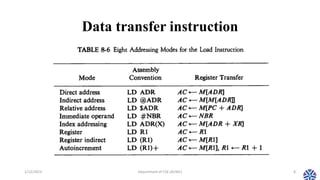
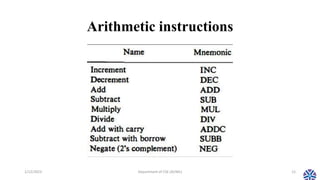
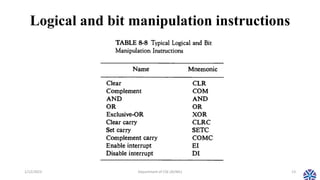
This document summarizes the topics covered in Session 14 of the CS304PC course on Computer Organization and Architecture. It discusses data transfer instructions, which move data without changing its contents. This includes load, store, move, input, output, push and pop instructions. It also examines addressing modes like immediate, register, indexed, and indirect addressing. The document then reviews data manipulation instructions, including arithmetic, logical/bitwise, and shift operations. It concludes by previewing that the next session will cover program control instructions.