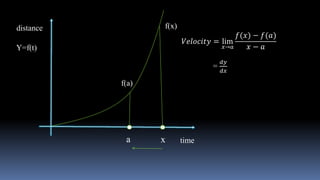
This document provides an introduction to differential equations. It defines key terms like differentiation, dependent and independent variables, ordinary and partial differential equations.
Differentiation is defined as how a quantity changes with respect to changes in another quantity. A differential equation is an equation that contains differential coefficients.
Ordinary differential equations contain a single independent variable, while partial differential equations contain at least two independent variables. Examples of both types of differential equations are provided.
The document also discusses the concepts of dependent and independent variables. The dependent variables in an equation are the variables being solved for, while the independent variables are the variables with respect to which the dependent variables change.