The document outlines an Android course with Java, covering key programming concepts such as strings, garbage collection, type casting, and control flow statements like if, switch, for, and while loops. Examples are provided to demonstrate syntax and usage for each topic, such as string manipulation, object-oriented programming features, and array handling. It serves as a comprehensive guide for beginners to learn the fundamental components of Java programming.










![For-Each Loop:-
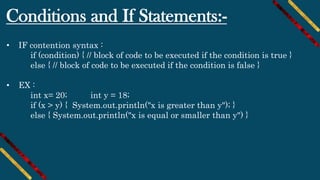
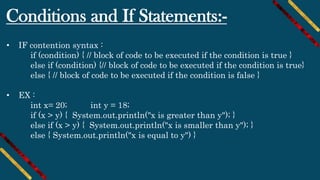
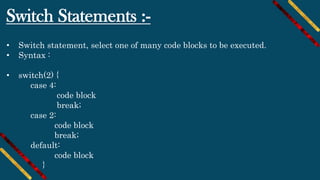
• Syntax :
for (type variableName : arrayName) {
// code block to be executed
}
EX :
String[] cars = {"Ahmed", "Mohamed", "Ali", "Mazda"};
for (String i : cars) {
System.out.println(i);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/t1fmthfmsz2wexavt8m4-signature-99af1c1c96f32ecd35bfbecd2077c0f5c28e4ef15499b7cdd6e415b052c86c4d-poli-191026141005/85/Android-course-session-2-java-basics-14-320.jpg)



![Arrays :-
• String [ ] cars;
String[] cars = {"Volvo", "BMW", "Ford", "Mazda"};
int[] myNum = {10, 20, 30, 40};
System.out.println(cars[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < cars.length; i++) {
System.out.println(cars[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/t1fmthfmsz2wexavt8m4-signature-99af1c1c96f32ecd35bfbecd2077c0f5c28e4ef15499b7cdd6e415b052c86c4d-poli-191026141005/85/Android-course-session-2-java-basics-18-320.jpg)
![Multidimensional Arrays :-
• int[][] myNumbers = { {1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7} };
int x = myNumbers[1][2];
System.out.println(x); // Outputs 7
for (int i = 0; i < myNumbers.length; ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < myNumbers[i].length; ++j) {
System.out.println(myNumbers[i][j]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/t1fmthfmsz2wexavt8m4-signature-99af1c1c96f32ecd35bfbecd2077c0f5c28e4ef15499b7cdd6e415b052c86c4d-poli-191026141005/85/Android-course-session-2-java-basics-19-320.jpg)
