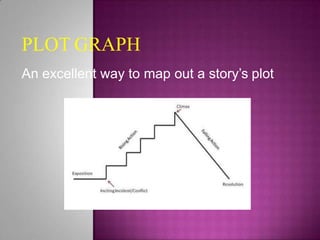
This document provides an overview of the key elements of short stories, including plot, setting, character, theme, and more. It explains that a short story contains few characters and a simple, swift plot involving an introduction, inciting incident, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution. A plot graph is recommended to map out these story elements. It also describes conflict, suspense, foreshadowing, flashbacks, and the climax as important to driving the narrative. Setting, character types, and resolving the central theme are also outlined as essential components of short stories.