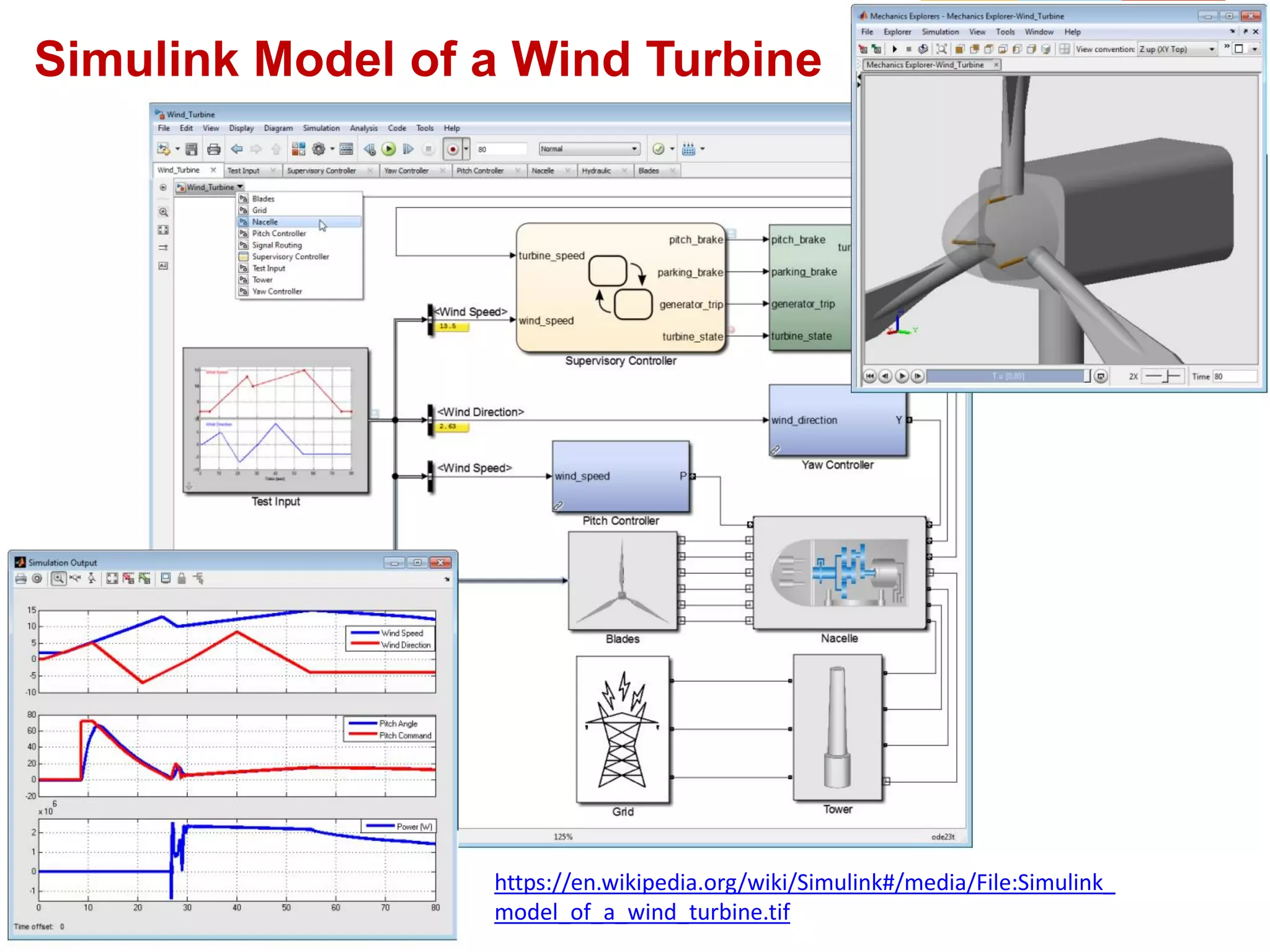
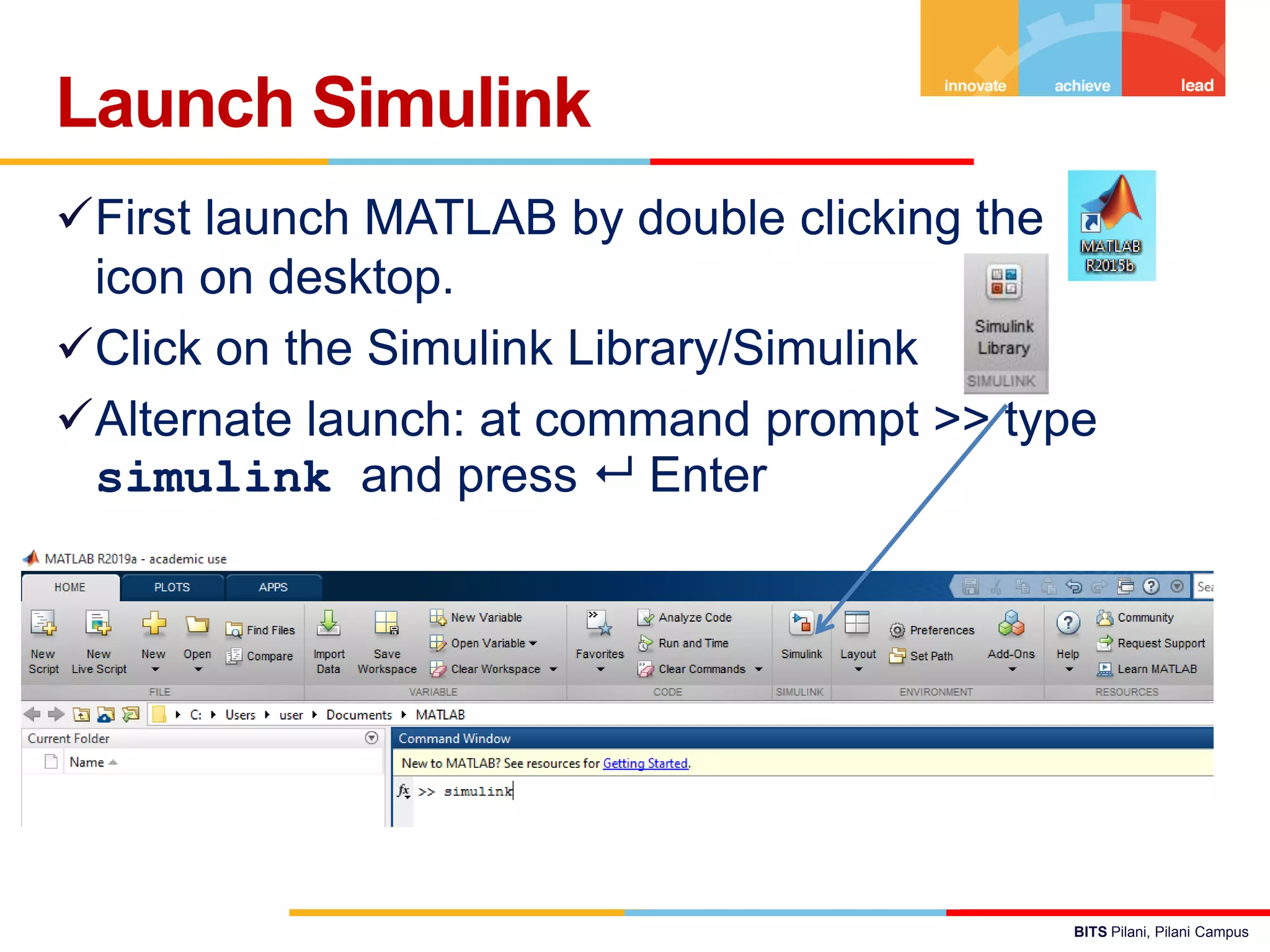
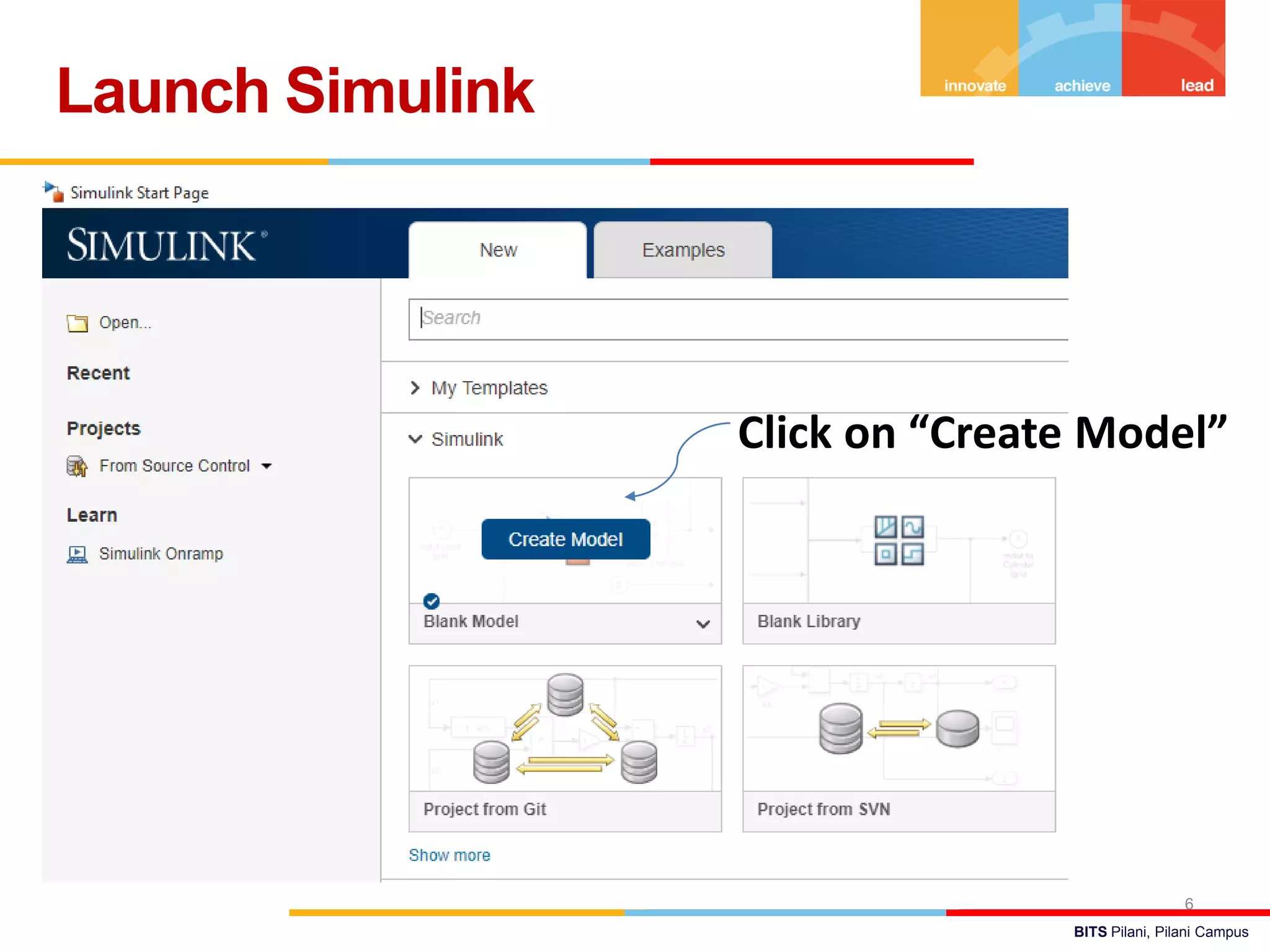
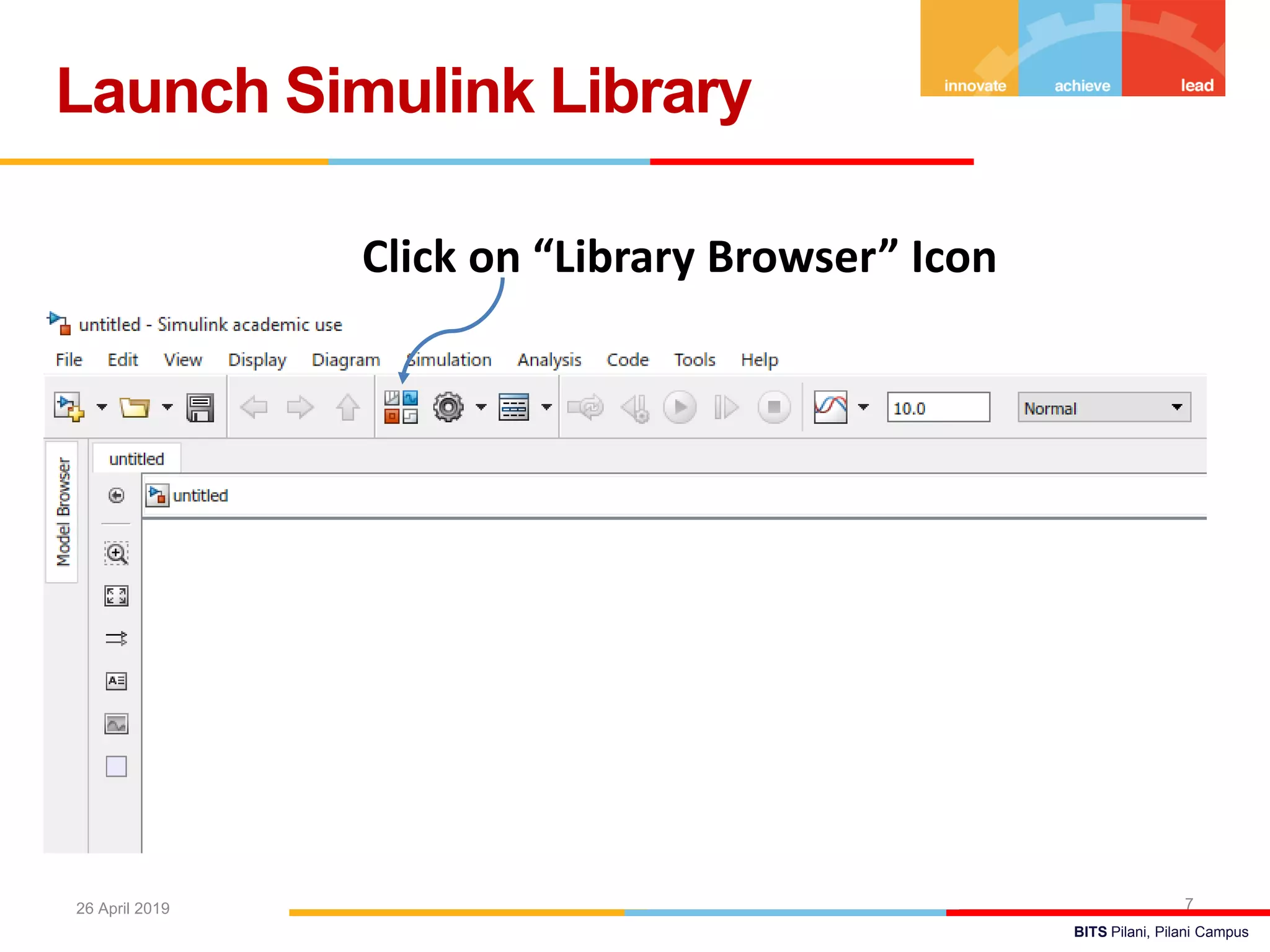
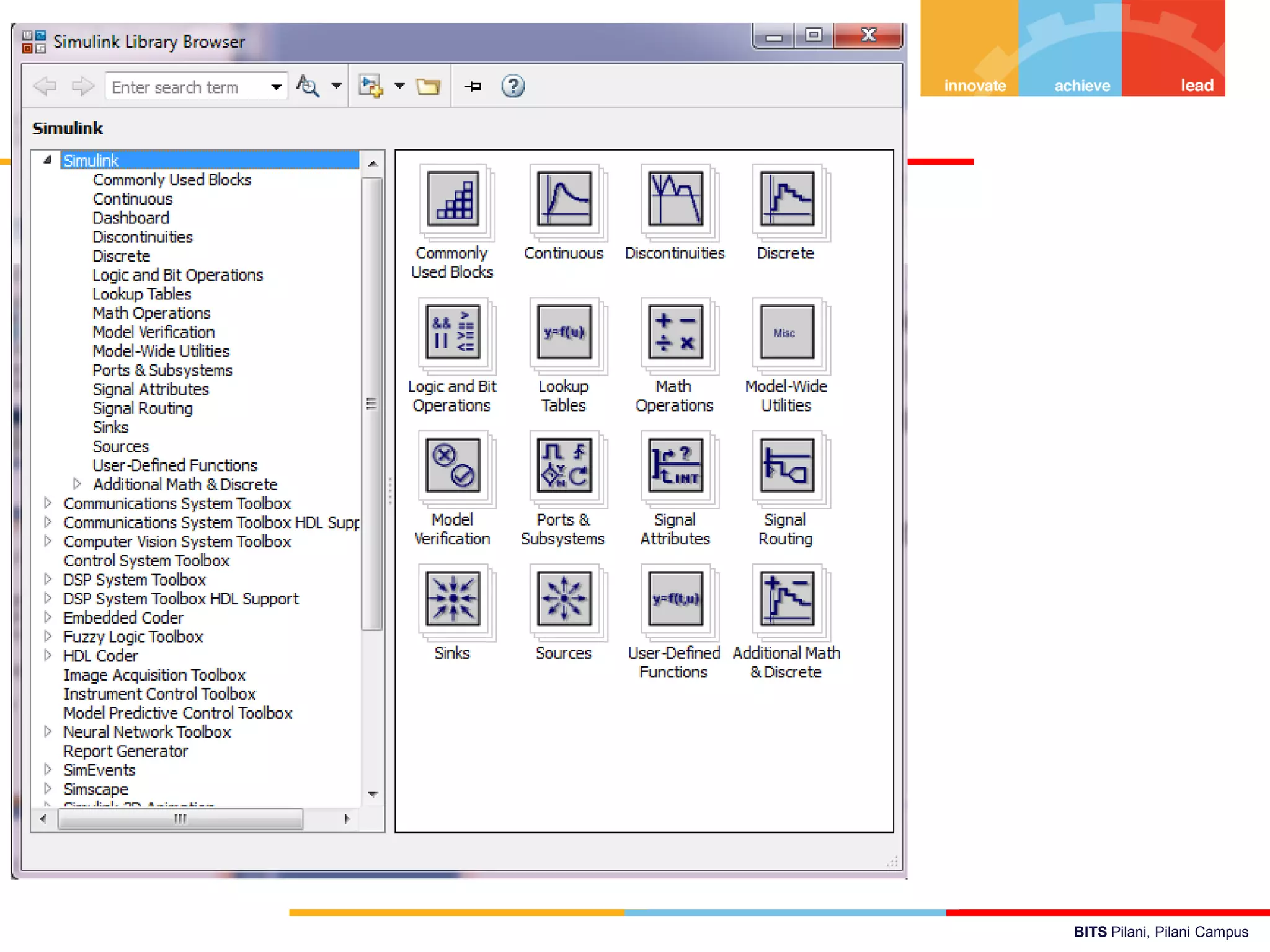
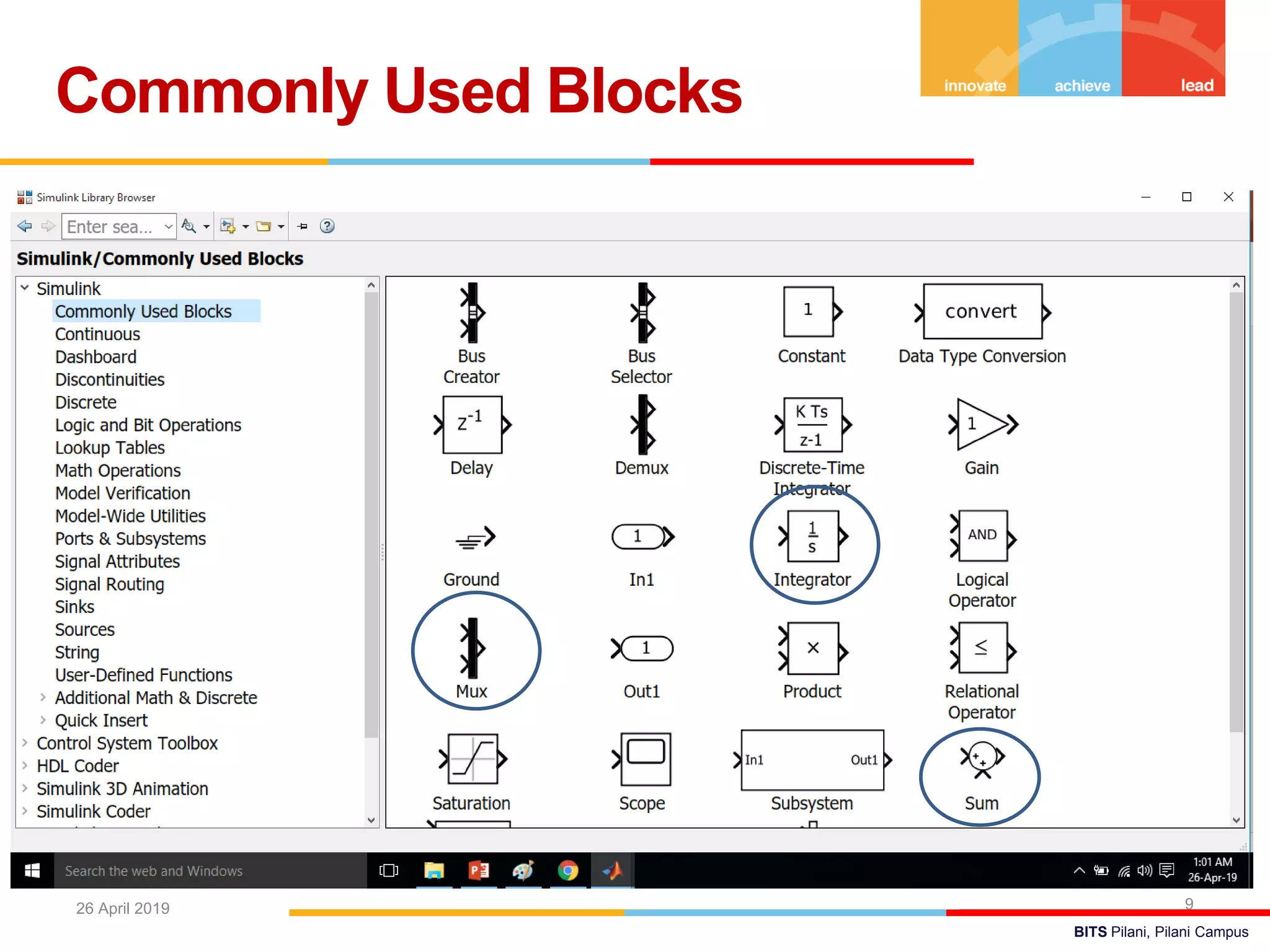
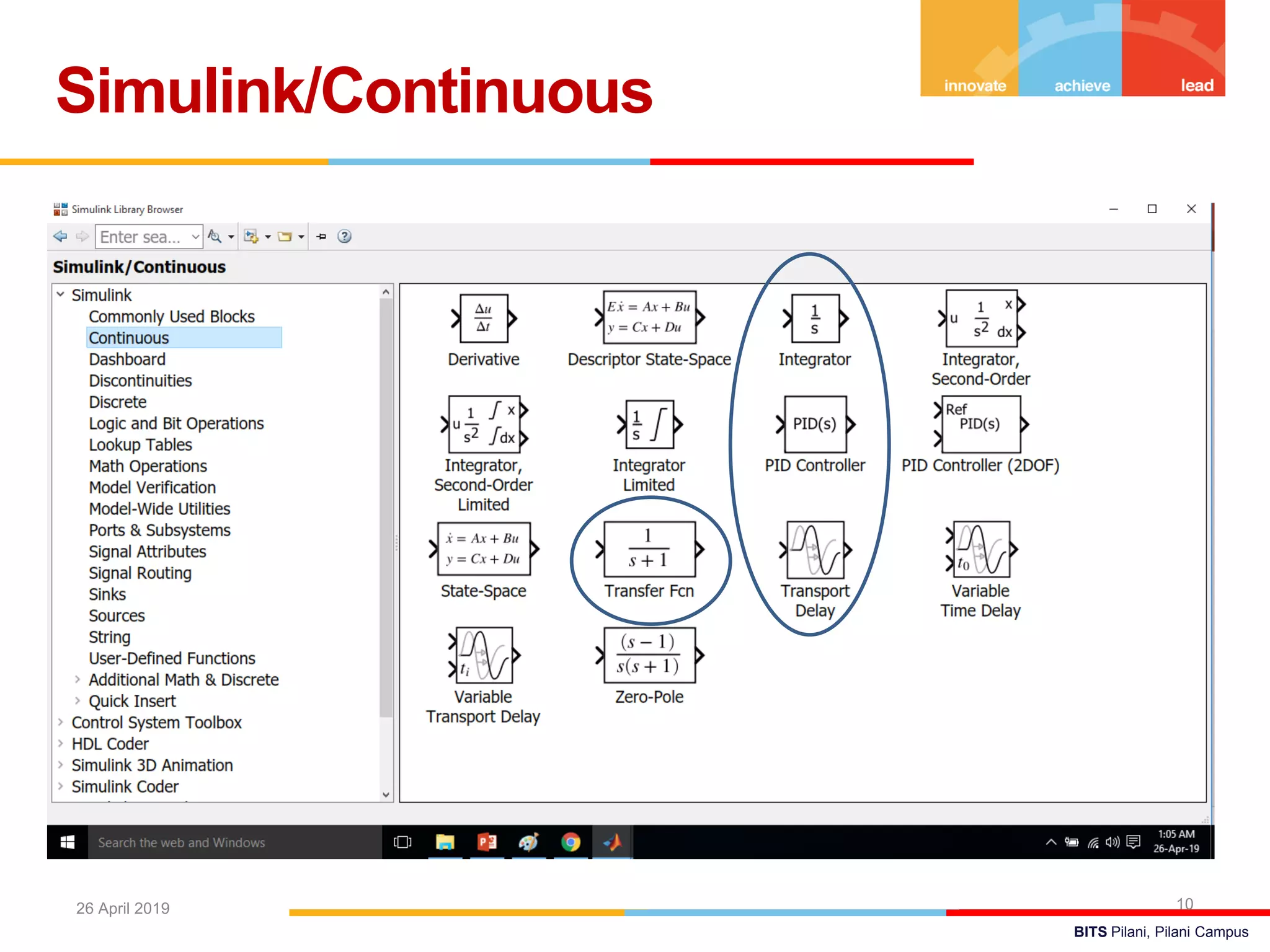
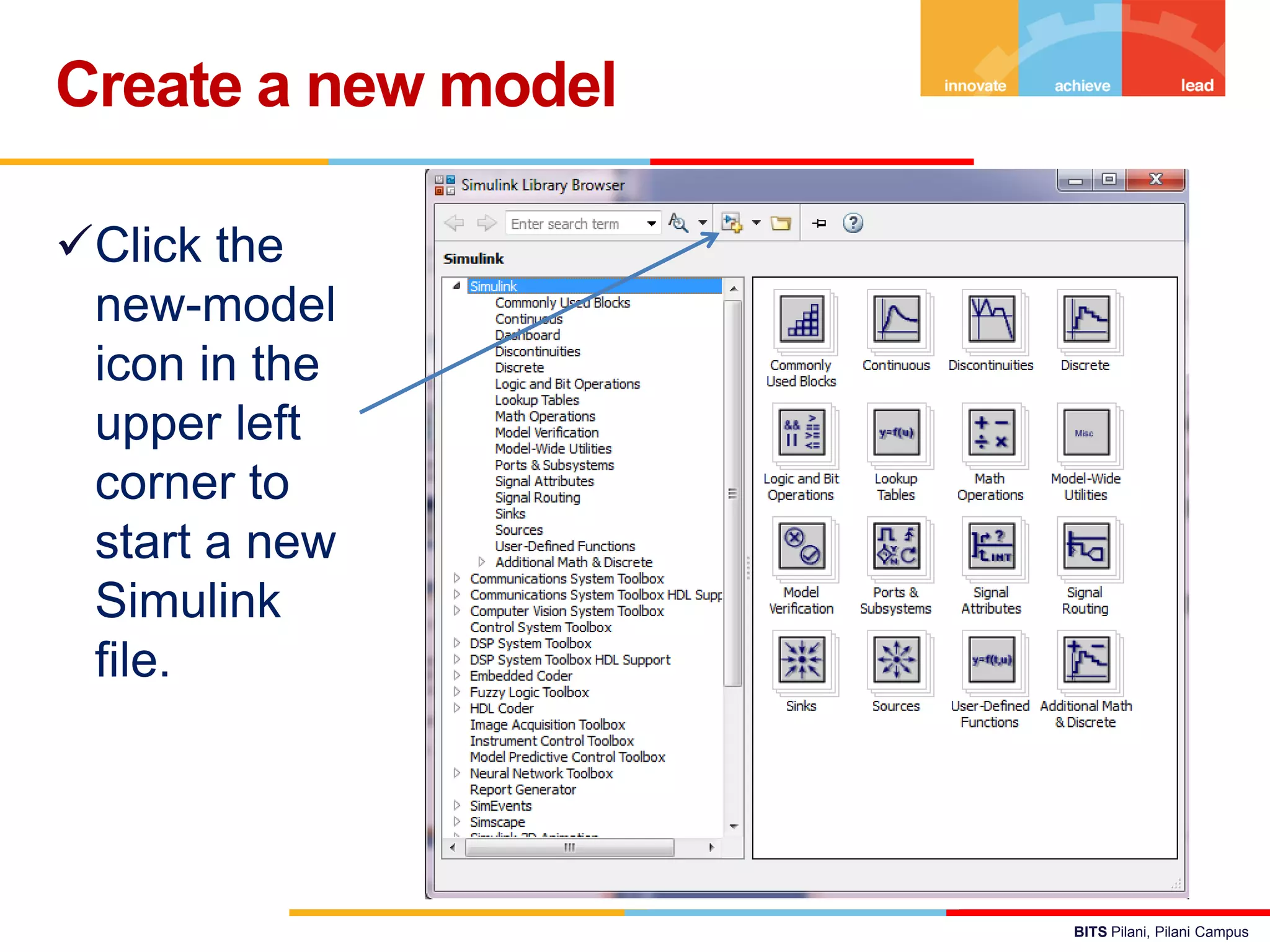
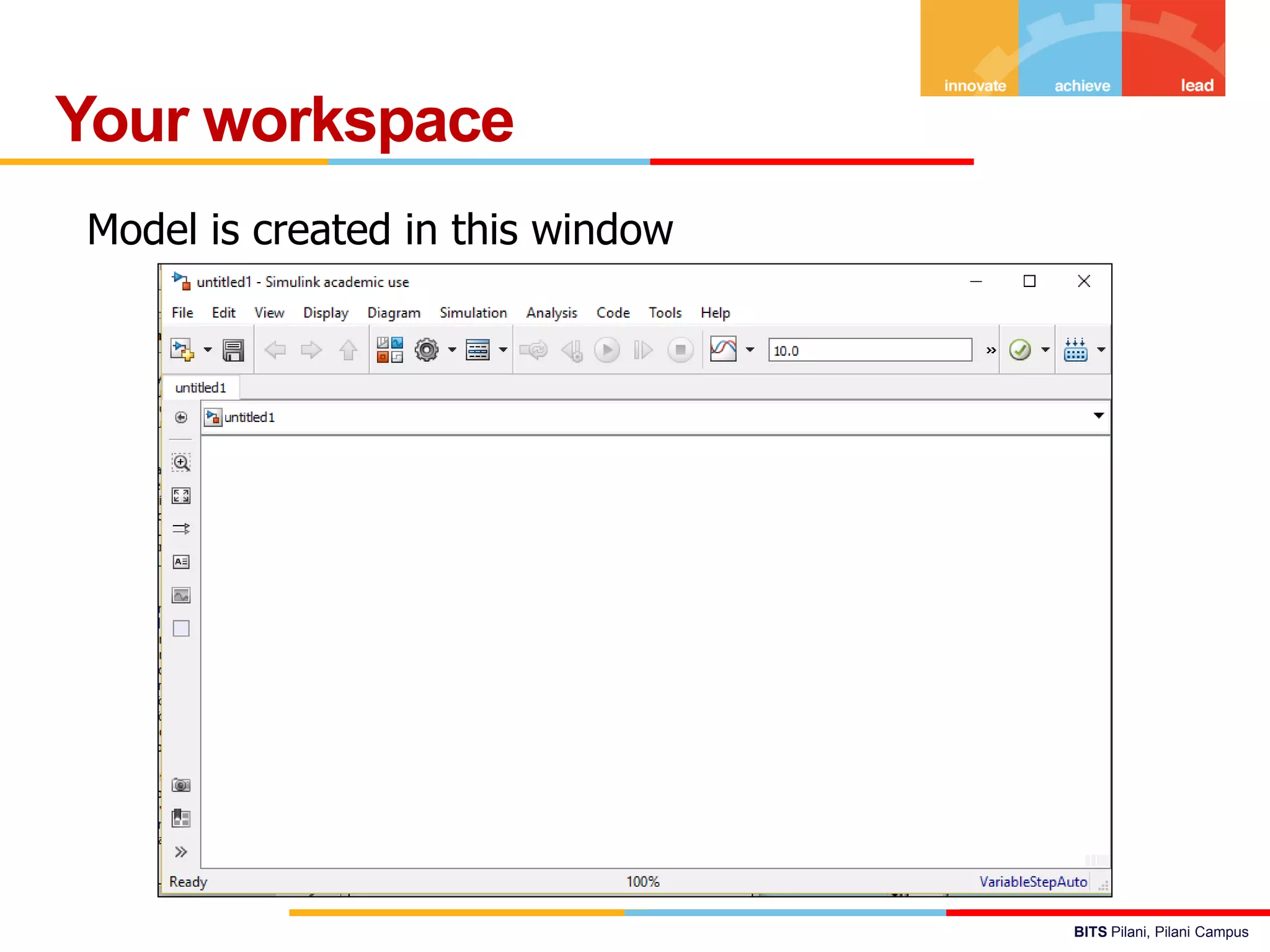
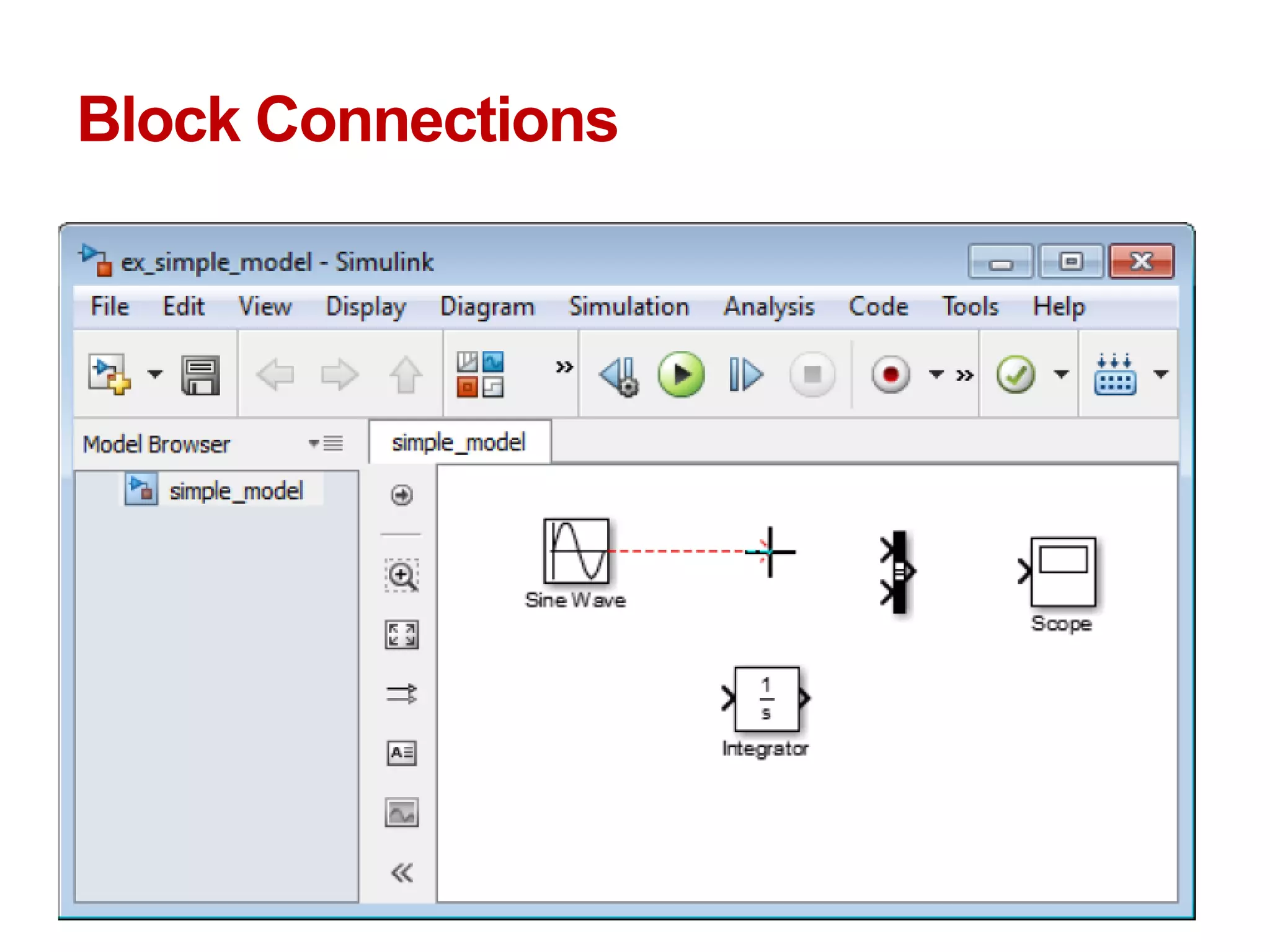
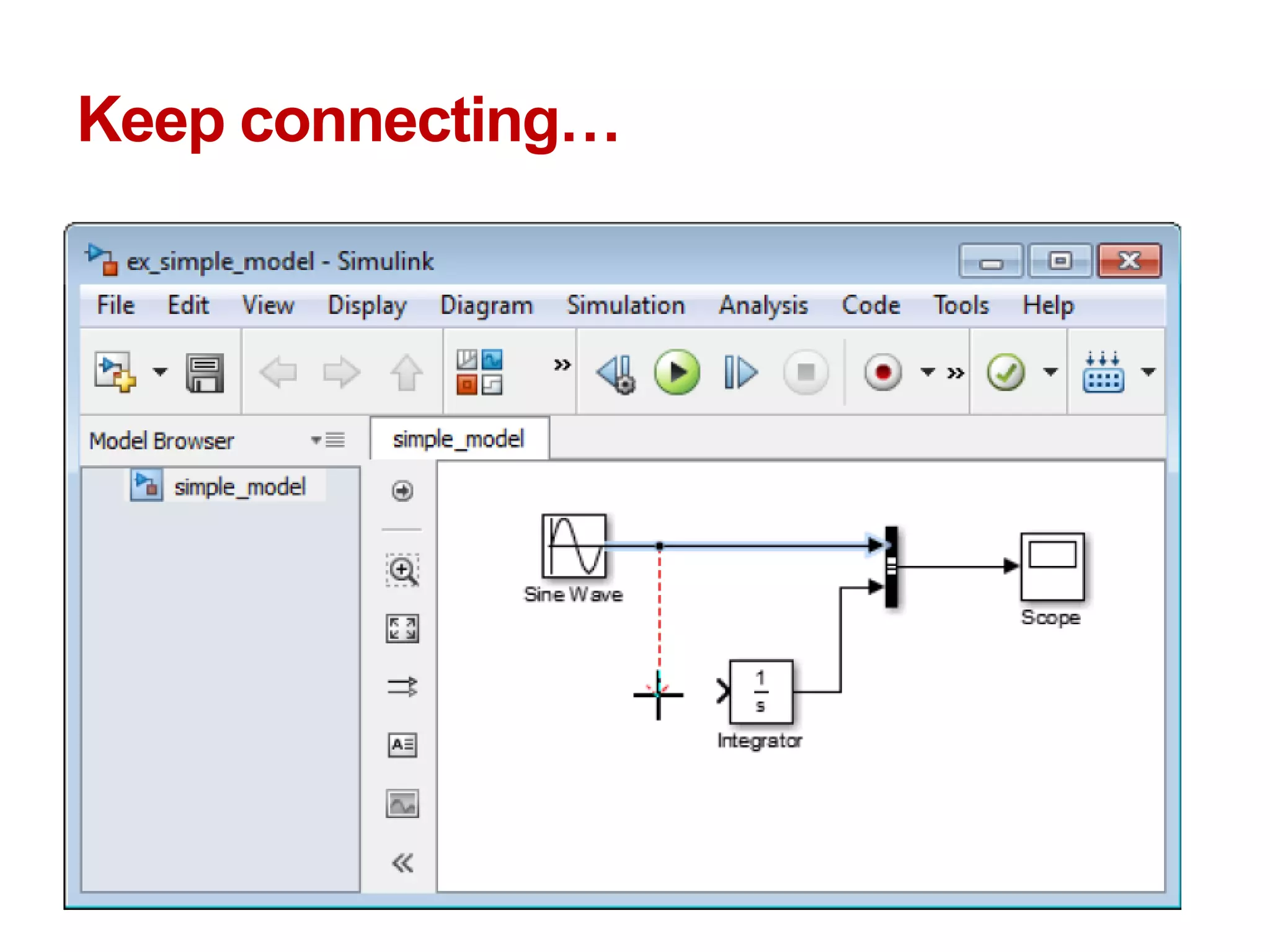
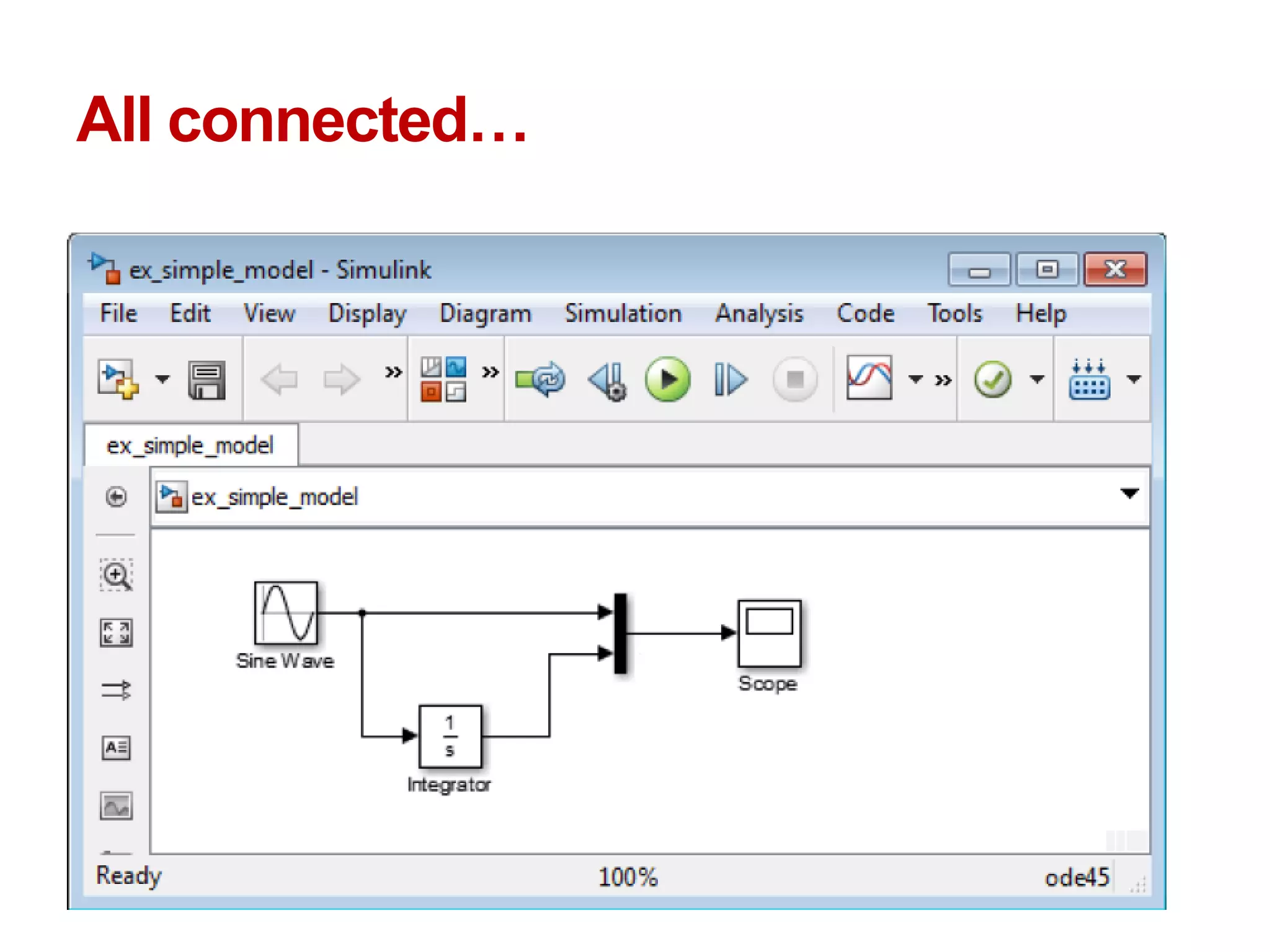
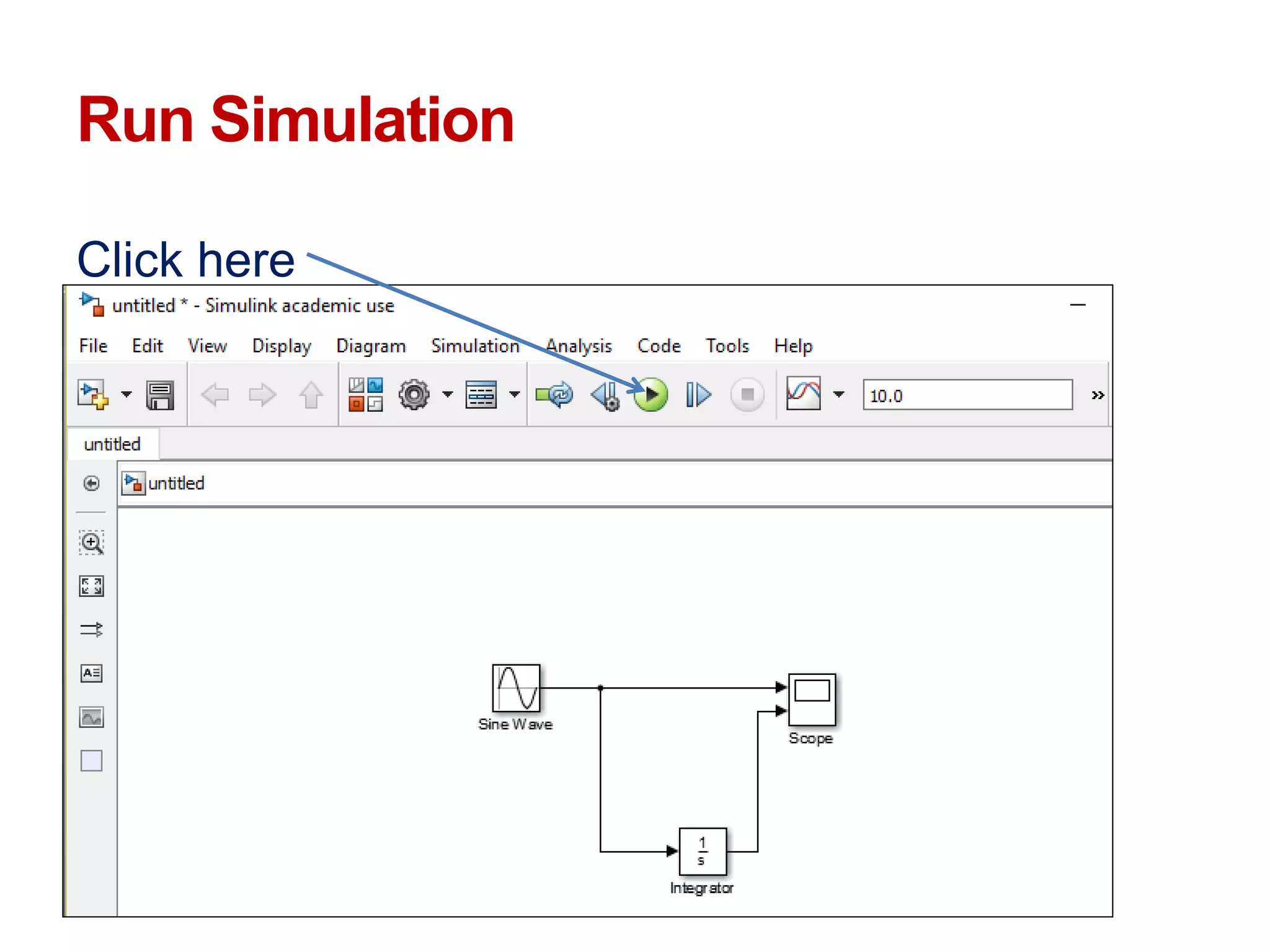
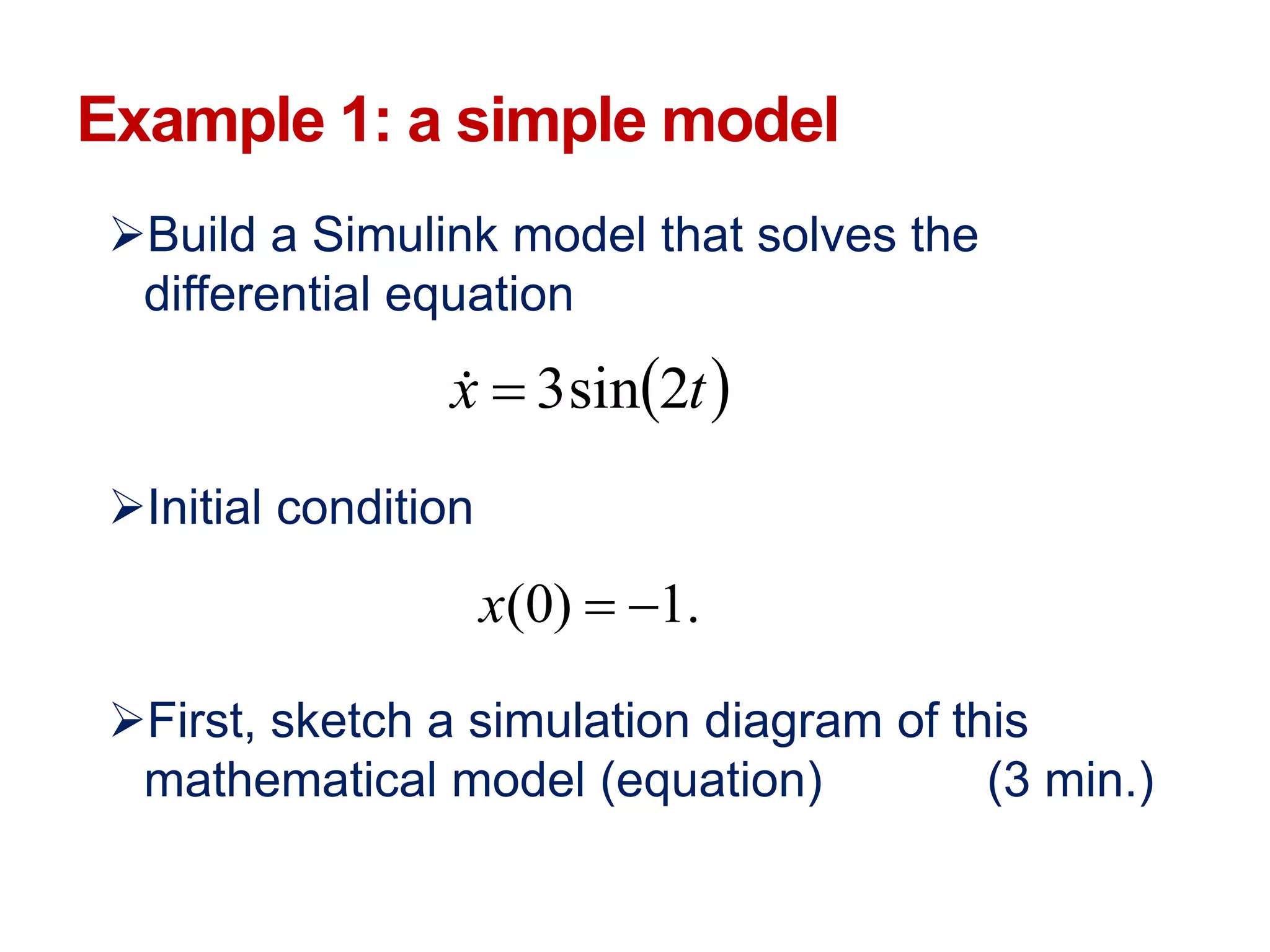
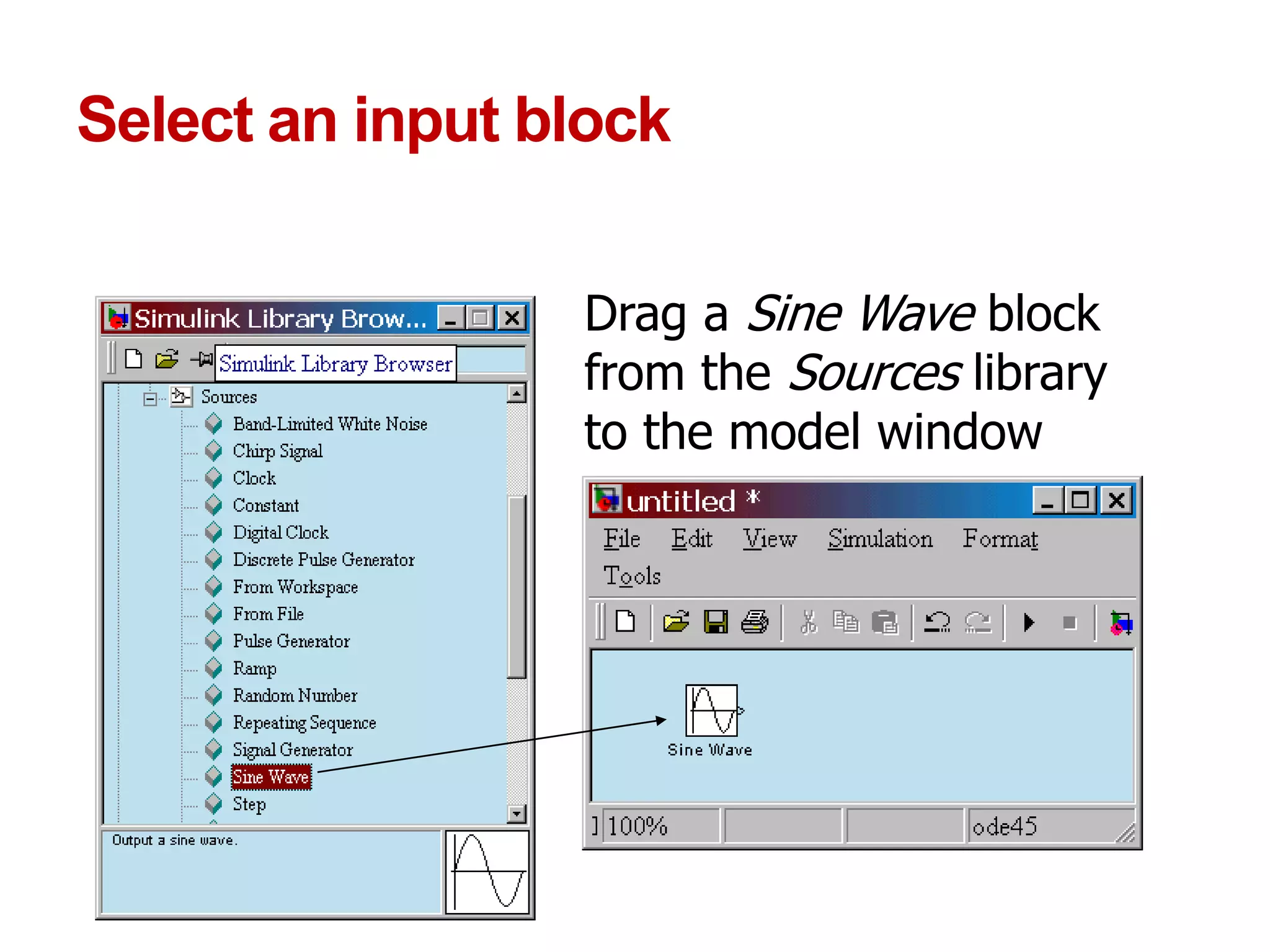
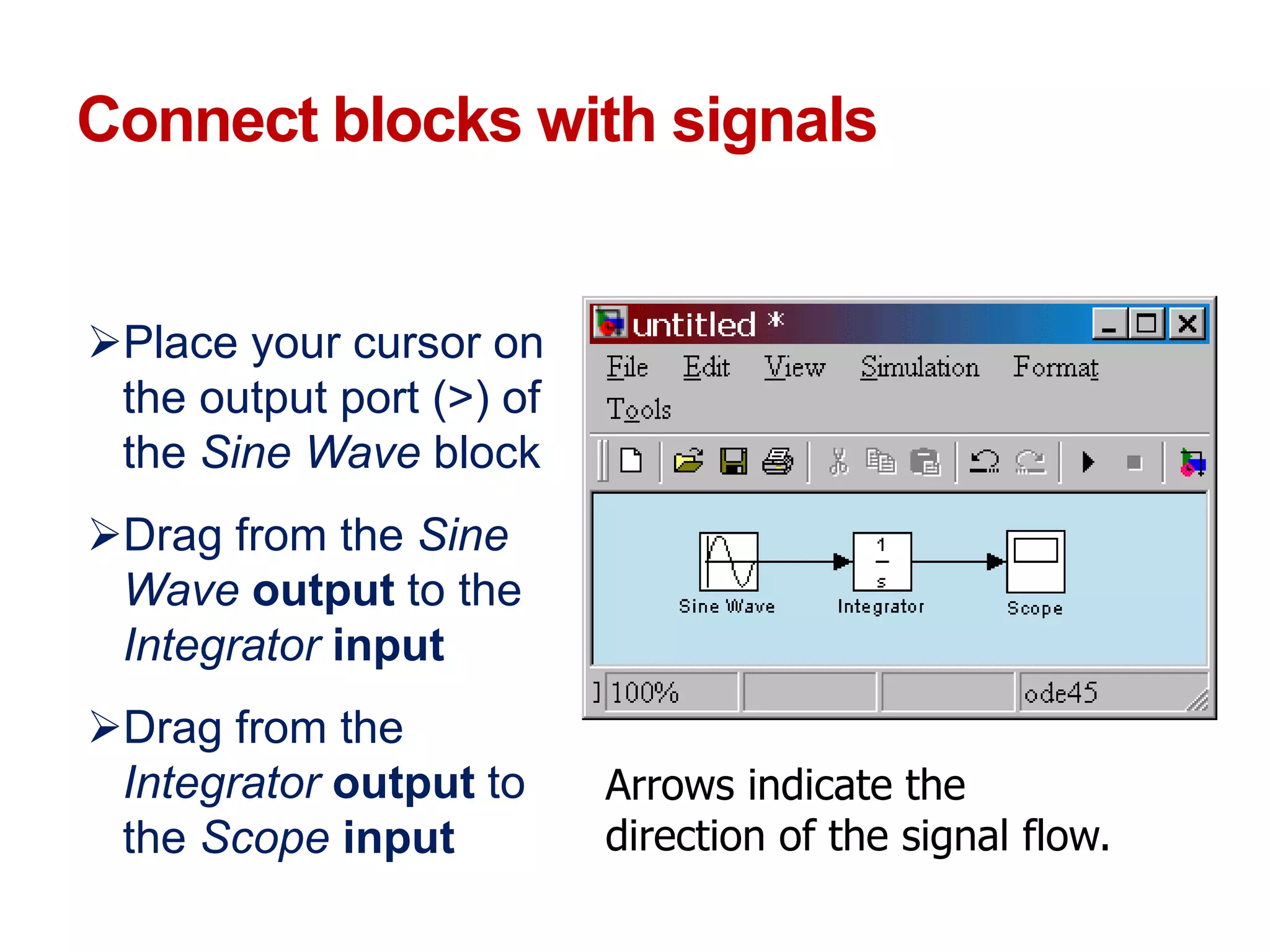
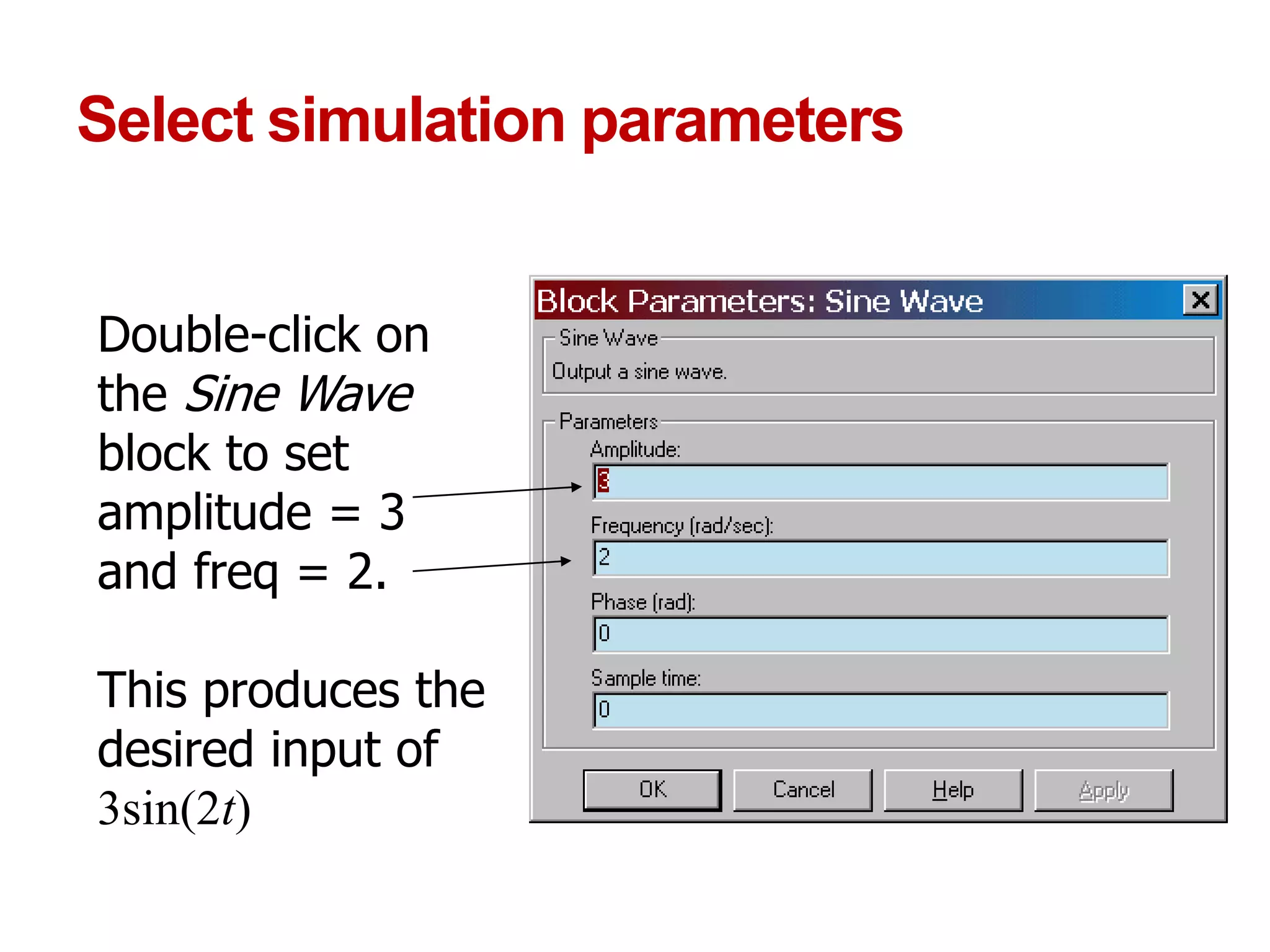
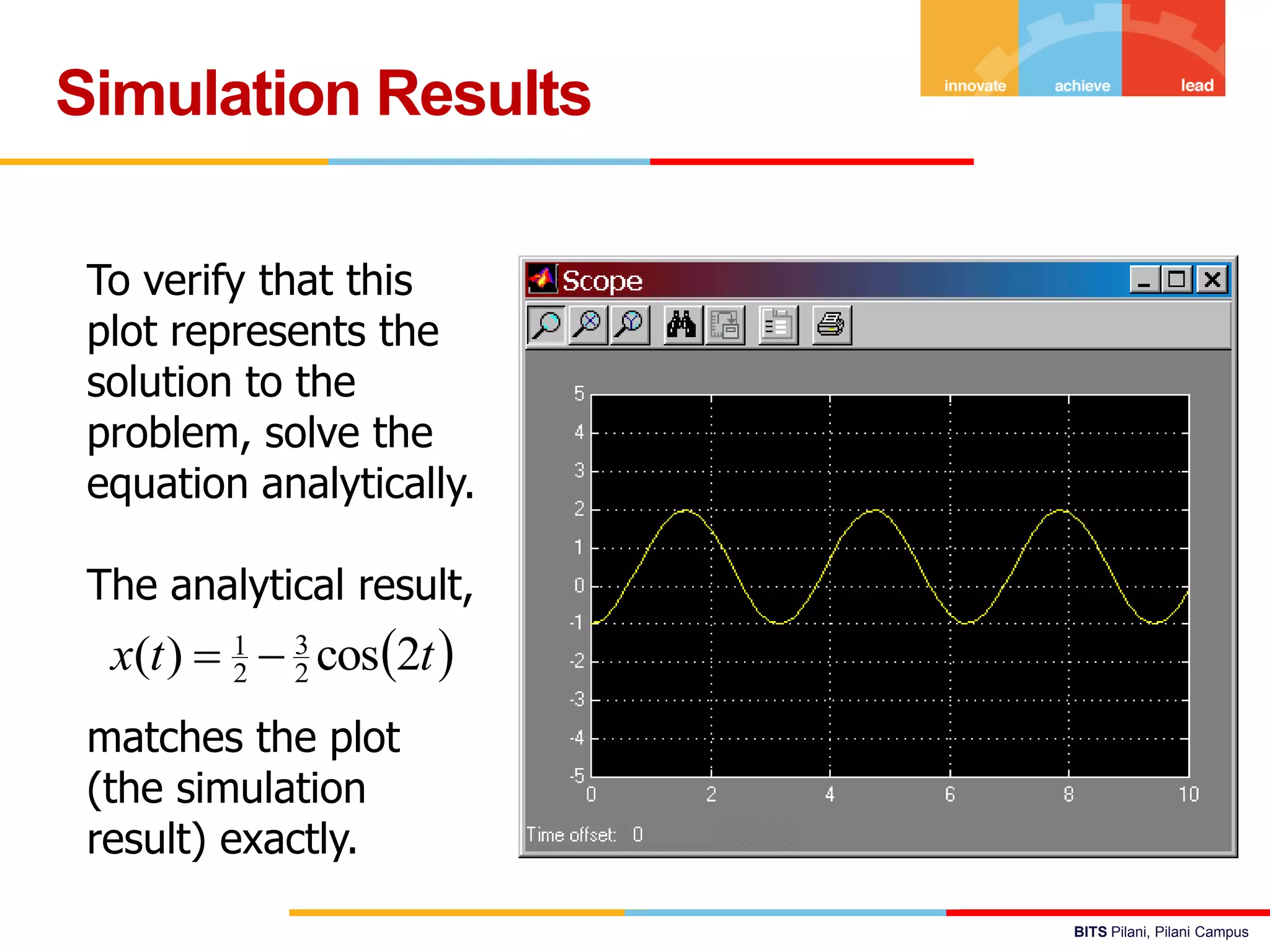
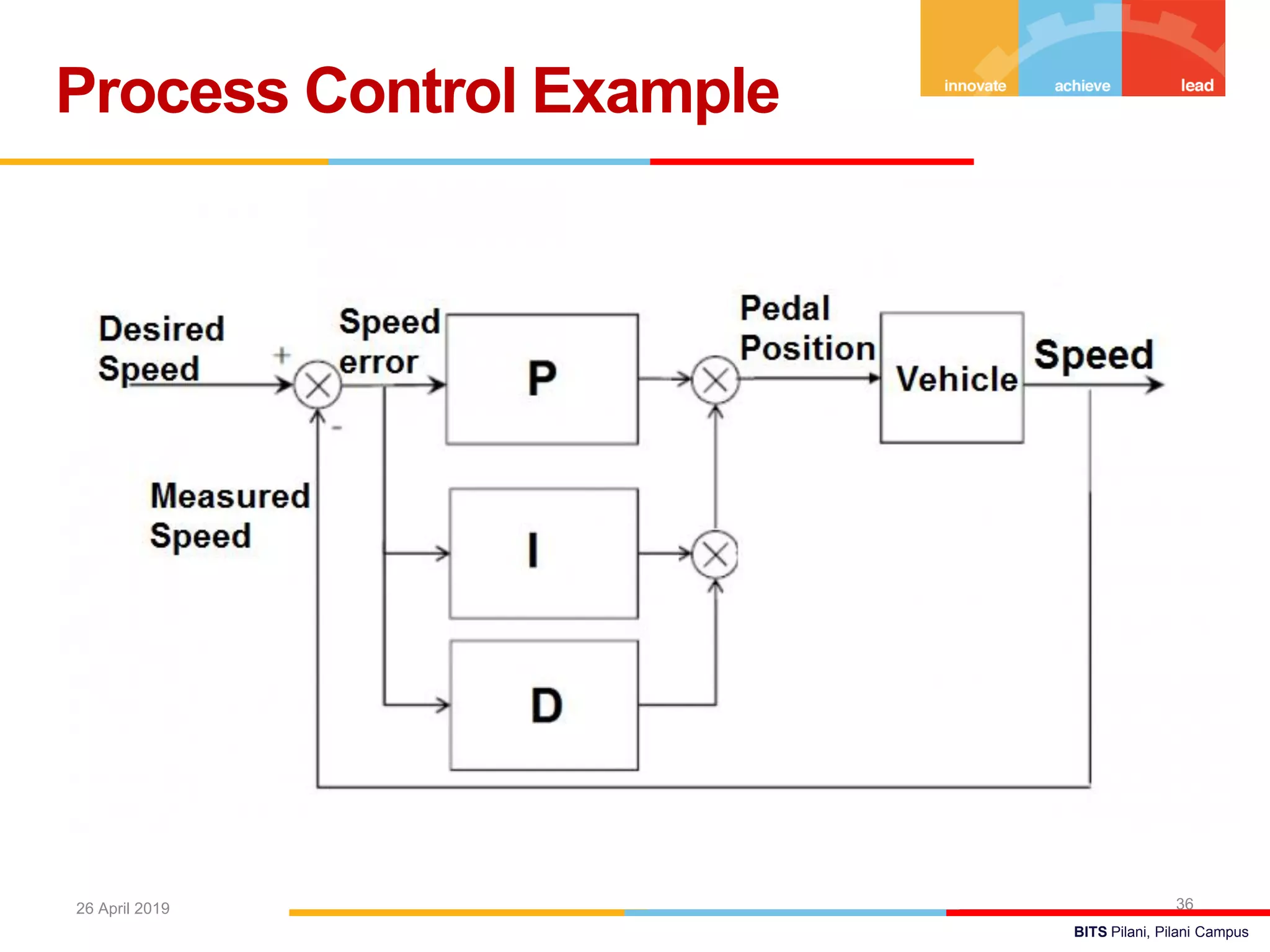
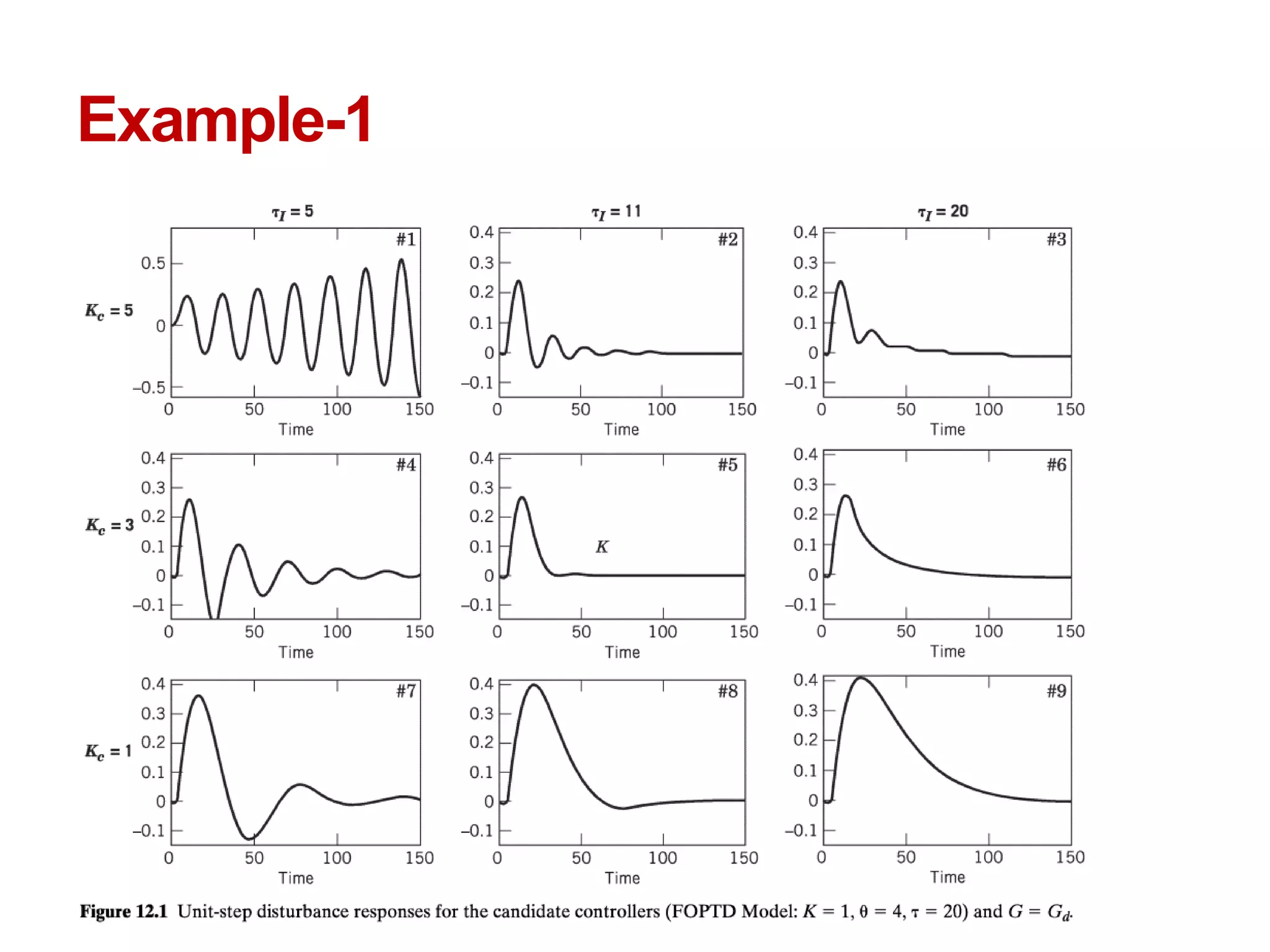
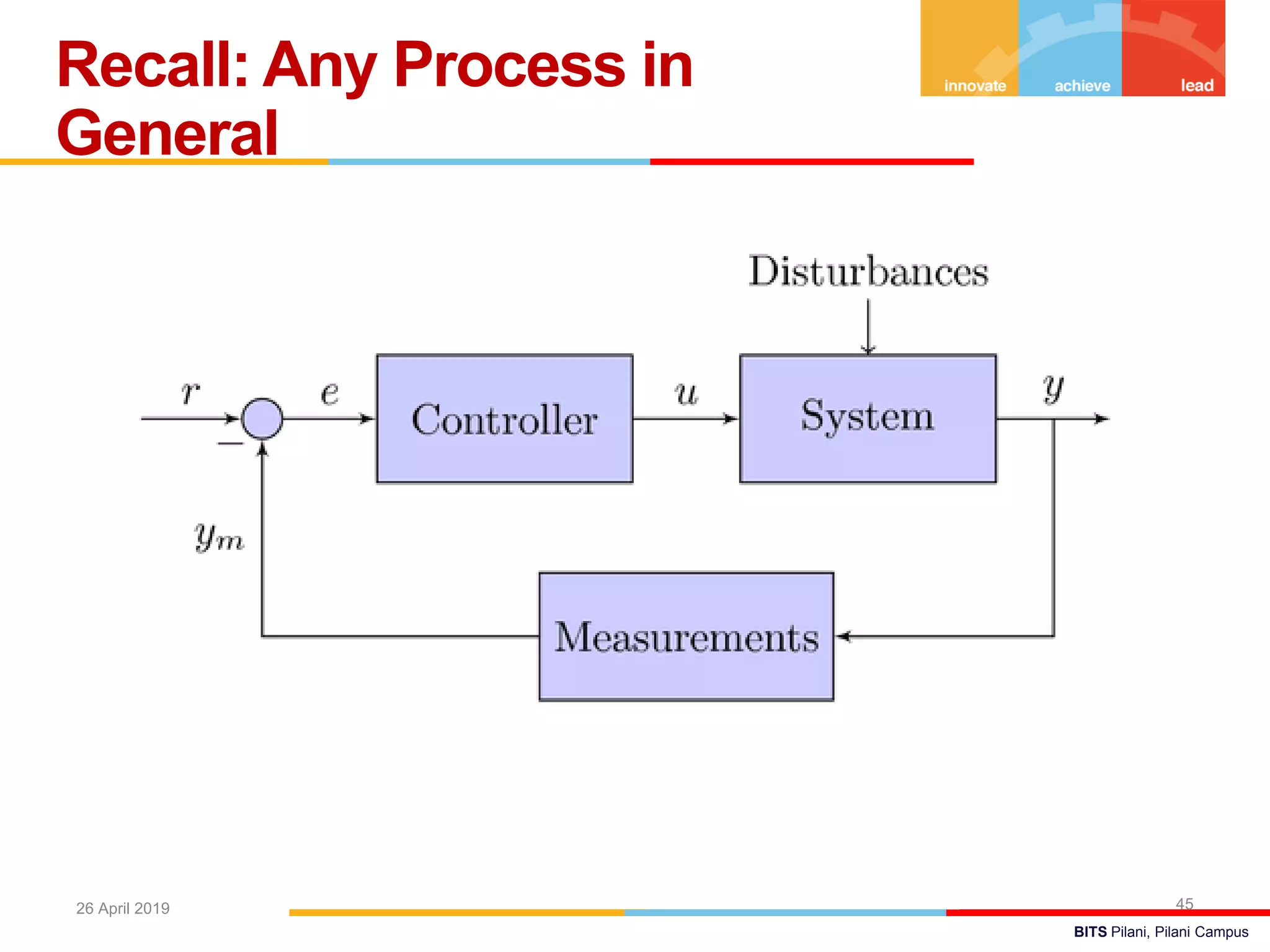
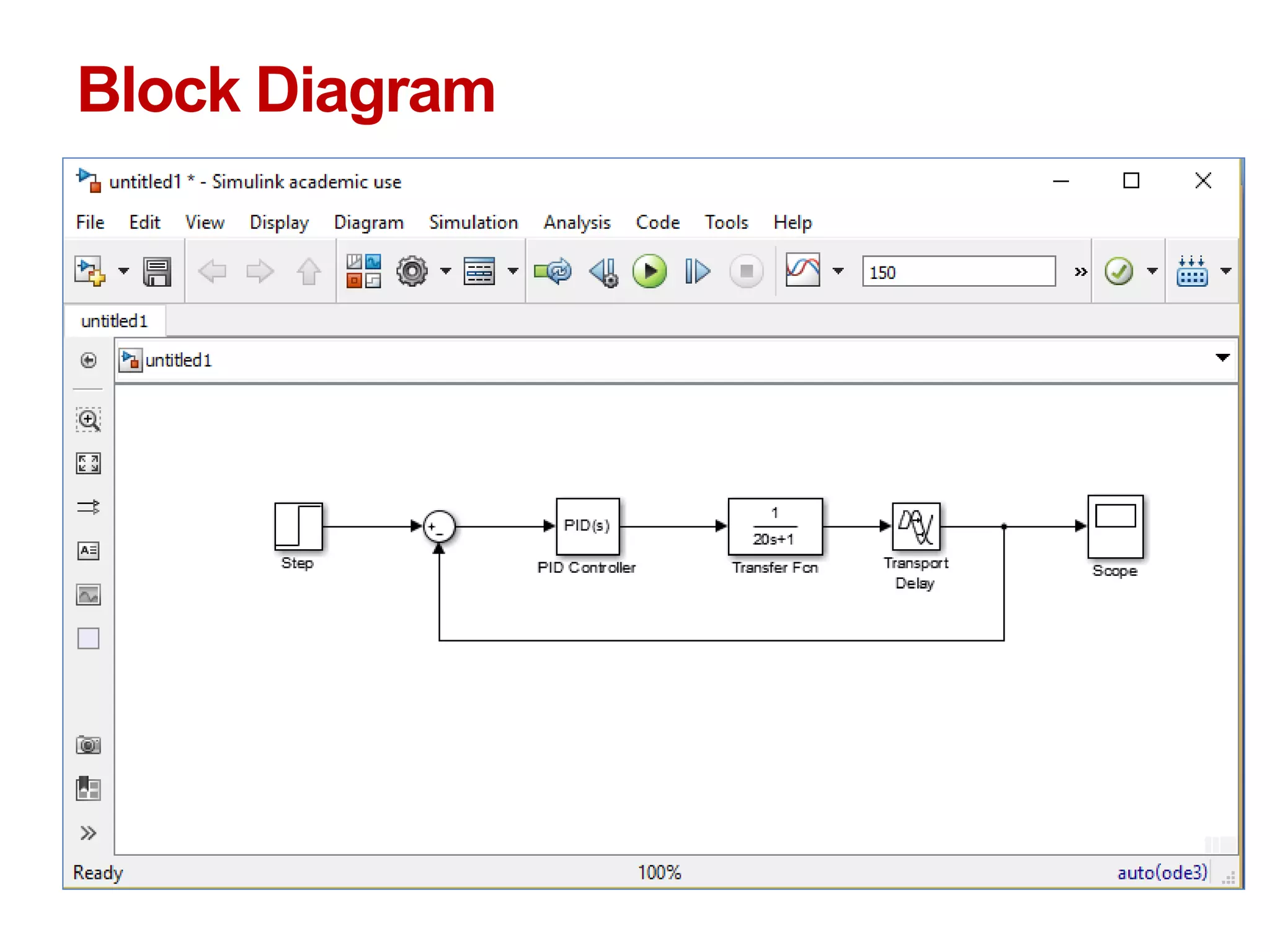
The document describes a presentation on using MATLAB and Simulink for process engineering. It discusses how Simulink can be used to model, simulate, and analyze multi-domain dynamic systems using graphical block diagrams. Examples are provided on building simple models in Simulink, including integrating a sine wave and modeling a first-order process. Process control applications are demonstrated, such as modeling different types of controllers and their effects.