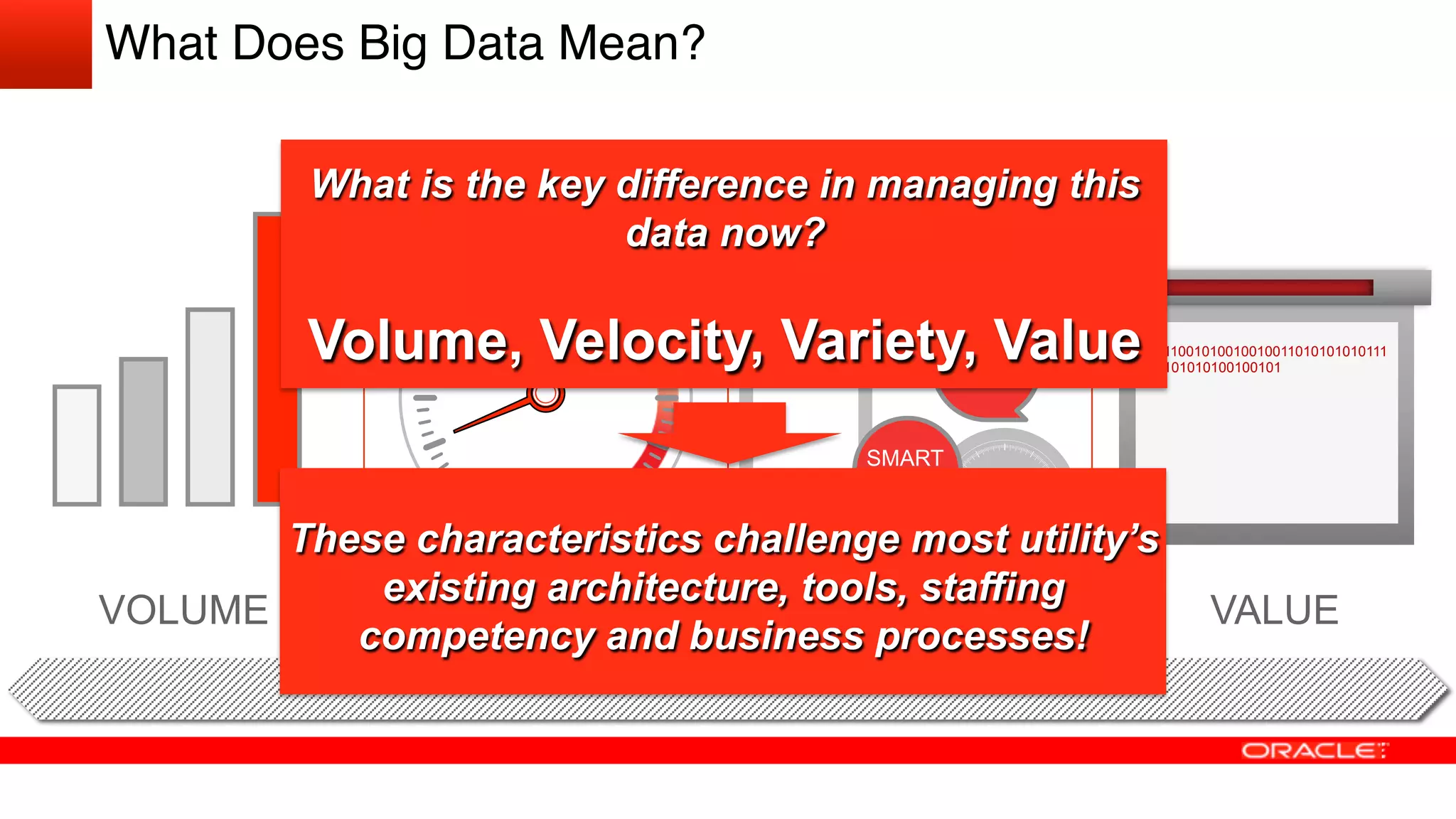
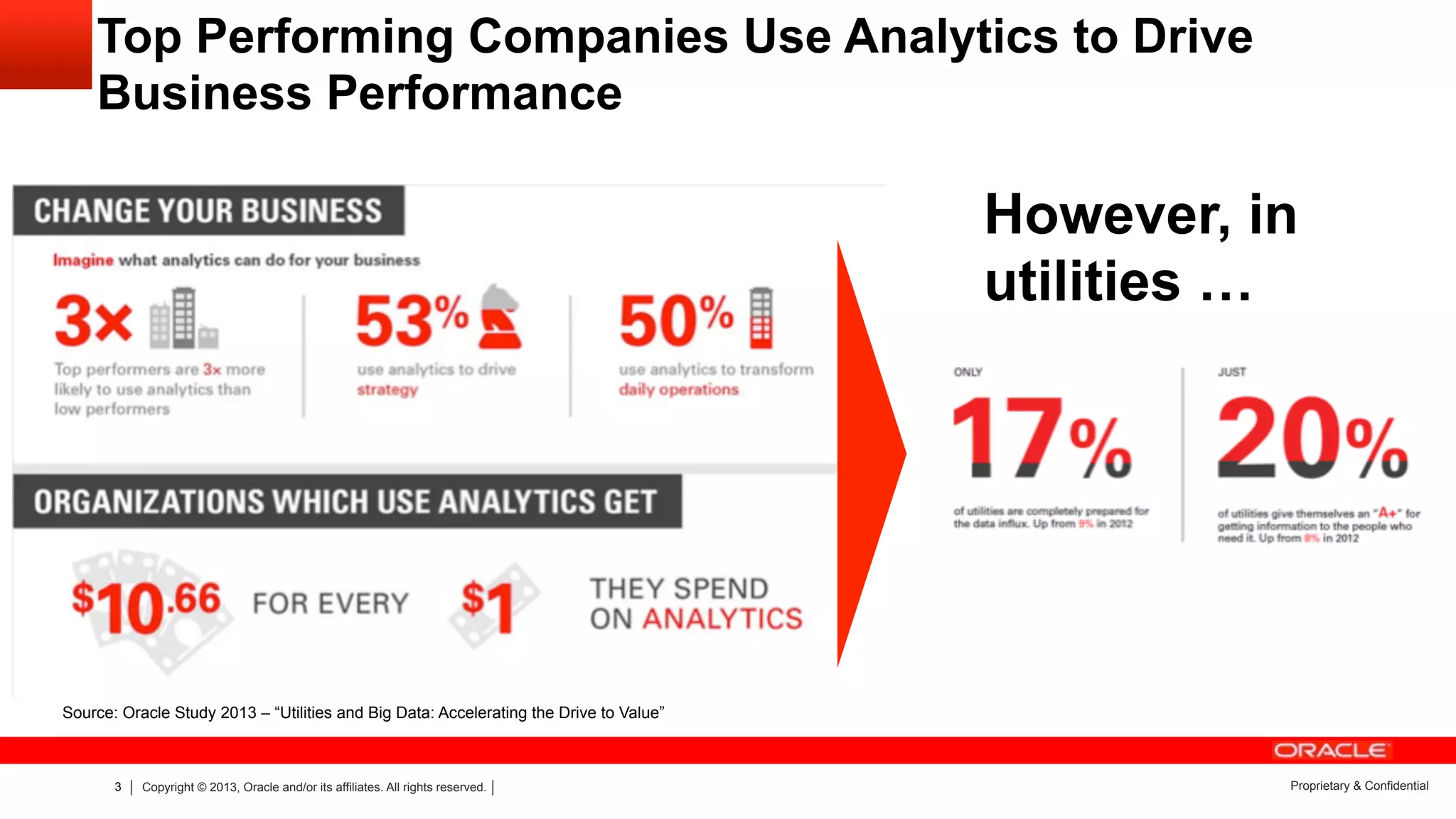
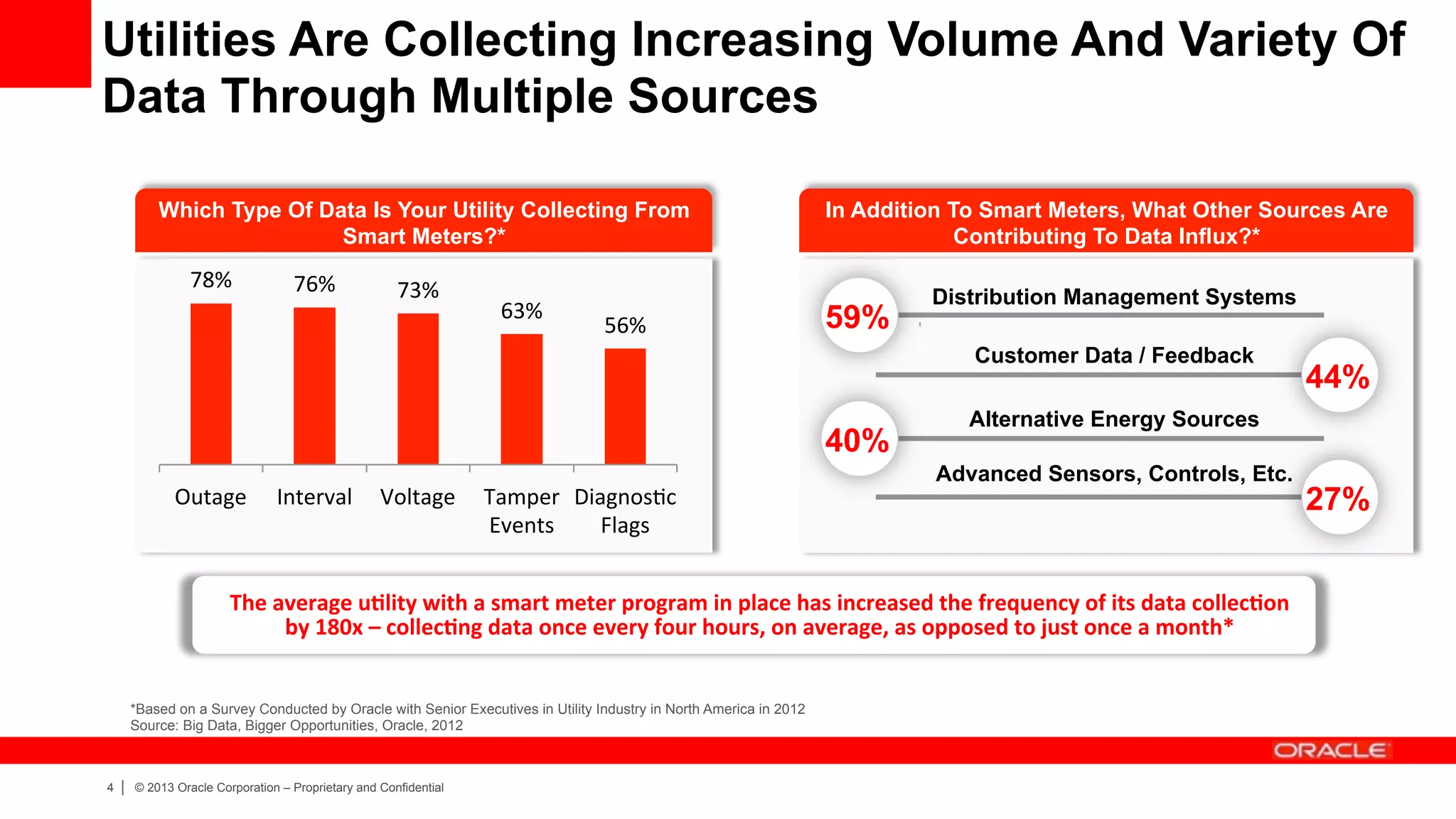
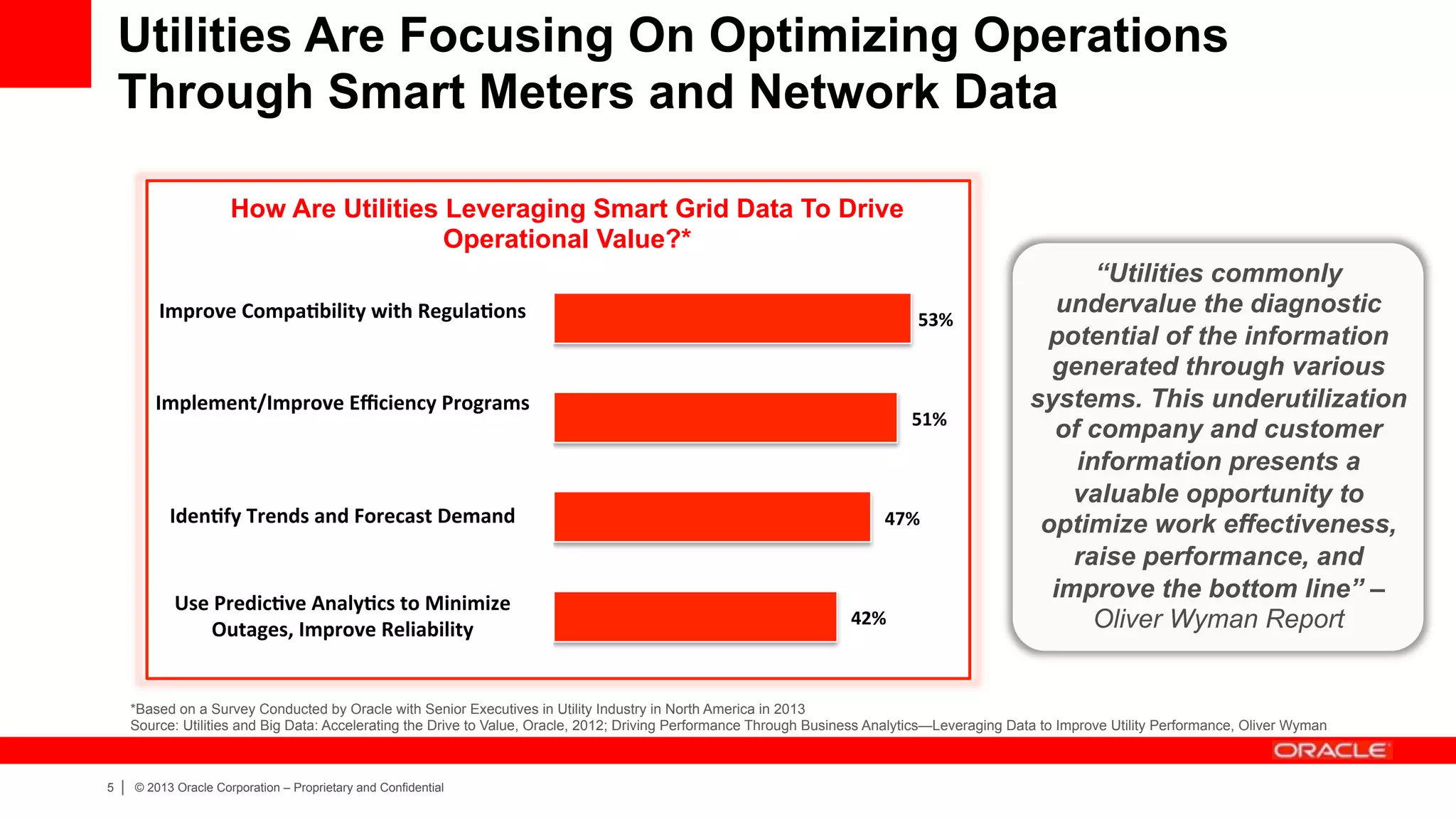
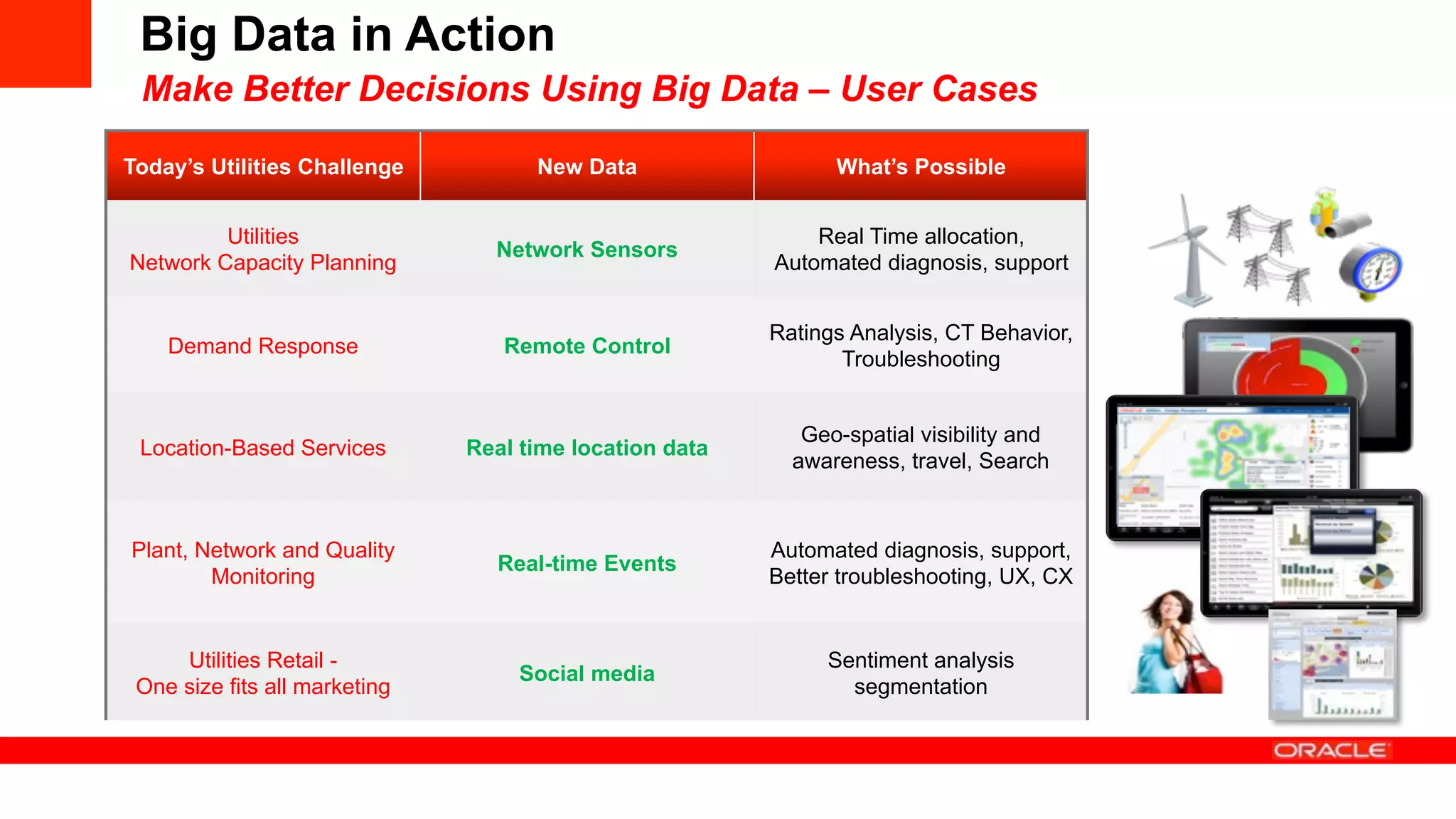
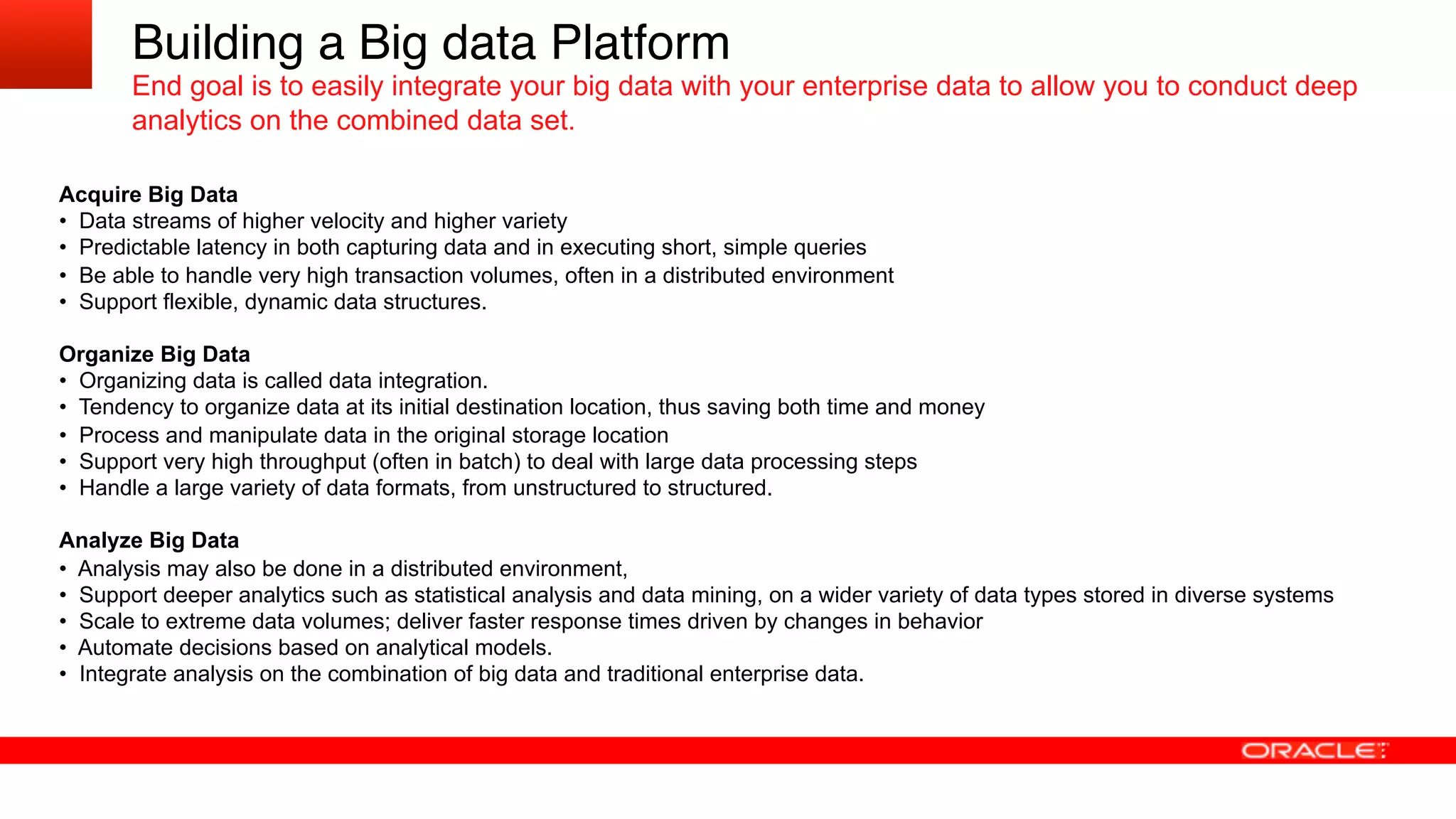
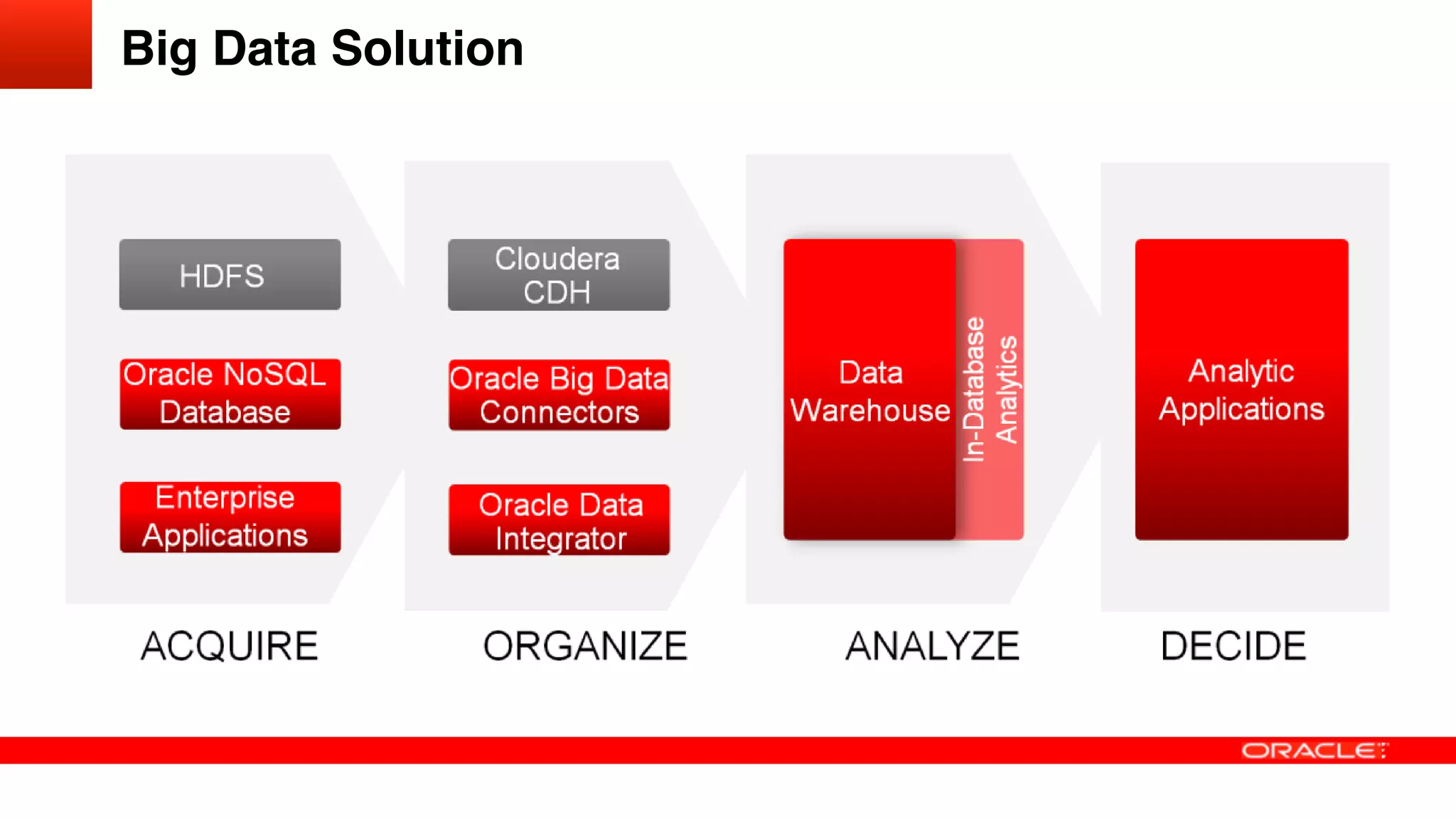
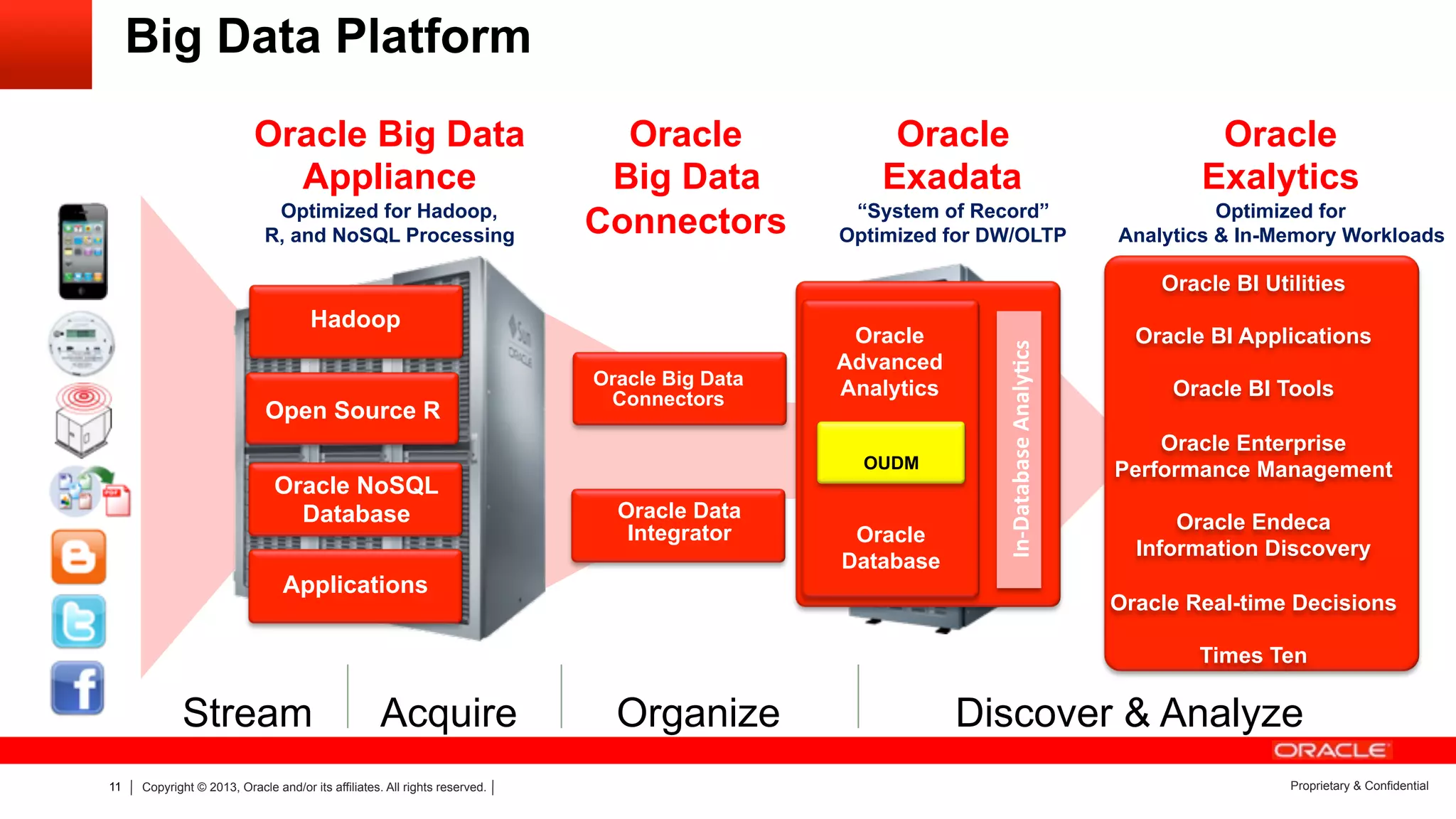
The document discusses how utilities are increasingly collecting and generating large amounts of data from smart meters and other sensors. It notes that utilities must learn to leverage this "big data" by acquiring, organizing, and analyzing different types of structured and unstructured data from various sources in order to make more informed operational and business decisions. Effective use of big data can help utilities optimize operations, improve customer experience, and increase business performance. However, most utilities currently underutilize data analytics capabilities and face challenges in integrating diverse data sources and systems. The document advocates for a well-designed data management platform that can consolidate utility data to facilitate deeper analysis and more valuable insights.