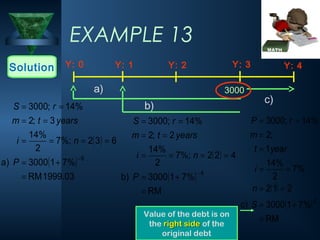
The document discusses simple and compound interest. It defines simple interest as interest calculated on the original principal for the entire period. Compound interest is calculated on a principal amount that changes over time as interest earns more interest. The key formulas for simple interest and compound interest are presented. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating simple and compound interest for various scenarios involving different principal amounts, interest rates, time periods, and compounding frequencies. Practice problems are also included for the reader to work through.