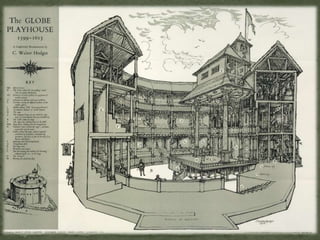
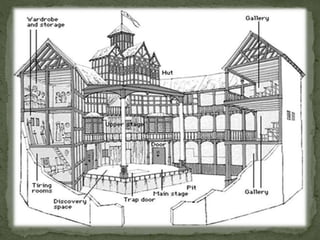
William Shakespeare was born in 1564 in Stratford-Upon-Avon, England to a prominent town official. He received an excellent education focused on grammar and literature. In the 1580s, he married Anne Hathaway and had three children, but the years between 1585-1595 are undocumented. He later moved to London and began working as an actor and playwright, producing some of the most renowned plays and poems in English literature. His plays are categorized as comedies, tragedies, and histories. Shakespeare and his acting company performed at theaters in London until building their own, called The Globe. He retired to Stratford in 1610 and died in 1616 at the age of 52.