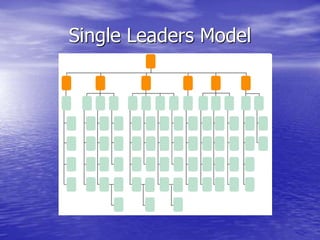
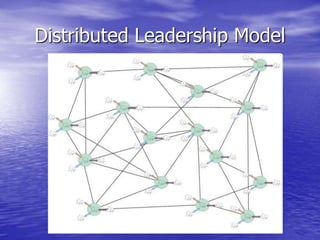
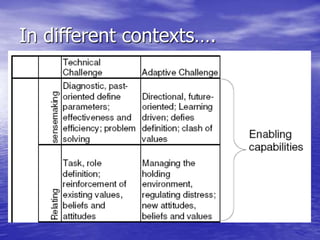
Distributed leadership involves sharing leadership responsibilities across an organization. It focuses on developing leadership capabilities in all people rather than designating a single leader. The key capabilities include sensemaking, relating, visioning, and inventing. Sensemaking involves interpreting information to develop understanding of challenges. It is an iterative social process focused on cues and plausibility over accuracy. Distributed leadership relies on many people in an organization engaging in sensemaking to recognize issues and opportunities in a dynamic environment.