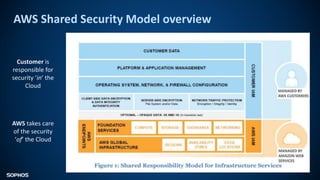
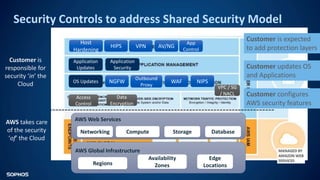
The document outlines AWS's shared security model, emphasizing that customers are responsible for security 'in' the cloud while AWS handles security 'of' the cloud. It details common threats such as ransomware, web application attacks, and denial-of-service, along with their consequences like data breaches and system restoration challenges. Sophos's role as a security competency partner is also highlighted, showcasing solutions that enhance security across various AWS services.