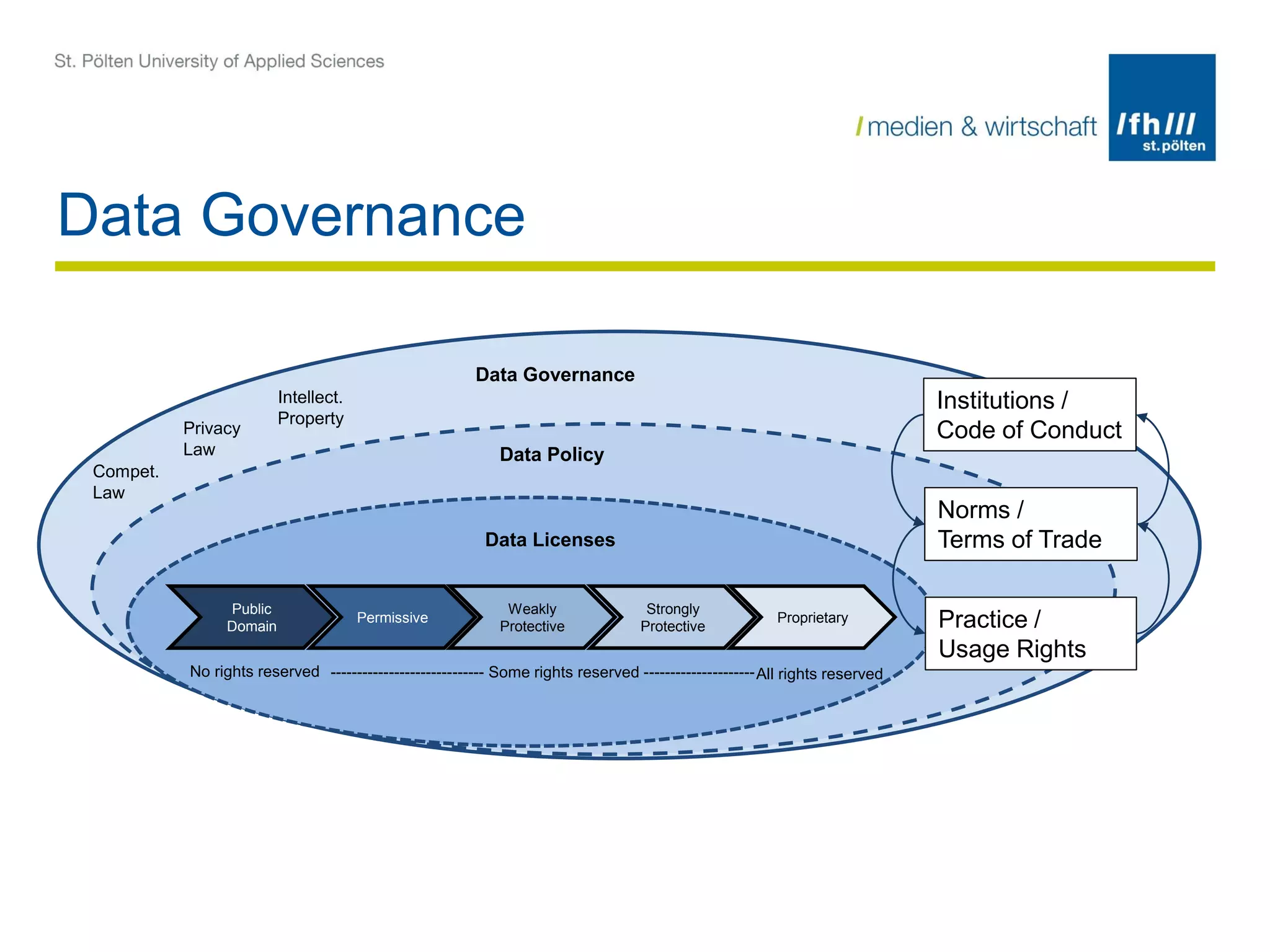
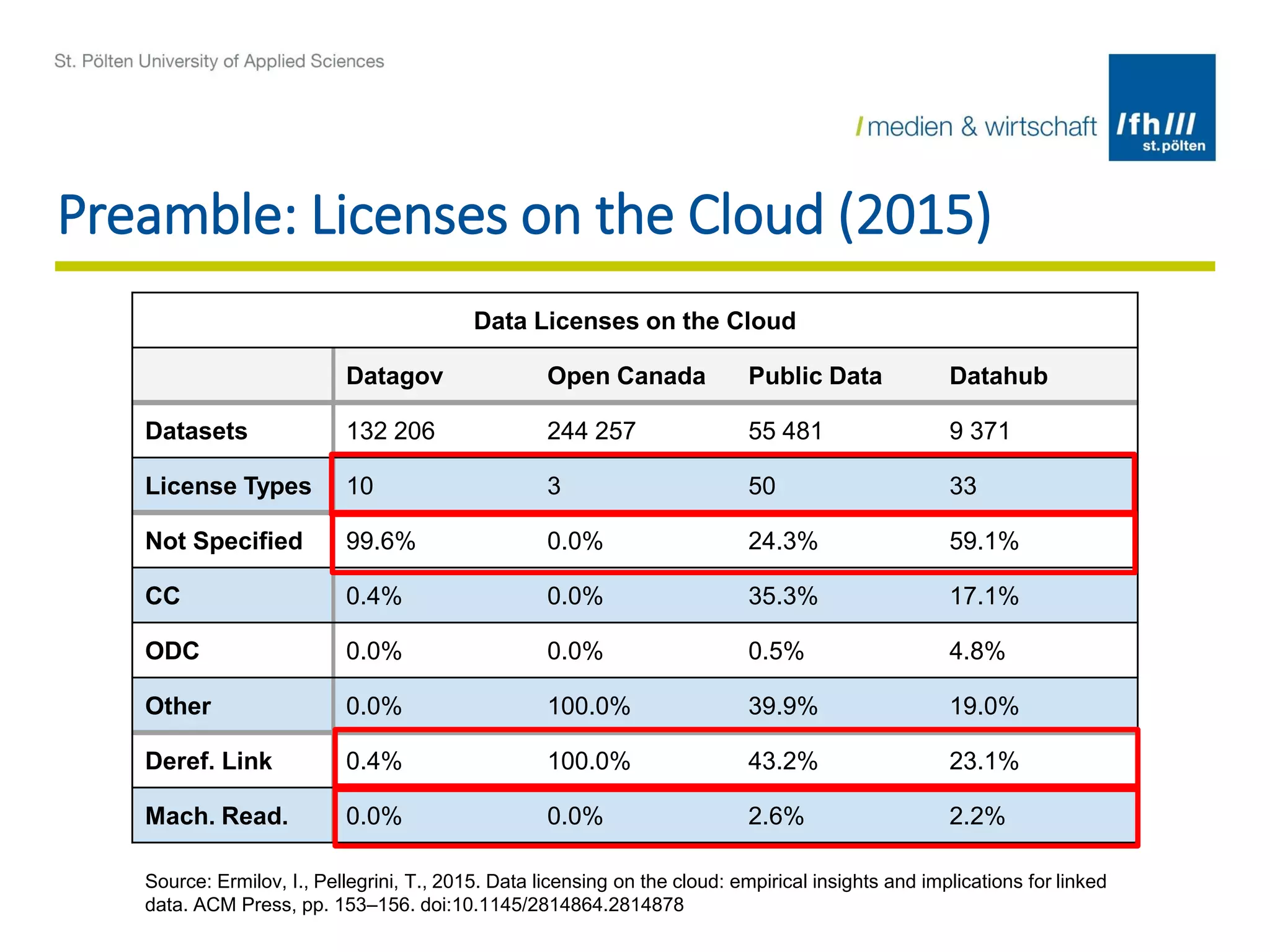
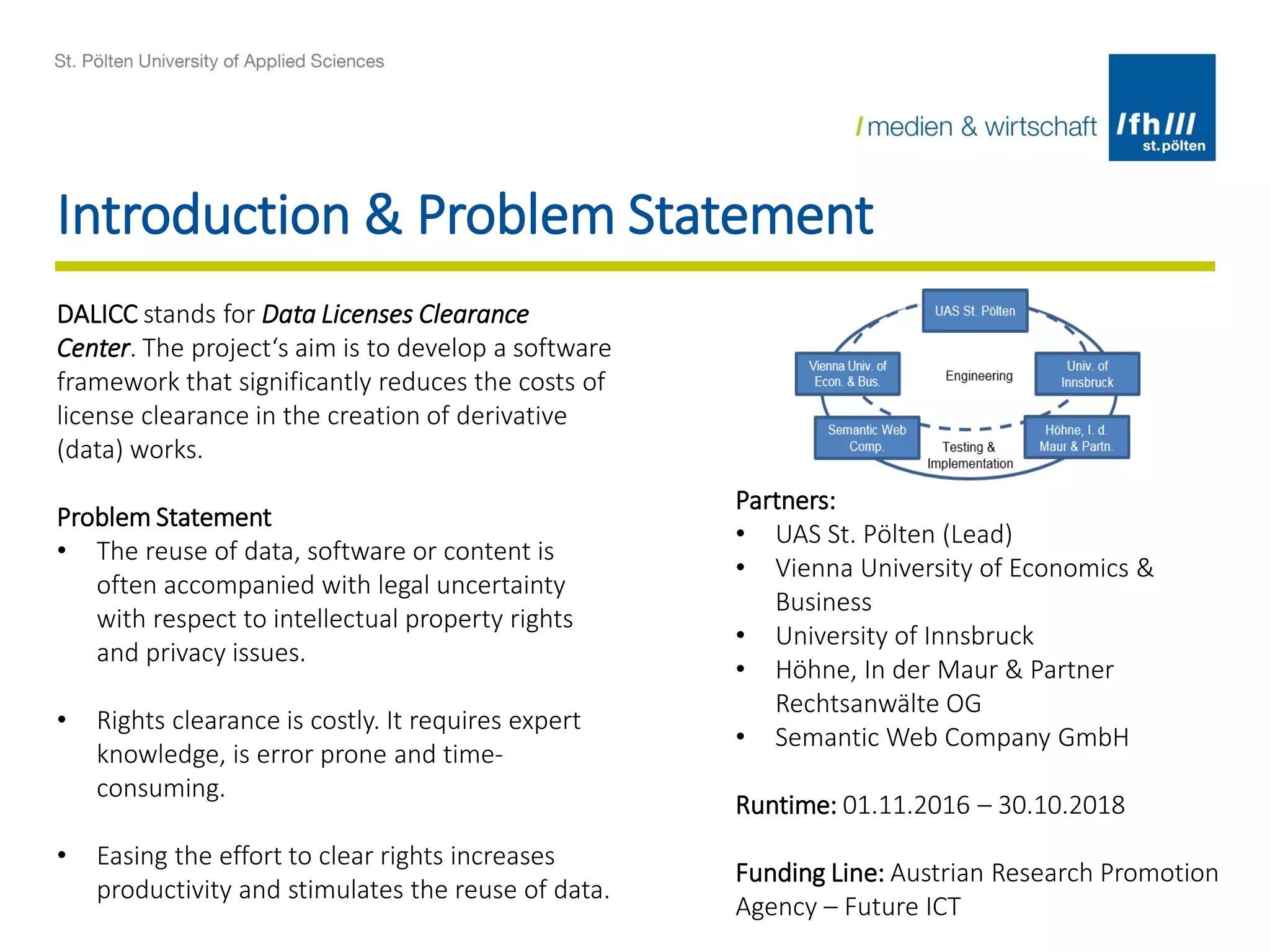
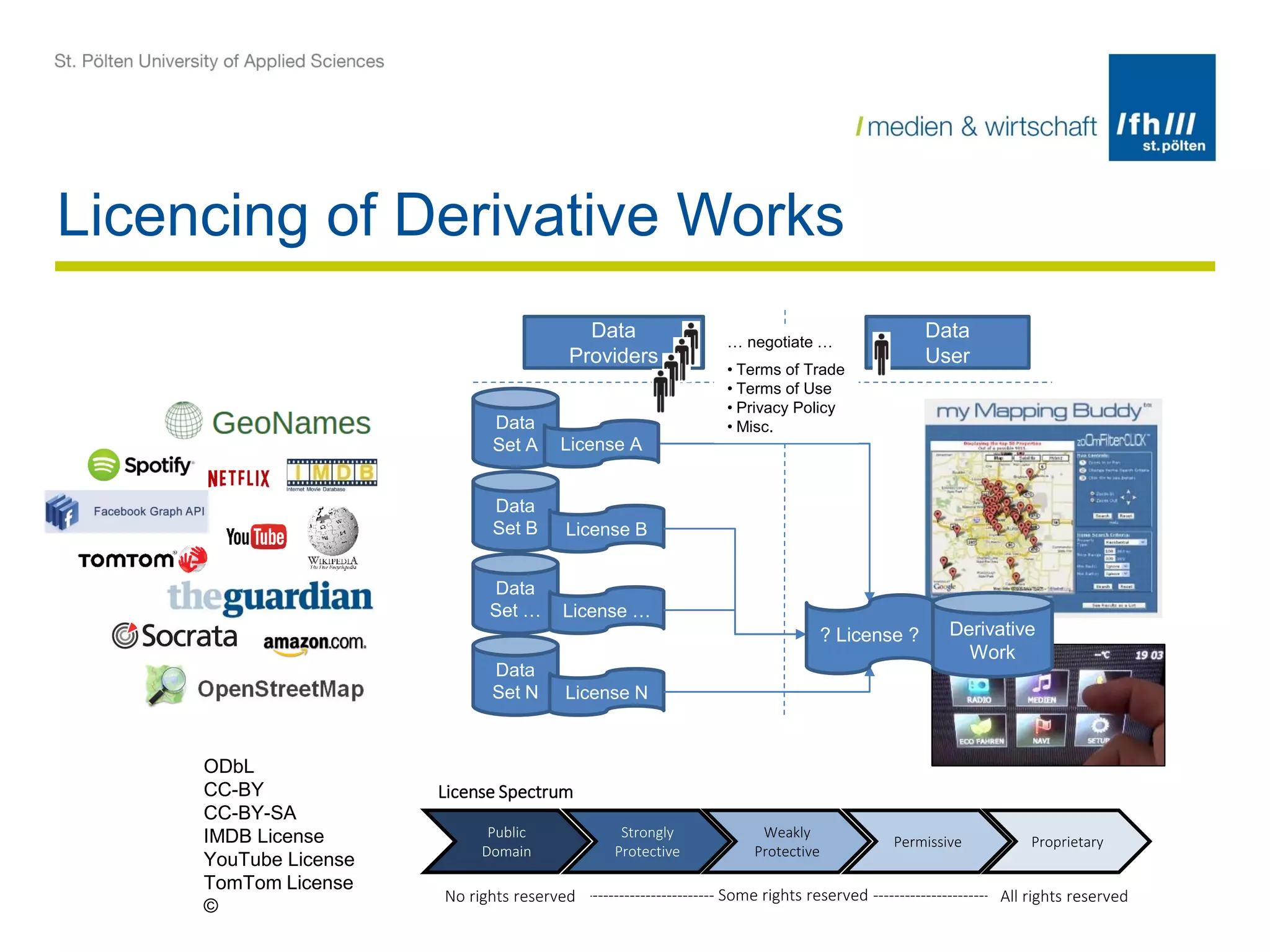
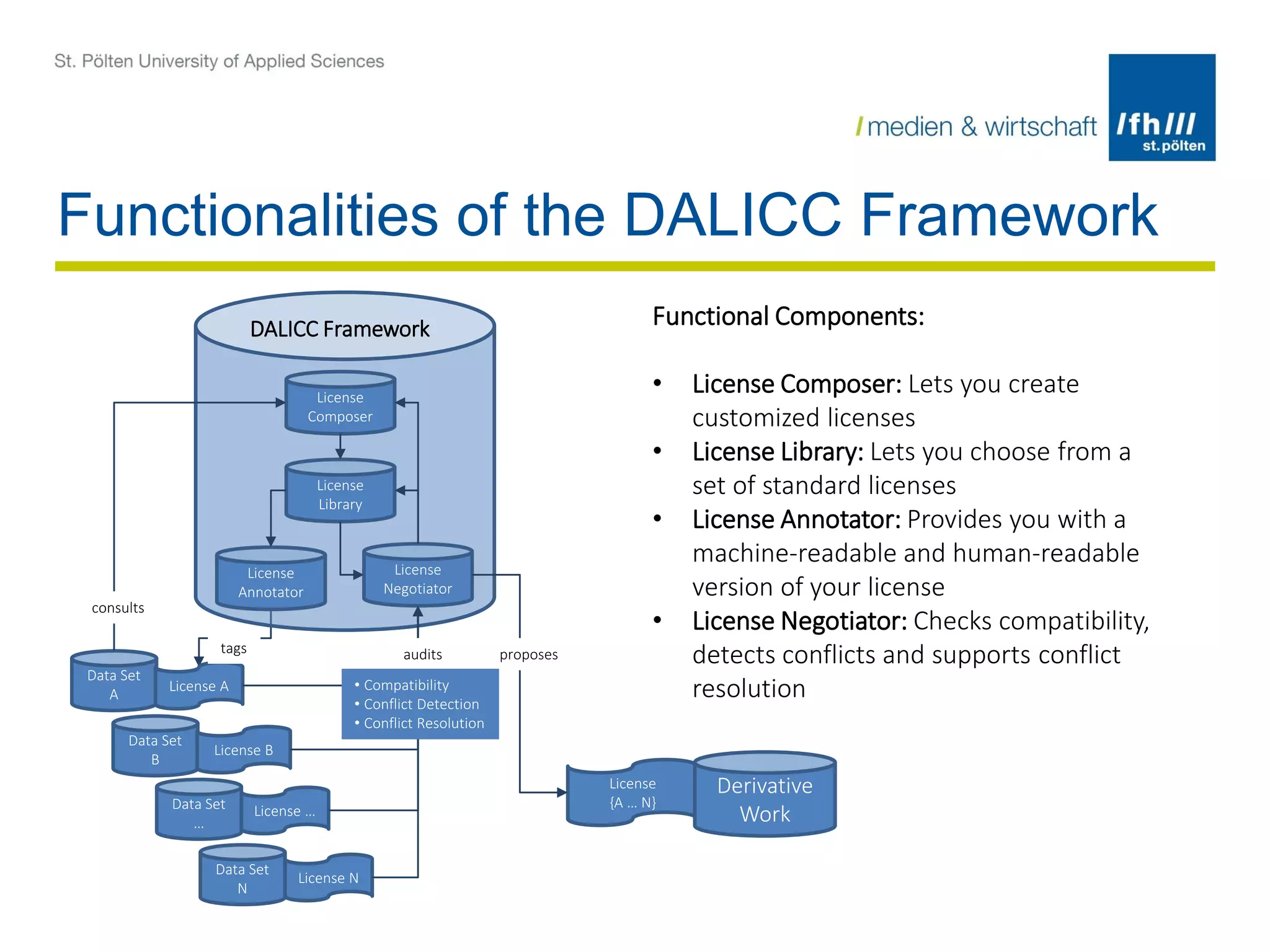
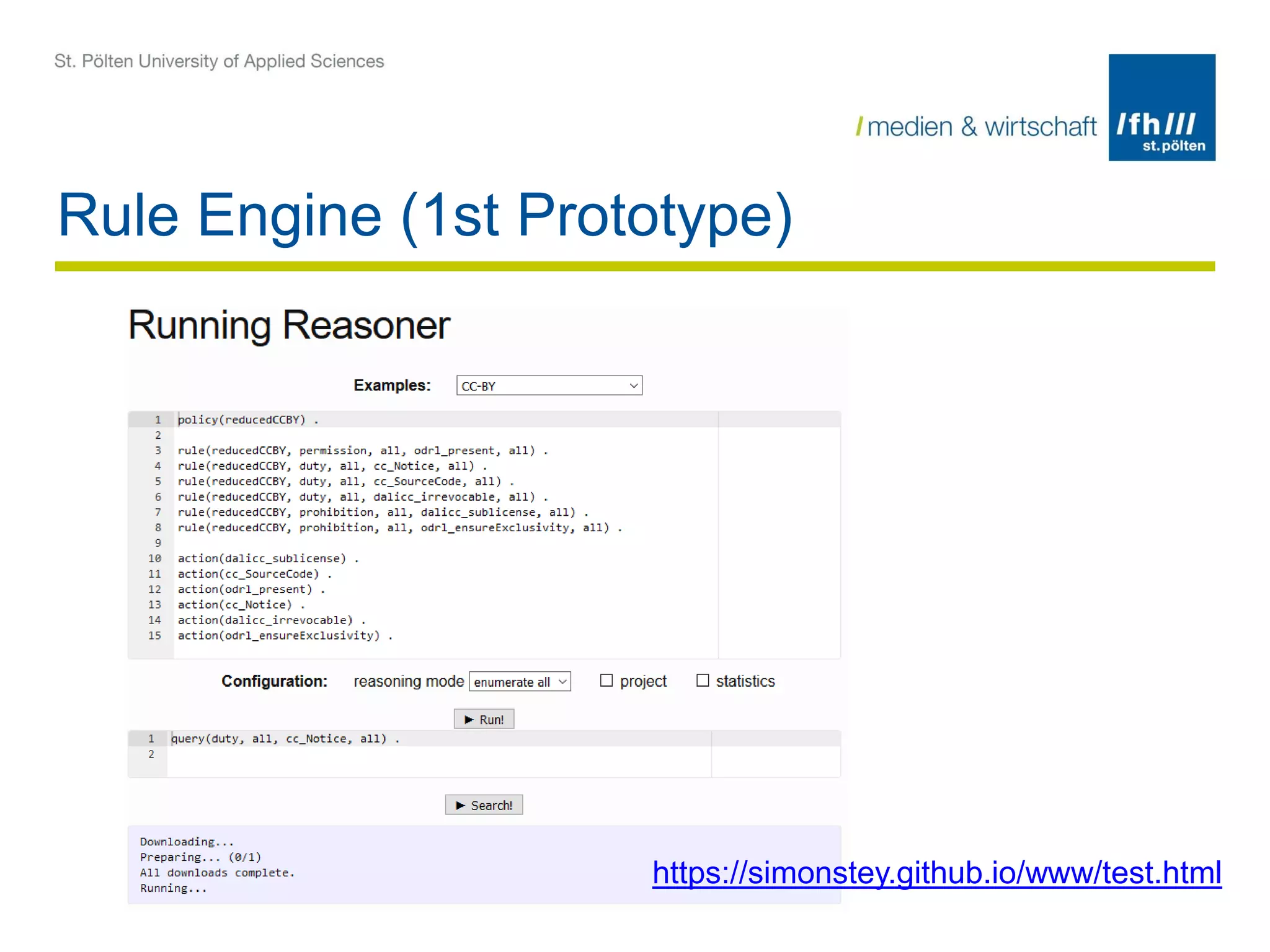
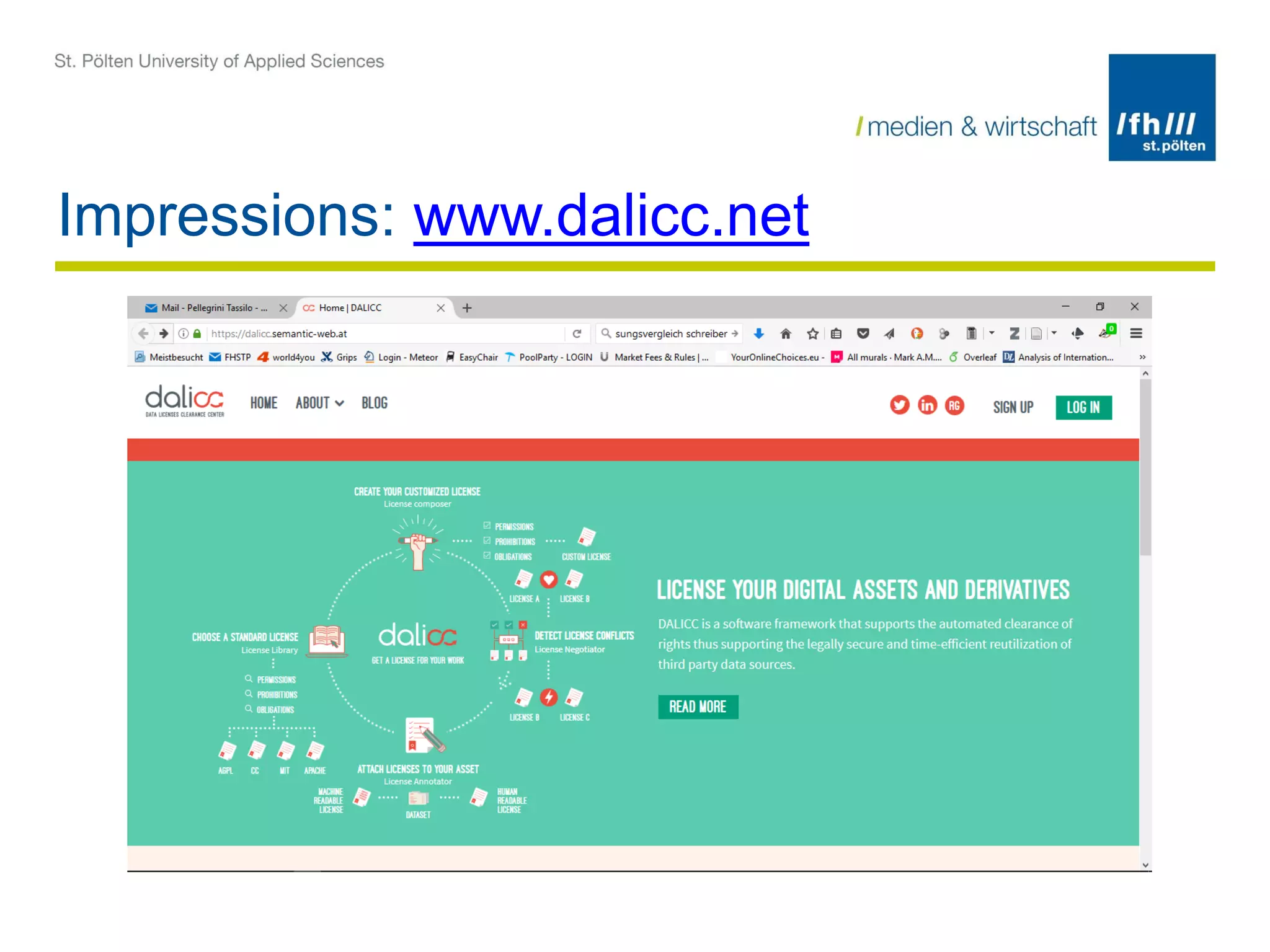
The document summarizes the DALICC (Data Licenses Clearance Center) project. The project aims to develop a software framework that reduces the costs of clearing licenses for derivative works by providing tools to choose licenses, check compatibility, and resolve conflicts. It will represent licenses in RDF and use rules and semantics to reason about licenses and detect inconsistencies. The framework will include components for composing, annotating, and negotiating licenses through a license library and API. The goal is to increase productivity and reuse of data by easing license clearance.