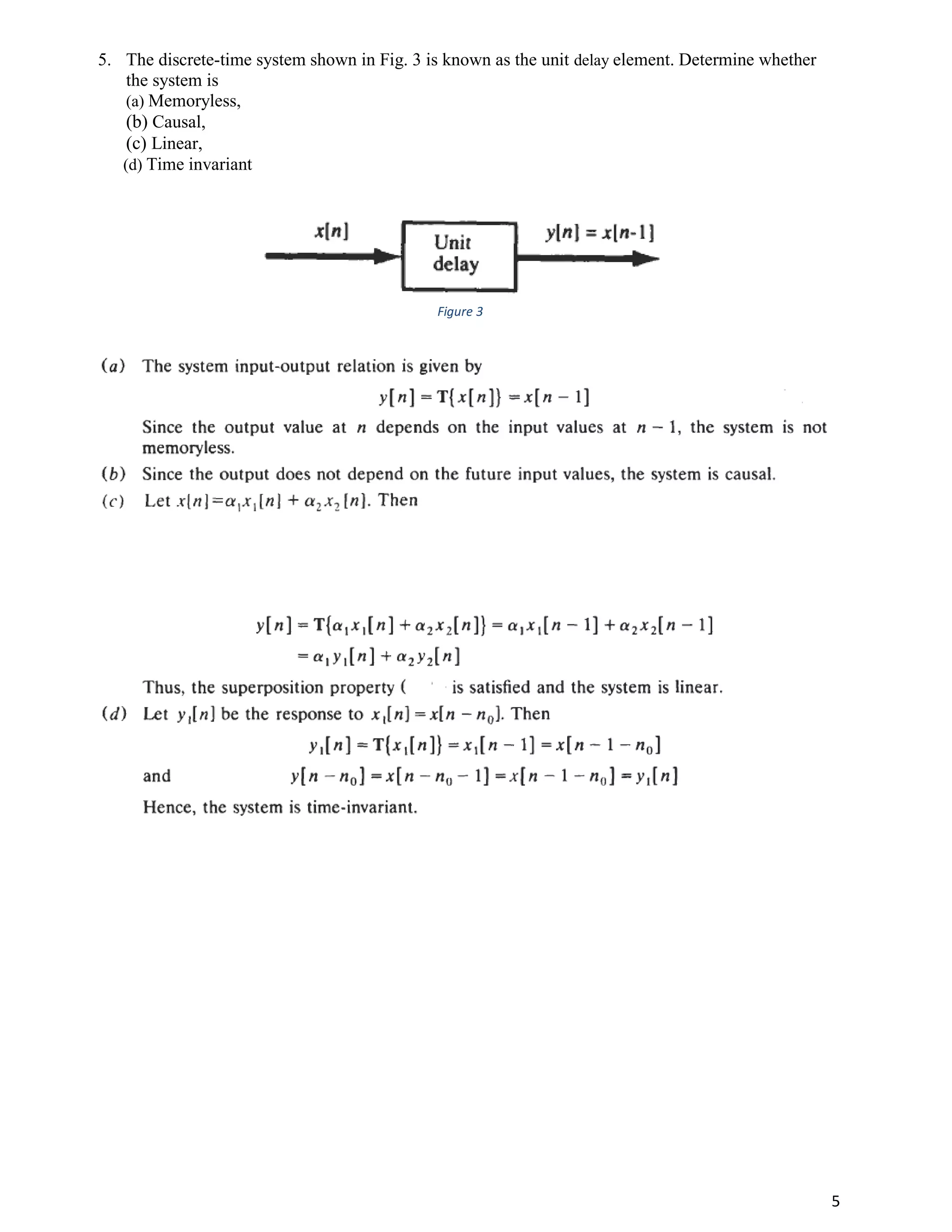
This document contains the solutions to an homework assignment on linear and nonlinear systems. It examines several examples and determines whether they are linear or nonlinear by applying the superposition principle. It also identifies examples as causal or non-causal. Finally, it analyzes some circuit examples and determines properties like memoryless, causal, linear, and time-invariant.

![2
2. Determine which signals are causal and non-causal
a. 𝑦[𝑛] = 𝑥[−𝑛]
b. 𝑦(𝑡) = 𝑥(𝑛 + 1)
Non Causal
c. 𝑦 ( 𝑡 ) = 𝑥 ( 𝑡 ) 𝑥 ( 𝑡 + 1)
Non Causal
d. 𝑦 ( 𝑡 ) = 𝑥 ( 𝑡 ) + 1
Causal As I is a dc value which is a constant and does not affect x(t)
3. Consider an RC circuit below. Find the input x(t) and output y(t) relationship for this circuit in
a. If 𝑥(𝑡) = 𝑉𝑠(𝑡) 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑦(𝑡) = 𝑉𝑐(𝑡)
b. If 𝑥(𝑡) = 𝑉𝑠(𝑡) 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑦(𝑡) = 𝑖(𝑡)
Figure 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hw2solution-150509180133-lva1-app6891/75/signal-and-system-Hw2-solution-2-2048.jpg)