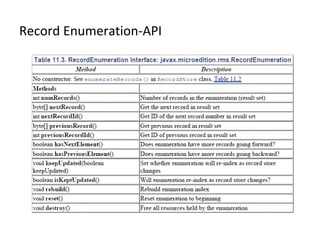
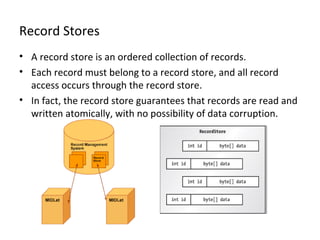
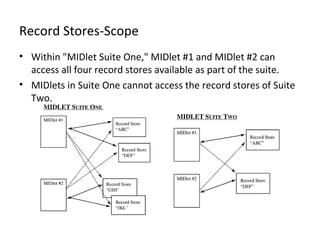
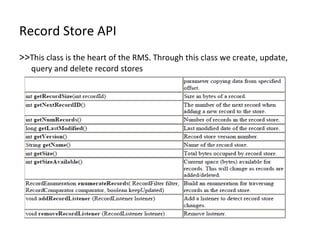
The document discusses Record Management System (RMS) in Java ME, which allows MIDlets to store data permanently without a file system. RMS provides a simple record-oriented database using record stores. A record store is a collection of variable-sized records identified by a unique ID. Records can be added, retrieved, updated, enumerated, and deleted through the RecordStore API.







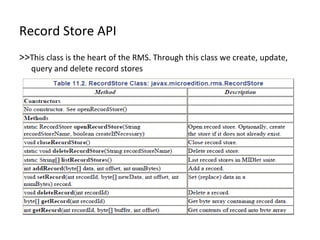

![Manage Record Store closeRecordStore () method closes a n open record. rs. closeRecordStore() ; Remember to clean up after yourself as much as possible. T o delete a record store and its contained records, call the static deleteRecordStore () method. RecordStore.deleteRecordStore("Address"); To find out all the record stores available to a particular MIDlet suite, call the listRecordStores () method: public static String[] listRecordStores()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session9-rms-101215100512-phpapp02/85/Session9-J2ME-Record-Management-System-13-320.jpg)
![Adding records The MIDlet invokes the addRecord () method of RecordStore class to insert a new record into the record store. public int addRecord(byte[] data, int offset, int numBytes) inserts a record represented by an array of bytes data with offset as its starting index and numBytes as its length. String brand = "Honda"; byte bytes[] = brand .getBytes(); int recID = rs .addRecord (bytes,0,bytes.length);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session9-rms-101215100512-phpapp02/85/Session9-J2ME-Record-Management-System-14-320.jpg)
![Manage Record Store closeRecordStore () method closes a n open record. rs. closeRecordStore() ; Remember to clean up after yourself as much as possible. T o delete a record store and its contained records, call the static deleteRecordStore () method. RecordStore.deleteRecordStore("Address"); To find out all the record stores available to a particular MIDlet suite, call the listRecordStores () method: public static String[] listRecordStores()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session9-rms-101215100512-phpapp02/85/Session9-J2ME-Record-Management-System-15-320.jpg)
![Retrieving Record There are two versions to retrieve a record: public int getRecord(int recordId, byte[] buffer, int offset) copies the data stored in the given record to the byte array represented by buffer. public byte[] getRecord(int record I d) returns a new copy of the data represented by recordId. byte[] retrieved = new byte[rs.getRecordSize( recID )]; rs.getRecord(id, retrieved, 0); String retrievedString = new String(retrieved); byte[] retrieved = rs.getRecord( recID ); String retrievedString = new String(retrieved);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session9-rms-101215100512-phpapp02/85/Session9-J2ME-Record-Management-System-16-320.jpg)
![Update Record To update a record use the method setRecord : public void setRecord(int recordId, byte[] newData, int offset, int numBytes) sets new information, a stream of bytes (newData) with offset as its starting index and numBytes as its length, at the record location represented by recordId. String brand = "Toyota"; byte data[] = newappt.getBytes(); r s.setRecord( recID , data, 0, data.length());](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session9-rms-101215100512-phpapp02/85/Session9-J2ME-Record-Management-System-17-320.jpg)