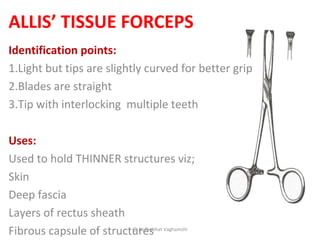
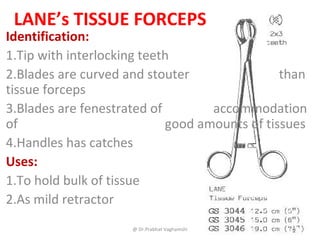
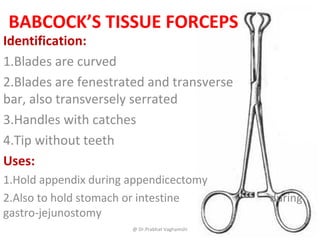
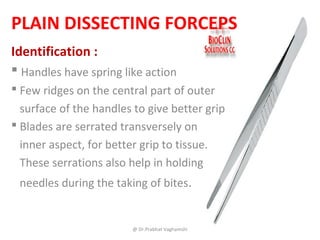
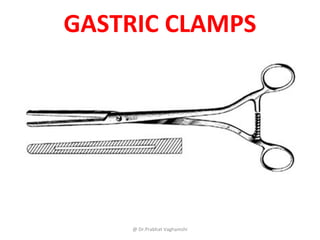
The document details various surgical instruments, their uses, and identification points. It covers instruments like cheatle forceps, dissecting forceps, retractors, and needle holders, providing information on types, functionalities, and specific examples. Additionally, it discusses lumbar punctures, contraindications, towel clips, and proctoscopes, emphasizing their roles in medical procedures.