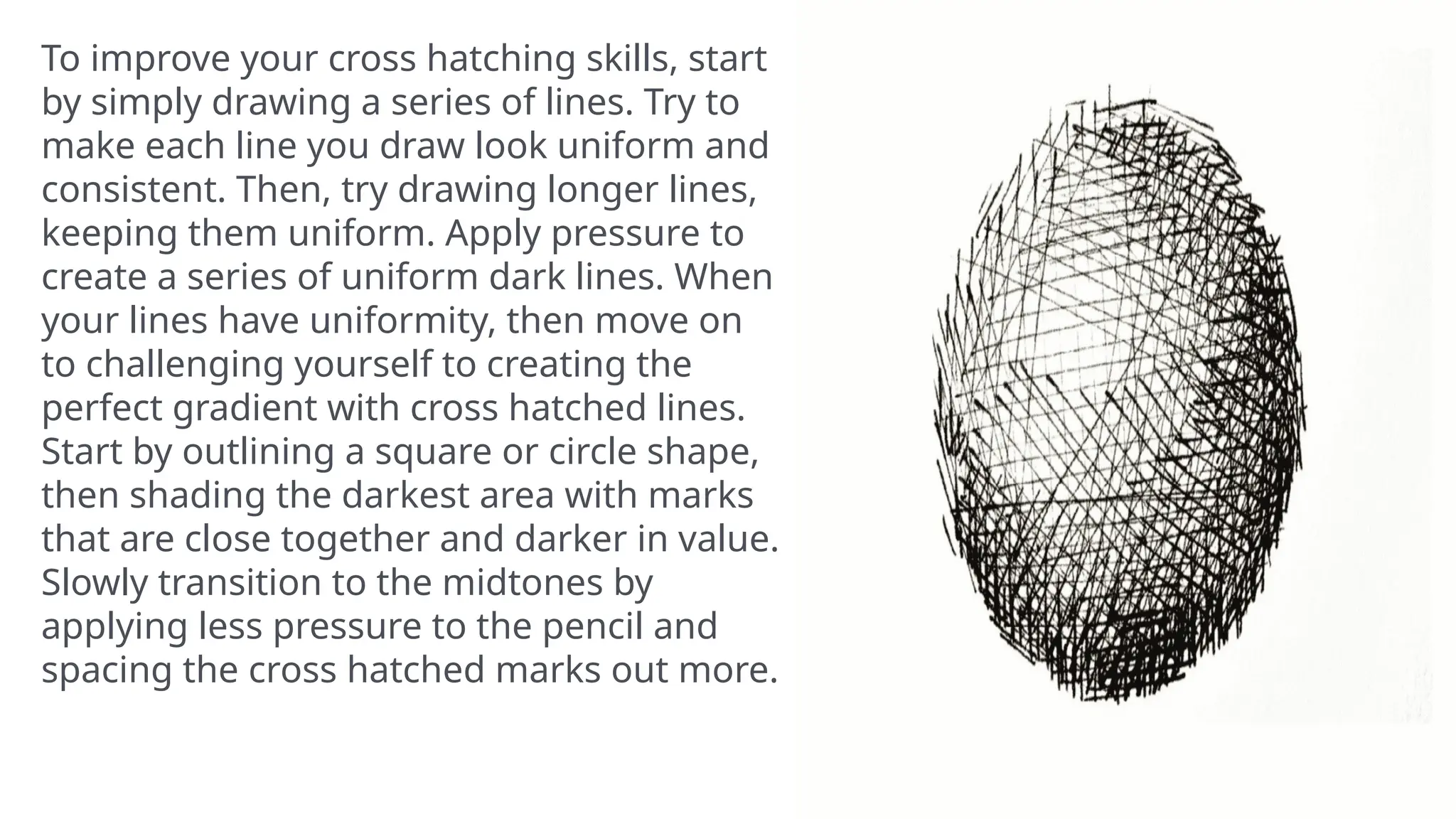
Shading is a vital artistic technique used to create tonal variations, enhancing the three-dimensional appearance of artworks. Various methods such as tonal shading, hatching, cross hatching, contour hatching, stippling, and scumbling help artists achieve different textures, depth, and value contrasts in their work. Mastering these techniques allows for greater control over light and shadow, resulting in more realistic and visually engaging pieces.