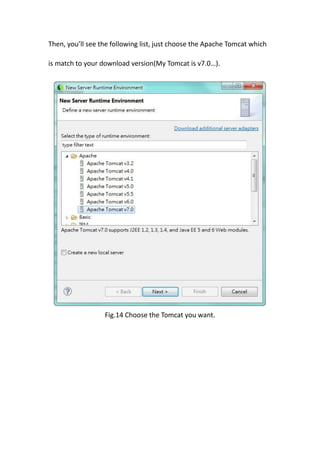
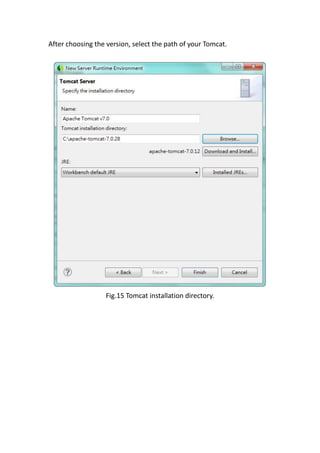
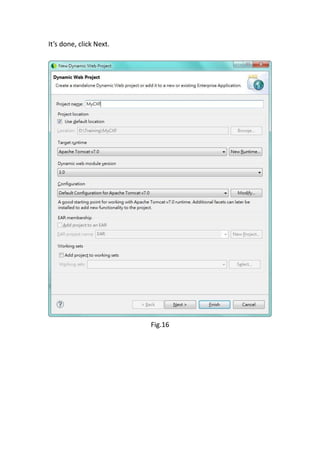
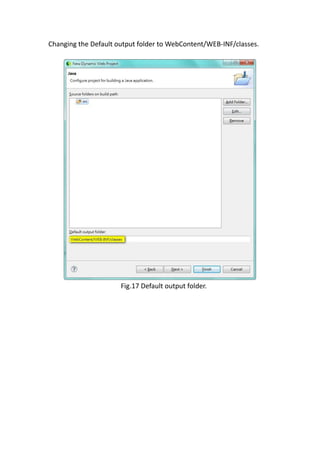
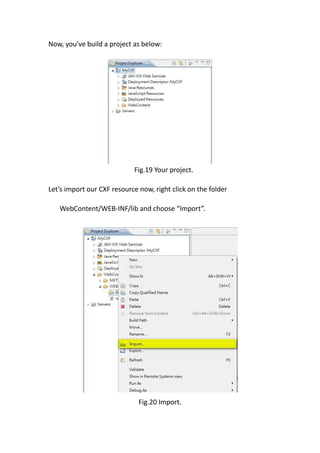
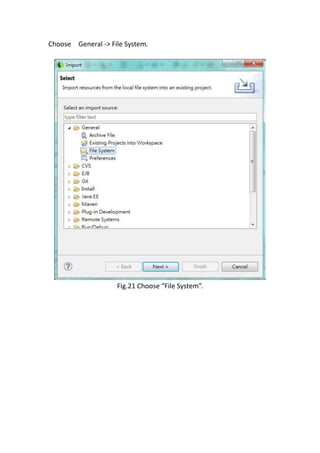
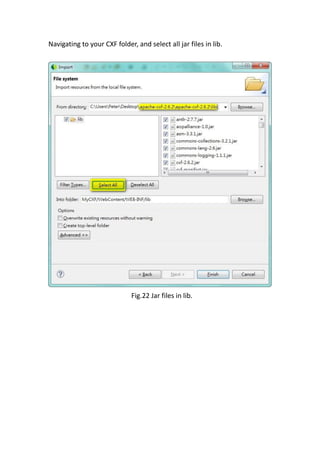
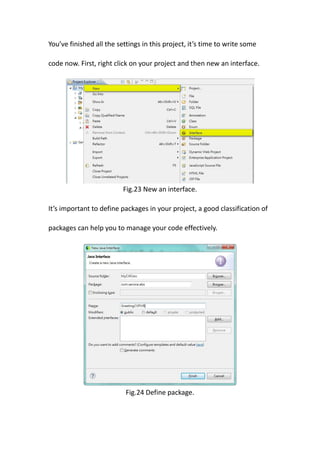
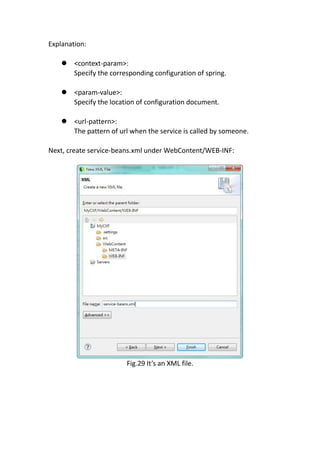
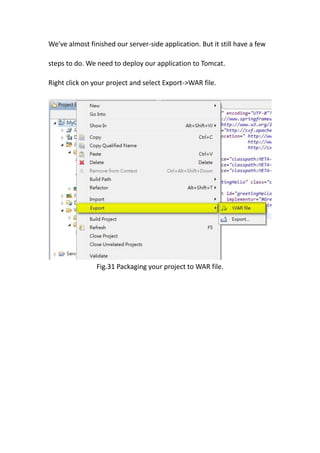
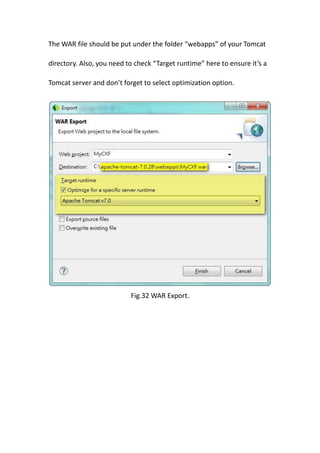
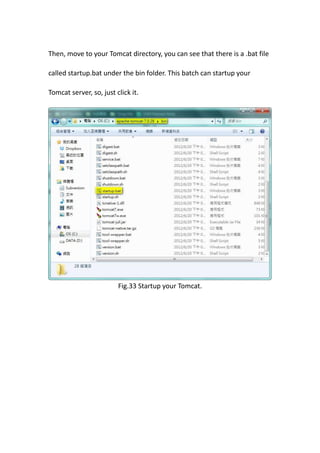
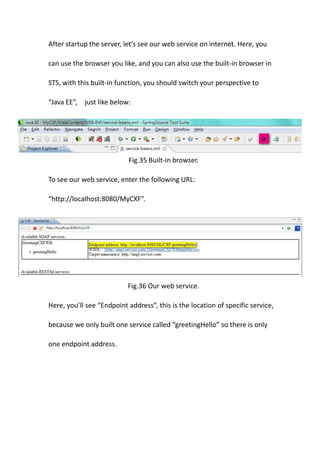
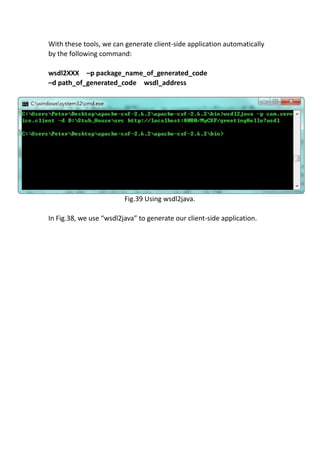
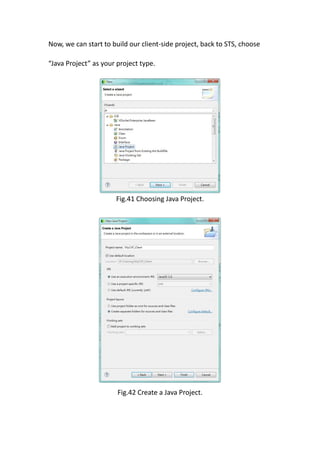
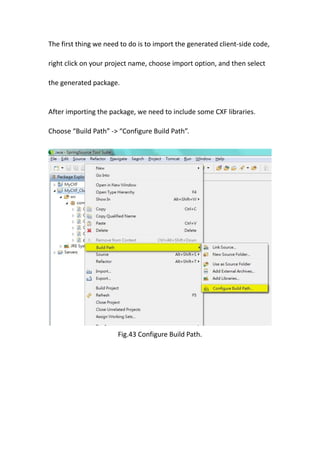
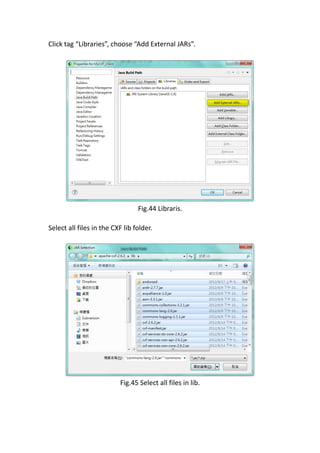
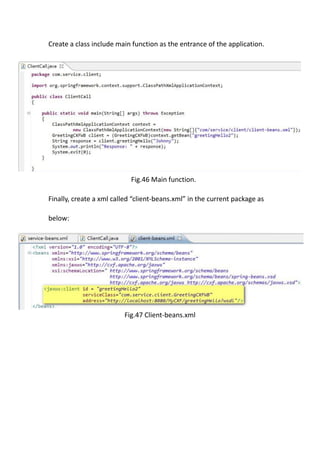
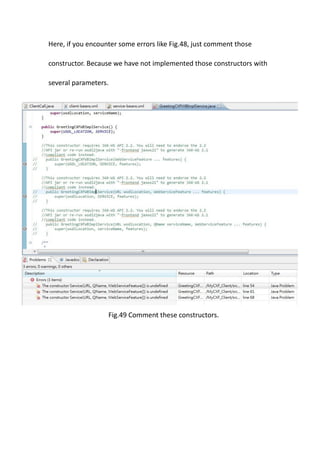
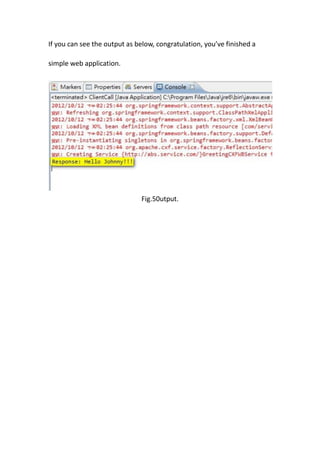
This document provides a tutorial for setting up a development environment to create a simple web service in Java using the Apache CXF framework. It describes how to install Spring Tool Suite (STS), Apache CXF, and Tomcat. It then guides the user through creating a web service interface and implementation class with JAX-WS annotations, configuring the web.xml and spring context files, building and deploying the WAR file to Tomcat, and using the WSDL to generate and test a client stub application.