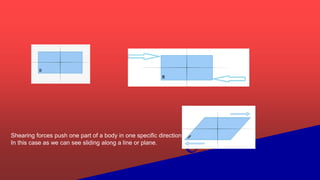
Shear forces act perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of a beam and can cause shear failure if the shear resistance is insufficient. Shear failure occurs when a material is pushed in different directions, potentially causing cracks or excessive deflection. It can happen due to issues like incorrect design assumptions, weak concrete strength, or misplaced steel reinforcement. To prevent shear failure, engineers must properly design shear reinforcement, using strong concrete and ensuring adequate and properly placed reinforcing rods.