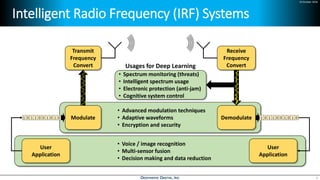
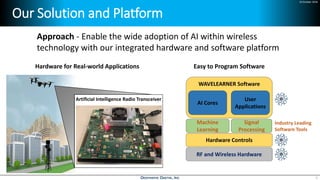
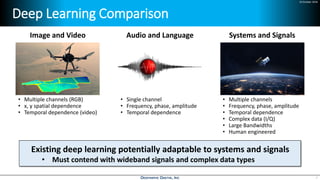
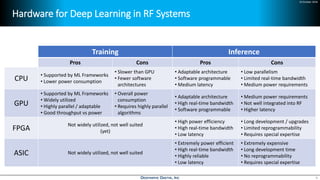
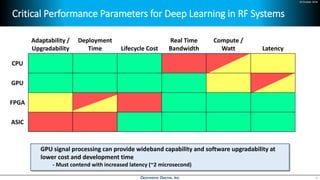
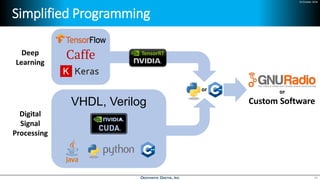
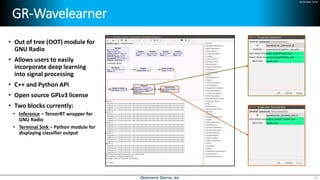
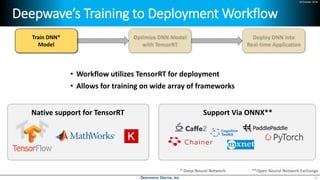
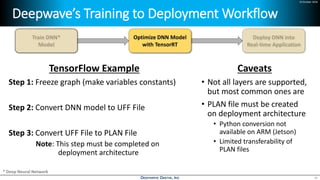
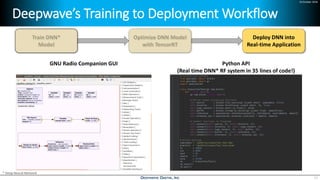
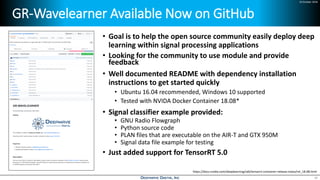
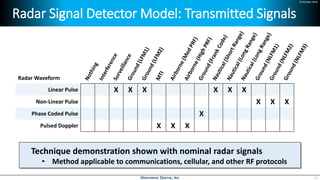
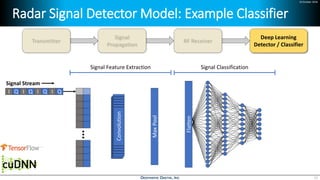
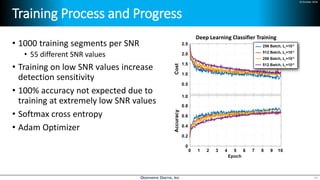
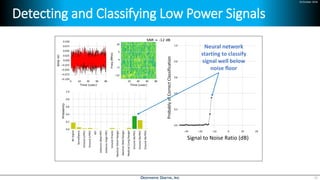
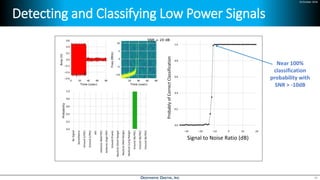
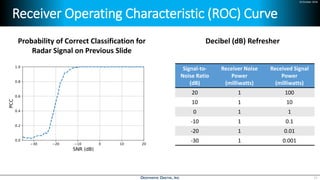
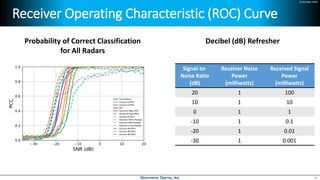
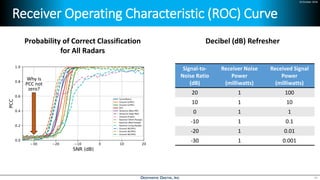
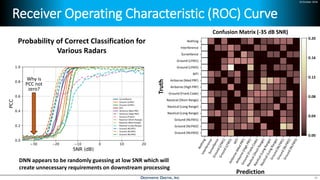
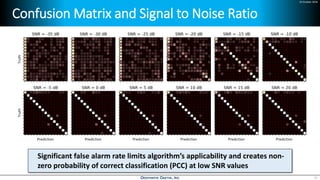
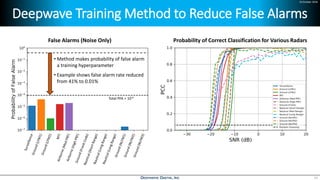
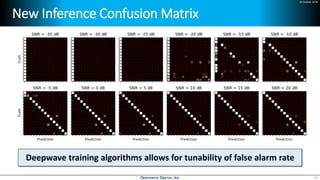
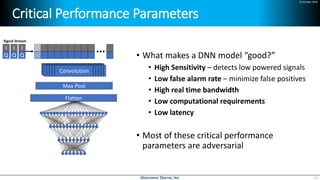
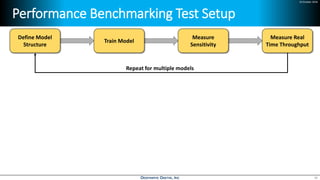
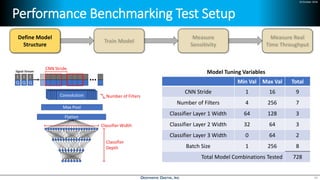
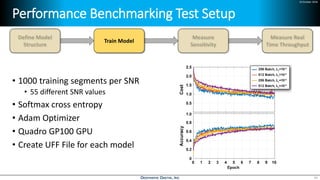
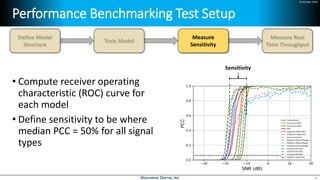
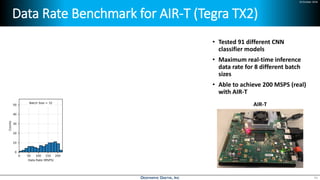
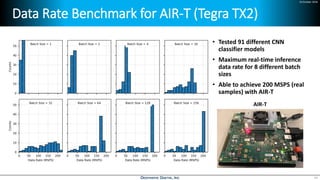
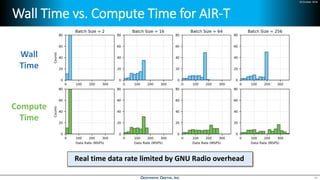
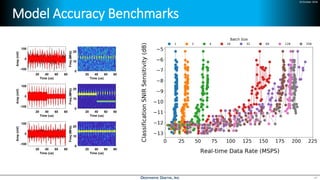
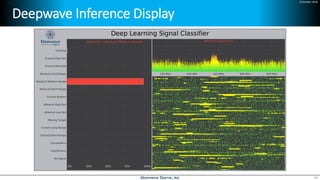
Deep learning is emerging across many applications but has yet to significantly impact radio frequency and wireless systems. Deepwave Digital is developing an artificial intelligence radio transceiver platform to enable the integration of deep learning capabilities into wireless technology. This includes an SDR framework and software that allows users to easily incorporate deep neural networks for applications such as signal detection and classification. Benchmark tests on the platform show it is capable of classifying signals in real-time with throughput of over 100 Mbps while maintaining high sensitivity even for low power signals.