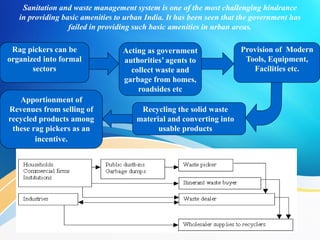
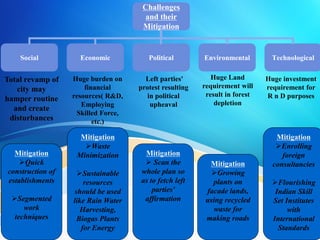
Ensuring World Class Civic Amenities in Urban India discusses challenges facing India's major cities like housing shortages, waste disposal, and power issues due to rapid urbanization. It proposes solutions like building high-rise housing, organizing waste pickers, and establishing public transport systems. However, challenges remain on implementation due to lack of coordination, funding, and long-term planning. The solution proposes establishing a pooled financing entity and improving human resources to better coordinate and fund solutions to ensure civic amenities in urban India.