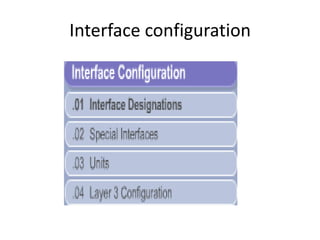
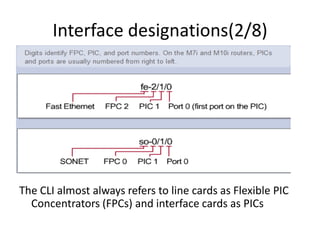
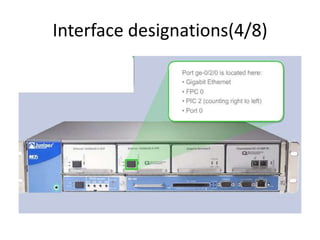
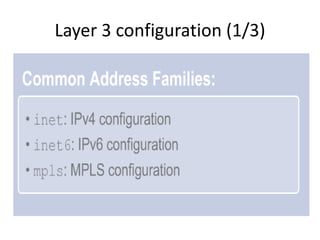
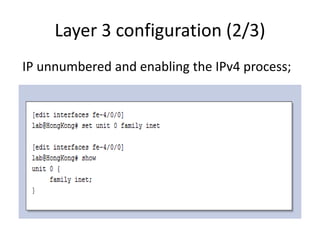
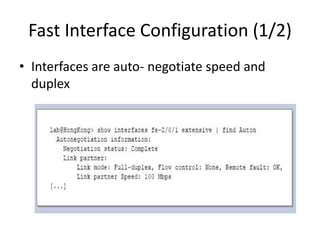
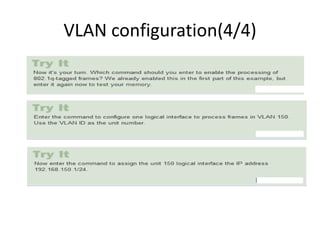
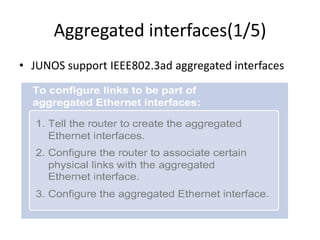
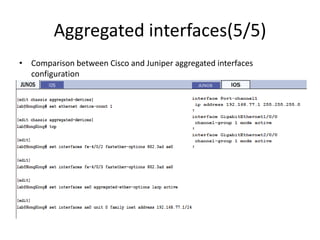
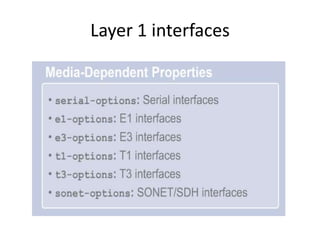
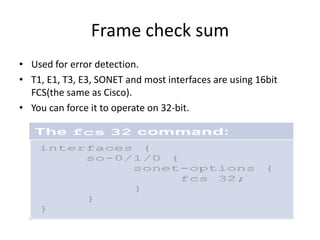
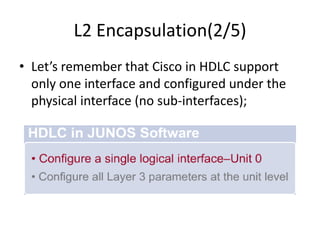
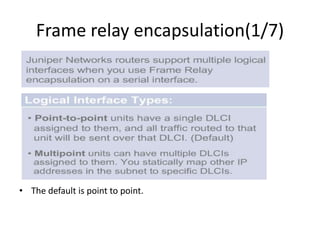
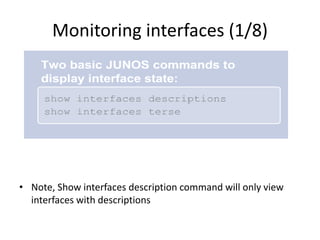
This document provides an overview of interface configuration and monitoring on Juniper networks devices. It discusses the naming conventions for interfaces, including Flexible PIC Concentrators (FPCs) and PICs. It also covers configuring various interface types such as Ethernet, VLAN, aggregated Ethernet, serial and loopback interfaces. The document demonstrates how to configure encapsulation types like HDLC, PPP and Frame Relay. It concludes with examples of commands to monitor interface status, descriptions, statistics and details.









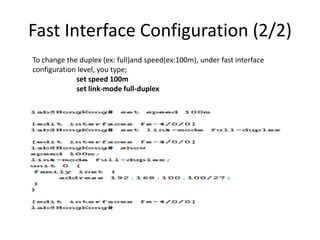
![Gigabit Ethernet Configuration (2/2)
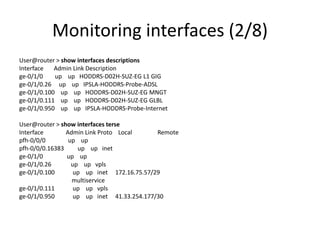
User@A-S01J-EG> show interfaces ge-0/0/20
Physical interface: ge-0/0/20, Enabled, Physical link is Up
Interface index: 199, SNMP ifIndex: 588
Description: ESP-Fathala-AUTO-L3VPN-1226-11
Link-level type: Ethernet, MTU: 1514, Speed: Auto, Duplex: Auto, BPDU Error: None, MAC-REWRITE Error: None, Loopback: Disabled, Source filtering: Disabled,
Flow control: Enabled, Auto-negotiation: Enabled, Remote fault: Online
Device flags : Present Running
Interface flags: SNMP-Traps Internal: 0x0
Link flags : None
CoS queues : 8 supported, 8 maximum usable queues
Current address: 2c:6b:f5:8b:29:14, Hardware address: 2c:6b:f5:8b:29:14
Last flapped : 2014-01-2303:38:42EET (1w0d 09:16 ago)
Input rate : 4819136 bps (922 pps)
Output rate : 1144728bps (851 pps)
Active alarms : None
Active defects : None
Interface transmit statistics: Disabled
Logical interface ge-0/0/20.0(Index 122) (SNMP ifIndex 594)
Flags: SNMP-Traps 0x0 Encapsulation: ENET2
Input packets : 0
Output packets: 13338516
Protocol eth-switch
Flags: Trunk-Mode
{master:0}
User@A-S01J-EG> configure private
warning: uncommitted changes will be discarded on exit
Entering configuration mode
{master:0}[edit]
User@A-S01J-EG# edit interfaces ge-0/0/20
{master:0}[edit interfaces ge-0/0/20]
User@A-S01J-EG# edit ether-options
{master:0}[edit interfaces ge-0/0/20 ether-options]
User@A-S01J-EG# set speed 100m
{master:0}[edit interfaces ge-0/0/20 ether-options]
ahmed.nosehy@SEMOHA-S01J-ALX-EG# set link-mode full-duplex
{master:0}[edit interfaces ge-0/0/20 ether-options]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session2-140311032829-phpapp01/85/Session-2-24-320.jpg)
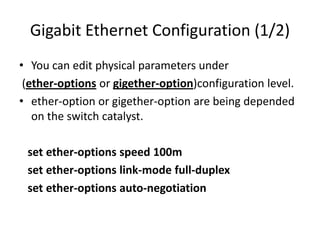
![VLAN configuration(2/4)
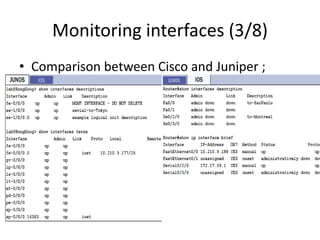
Example of editing vlan configuration
{master:0}[edit interfaces]
User @ switch # edit ge-0/0/19
{master:0}[edit interfaces ge-0/0/19]
User @ switch # show
description ESP-Hiltion-Ramsis-INT-30622-6;
{master:0}[edit interfaces ge-0/0/19]
User @ switch # set vlan-tagging
{master:0}[edit interfaces ge-0/0/19]
User @ switch # set unit 10 vlan-id 100
{master:0}[edit interfaces ge-0/0/19]
User @ switch # set unit 11 vlan-id 200
User @ switch # set unit 11 family inet address 2.2.2.2/30
{master:0}[edit interfaces ge-0/0/19]
User @ switch # show
description ESP-Hiltion-Ramsis-INT-30622-6;
vlan-tagging;
unit 10 {
vlan-id 100;
family inet {
address 1.1.1.1/30;
}
}
unit 11 {
vlan-id 200;
family inet {
address 2.2.2.2/30;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session2-140311032829-phpapp01/85/Session-2-26-320.jpg)


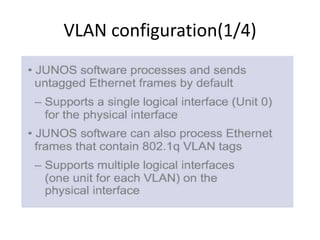
![Aggregated interfaces(4/5)
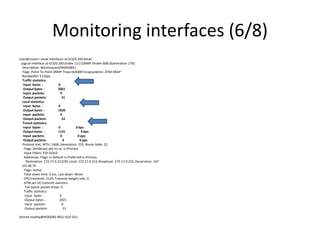
{master:0}[edit]
user@sw-EG# set interfaces ge-1/0/19 ether-options 802.3ad ae0
{master:0}[edit]
user@sw-EG# set interfaces ge-1/0/20 ether-options 802.3ad ae0
{master:0}[edit]
user@sw-EG#
user@sw-EG# show interfaces | find ge-1/0/19
ge-1/0/19{
description ESP-CIB-SmartV-L3VPN-17898-4;
ether-options {
802.3ad ae0;
ge-1/0/20{
description NTRA-Test;
ether-options {
802.3ad ae0;
}
}
{master:0}[edit]
user@sw-EG# set interfaces ae0 aggregated-ether-options lacp active
{master:0}[edit]
user@sw-EG# set interfaces ae0 unit 200 family inet address 3.3.3.3/30
{master:0}[edit]
user@sw-EG# show interfaces ae0
aggregated-ether-options {
lacp {
active;
}
}
unit 200 {
family inet {
address 3.3.3.3/30;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session2-140311032829-phpapp01/85/Session-2-32-320.jpg)
















![Monitoring interfaces (8/8)
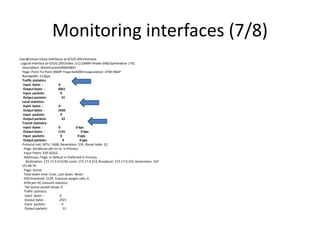
user@router> monitor interface at-0/3/0.200
HODDRS-R01J-SUZ-EG Seconds: 23 Time: 18:11:55
Delay: 2/0/21
Interface: at-0/3/0.200, Enabled, Link is Up
Flags: Point-To-Point SNMP-Traps 0x4000
Encapsulation: ATM-SNAP
VCI 48.79
Local statistics: Current delta
Input bytes: 0 [0]
Output bytes: 1920 [0]
Input packets: 0 [0]
Output packets: 22 [0]
Remote statistics:
Input bytes: 0 (0 bps) [0]
Output bytes: 1141 (0 bps) [0]
Input packets: 0 (0 pps) [0]
Output packets: 9 (0 pps) [0]
Traffic statistics:
Input bytes: 0 [0]
Output bytes: 3061 [0]
Input packets: 0 [0]
Output packets: 31 [0]
Protocol: inet, MTU: 1608, Flags: Is-Primary
VCI 48.79, Flags: Active 0x400
Total down time: 0 sec, Last down: Never
Traffic statistics:
Input bytes : 0
Output bytes : 2921
Input packets: 0
Output packets: 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session2-140311032829-phpapp01/85/Session-2-59-320.jpg)
