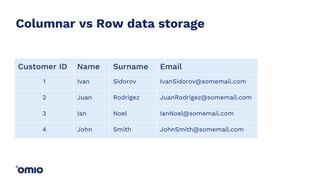
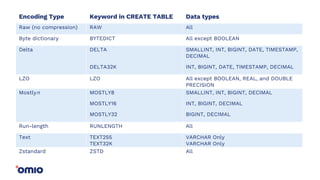
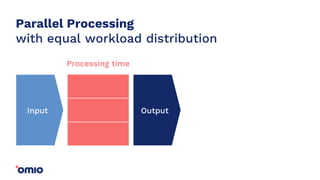
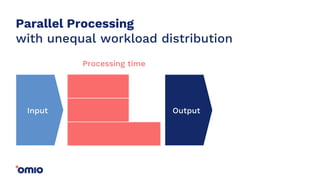
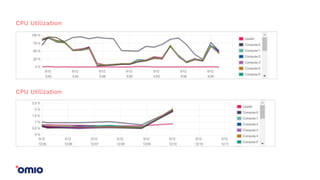
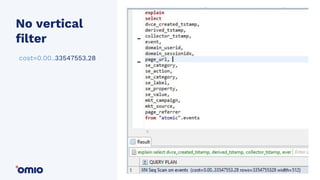
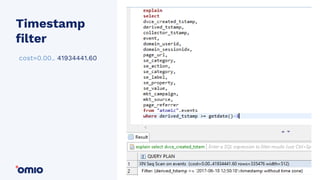
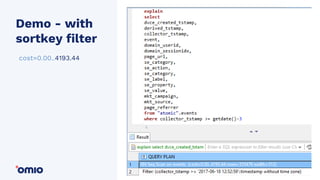
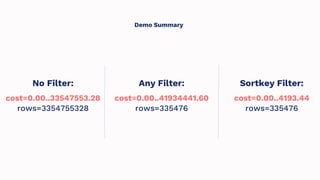
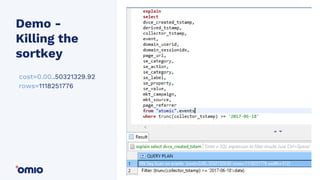
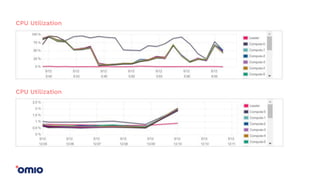
Amazon Redshift is a fully managed data warehouse service that allows for petabyte-scale analytics on data stored in columns. It uses a massively parallel processing architecture and columnar data storage to improve query performance. Defining sort keys and distribution keys appropriately is crucial to influence how data is stored and queries are processed in parallel across nodes. Automatic features like concurrency scaling, resize operations, and backups help ensure the warehouse scales and remains available as data and usage grow over time.