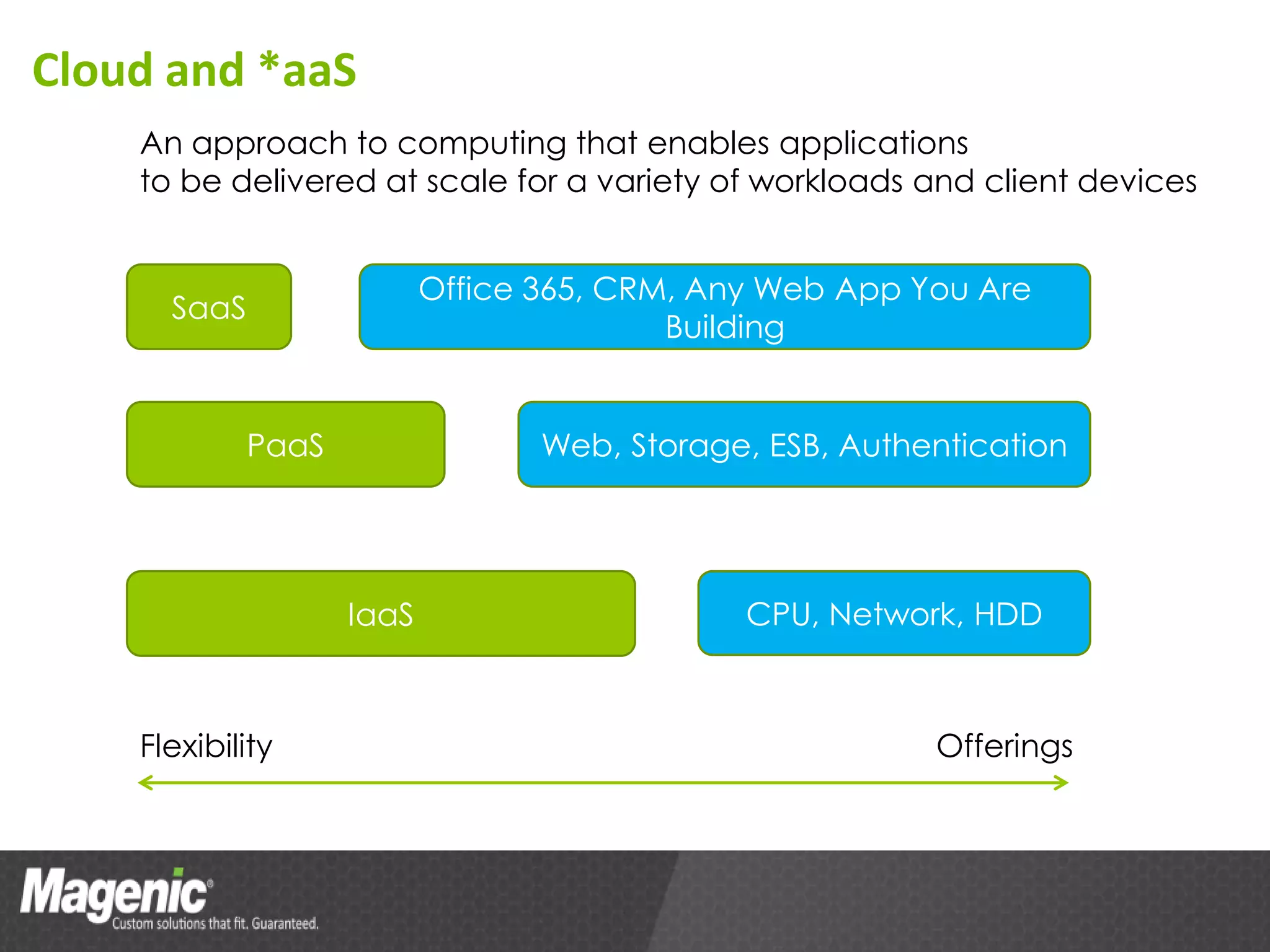
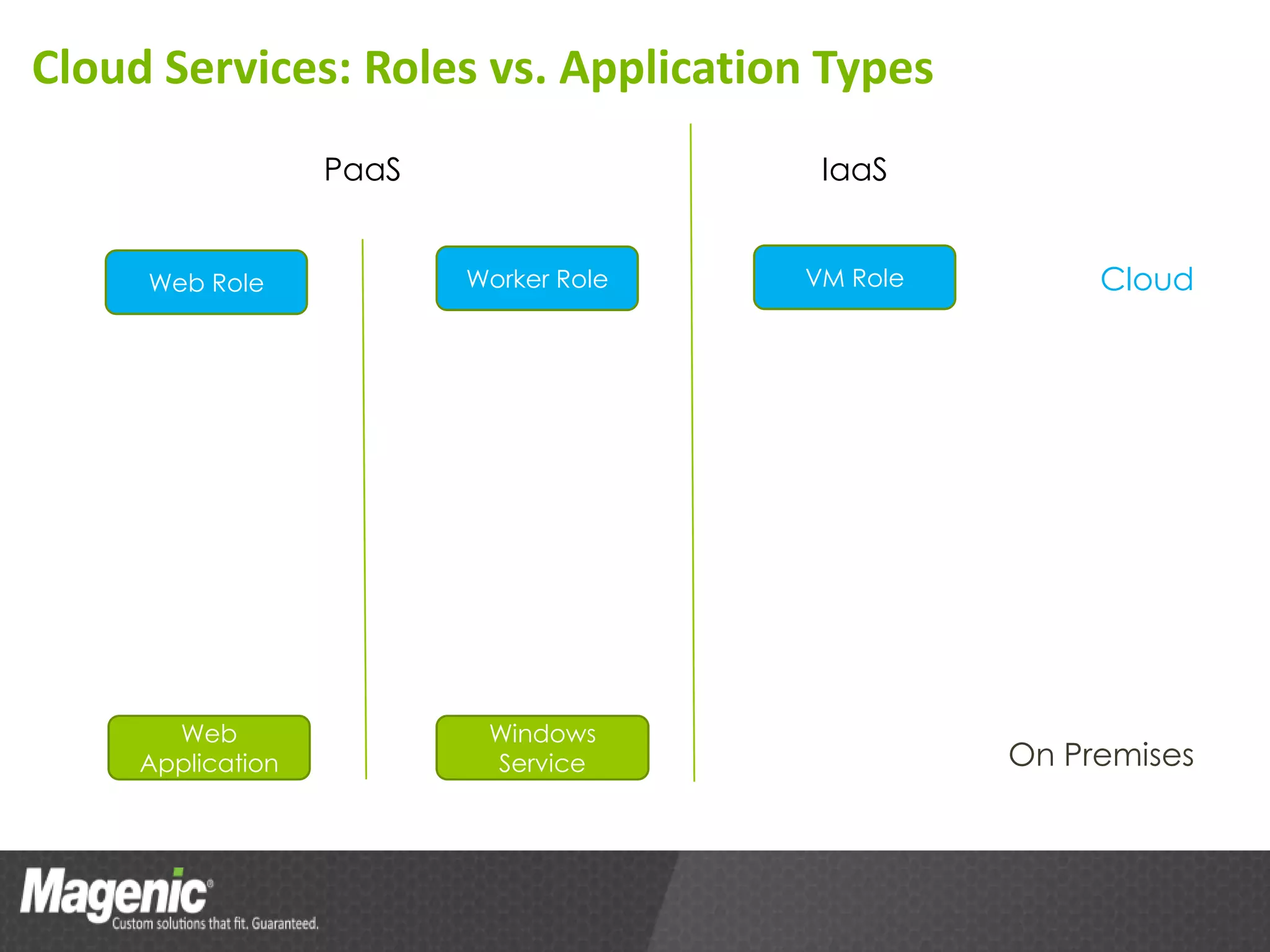
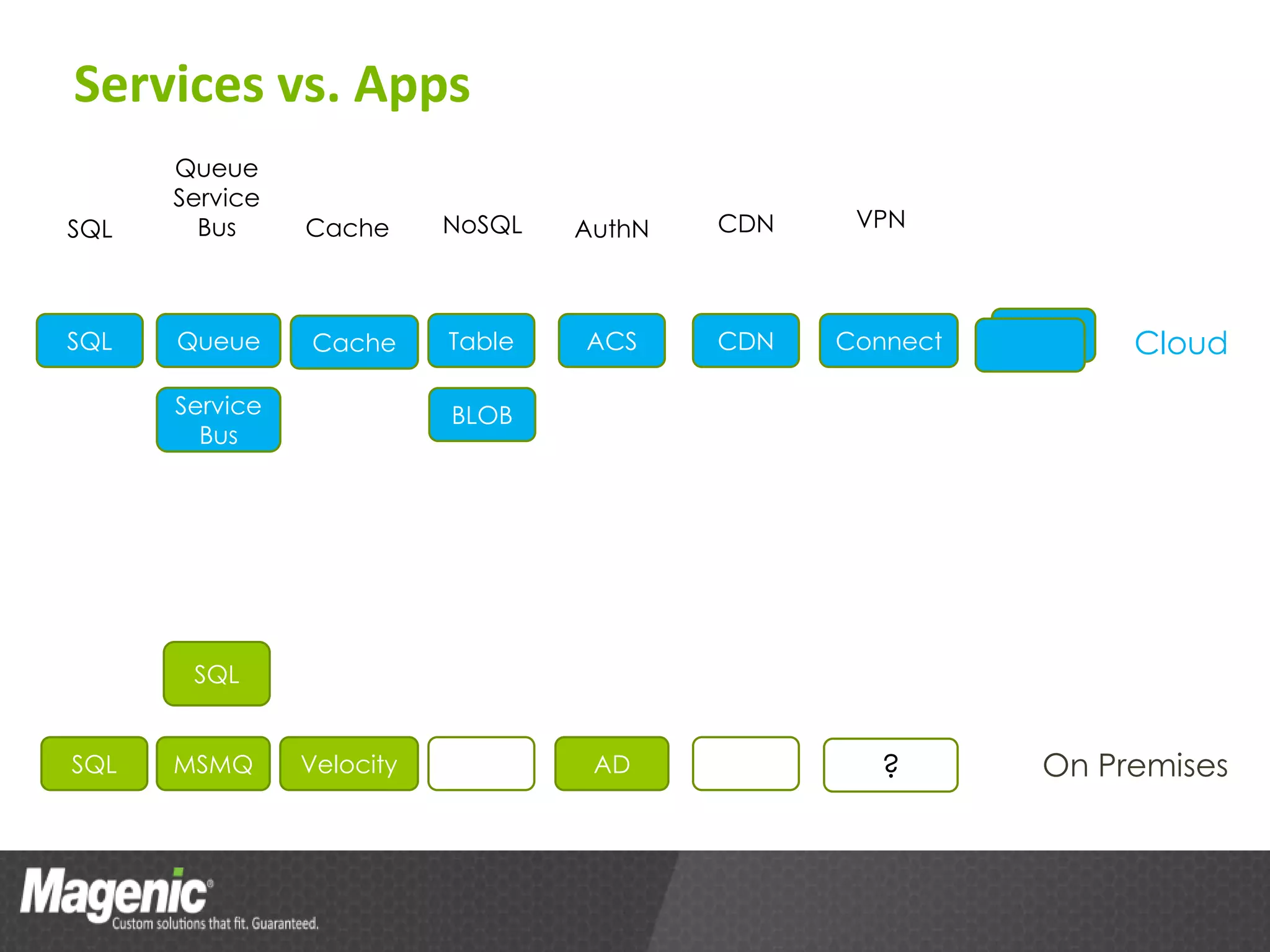
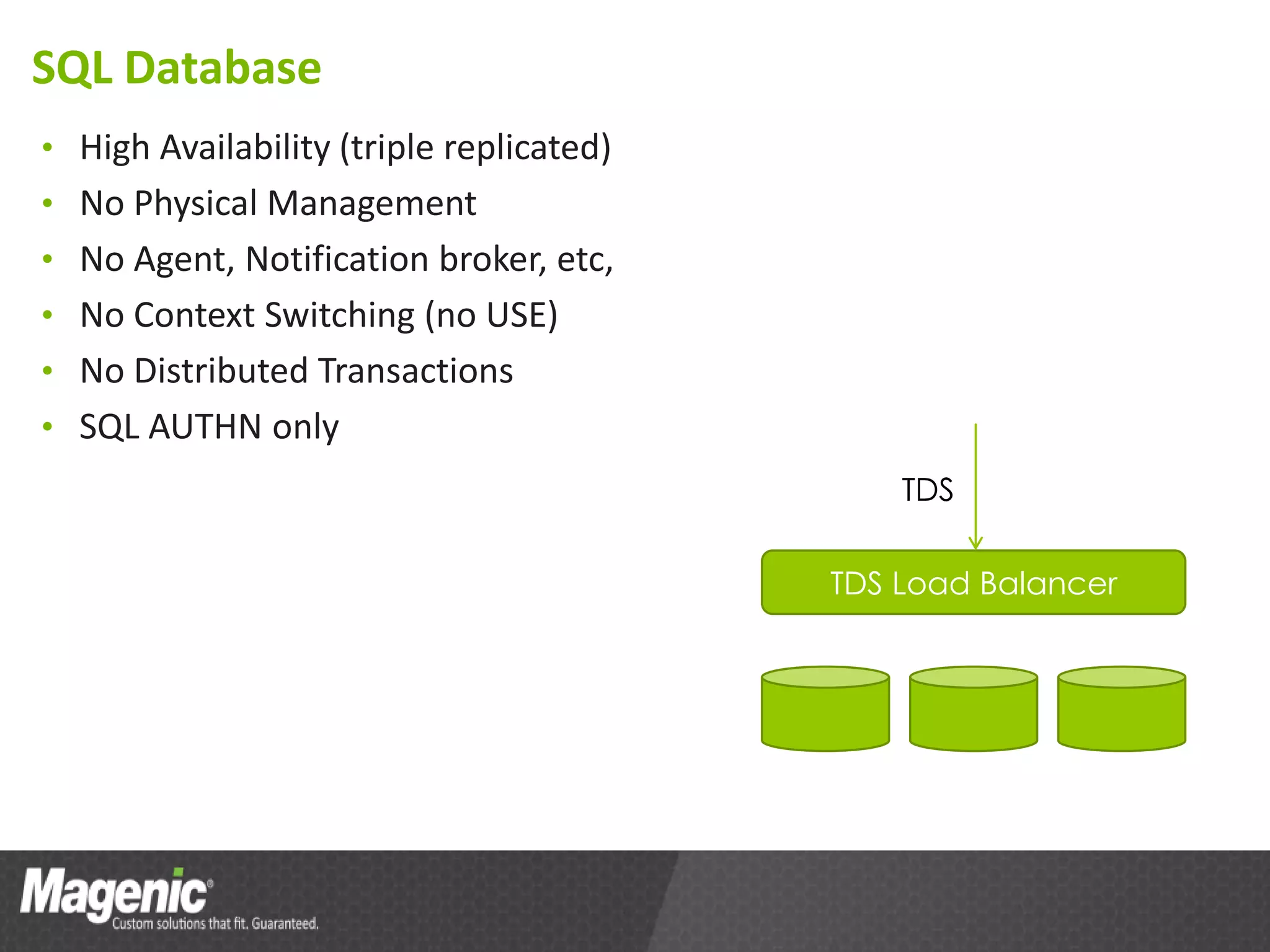
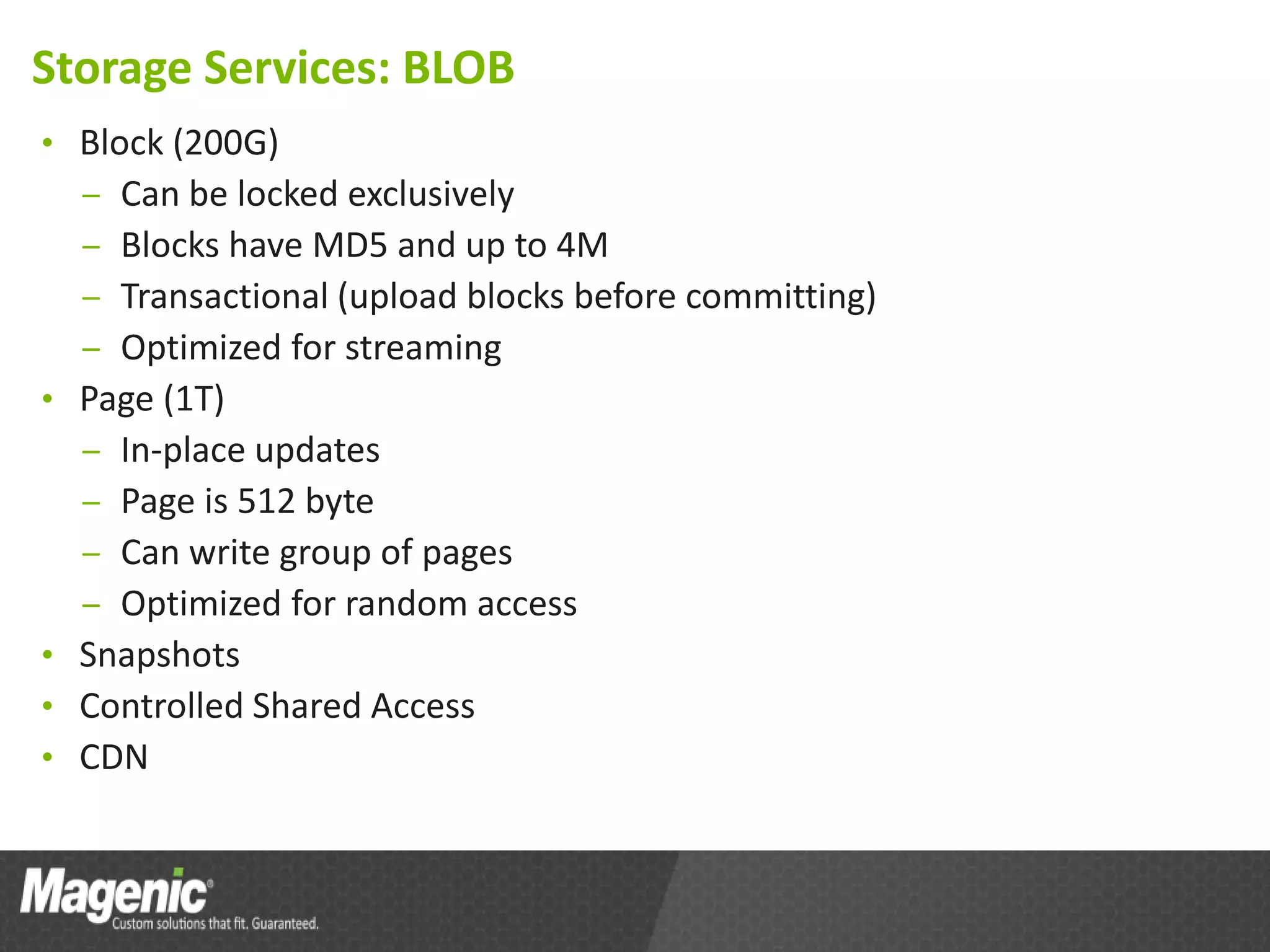
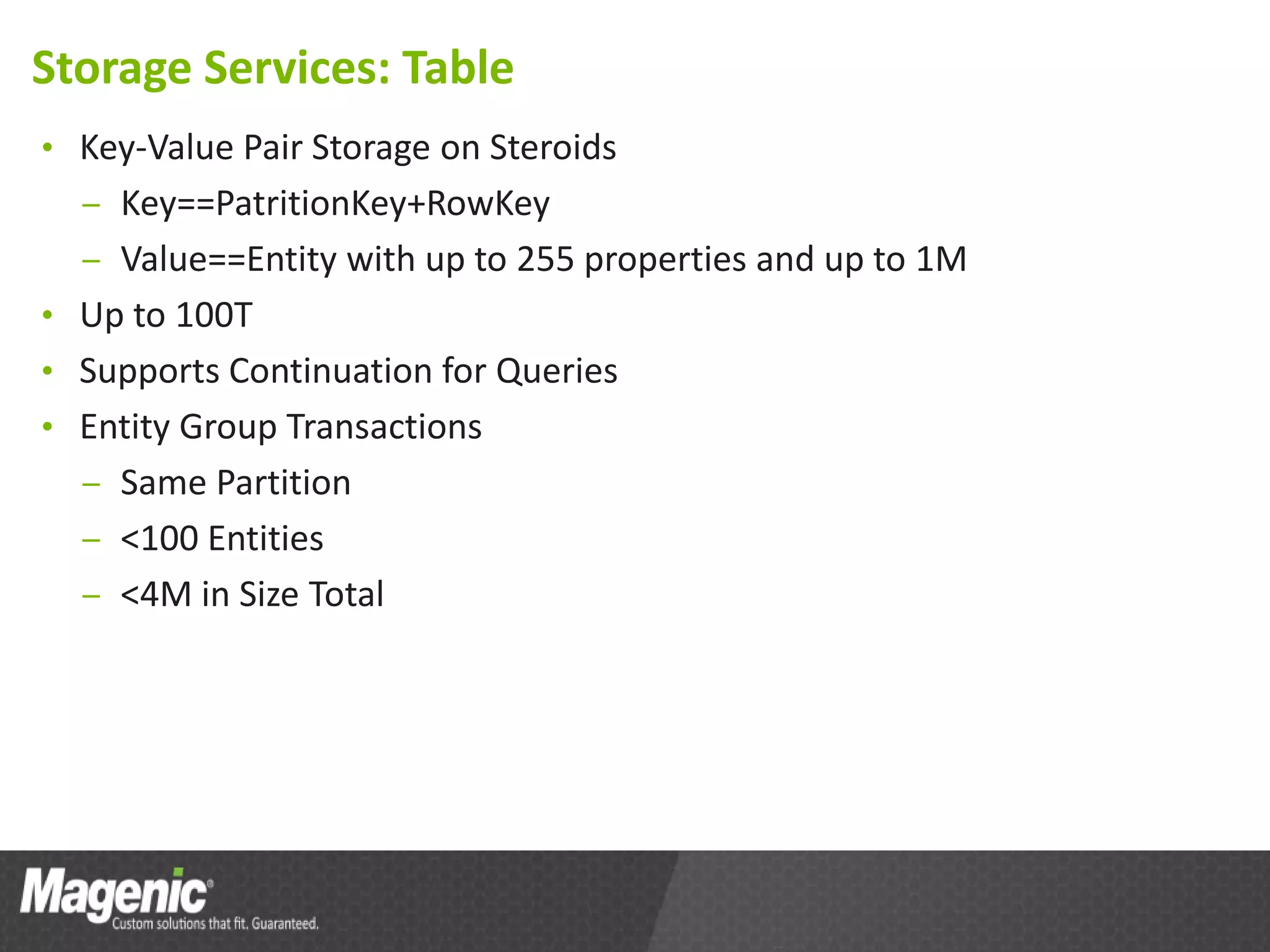
The document provides an overview of Azure cloud services, including definitions of cloud computing and different service models such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. It discusses various storage services, application design from a developer's perspective, and tools for development in Azure, emphasizing benefits like high availability and simplified development processes. An action plan for getting started with Azure is also outlined, encouraging readers to explore the platform and measure performance benefits.






![App Design Guidelines
• Proof of Concept + Measure [performance]
• Calculate Cost](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/session1-azureoverview-120705130216-phpapp01/75/Session-1-IaaS-PaaS-SaaS-Overview-14-2048.jpg)