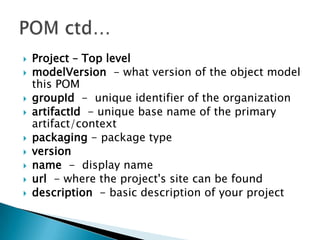
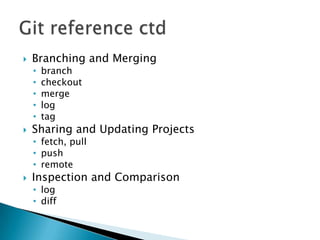
This document provides an overview of source control and version control using Git and GitHub. It discusses setting up projects with Maven and developing projects locally before pushing changes to GitHub repositories. The key points covered include: setting up source control with Git, forking and cloning repositories on GitHub, making changes locally and pushing updates via pull requests. Maven is also introduced for building Java projects and managing dependencies in an automated way.







![ public class AppTest{
public static void main(String [] args){
System.out.println("Hello Jaffna!");
}
}
Compile using command line
• Javac AppTest.java
• Java AppTest](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session2-120420210937-phpapp01/85/Session-2-8-320.jpg)