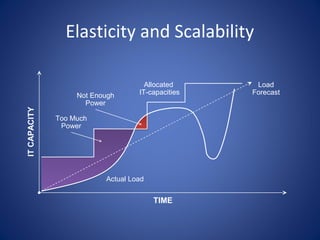
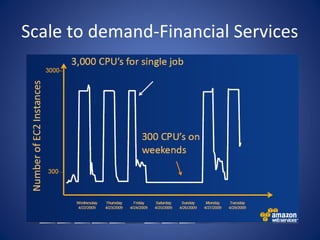
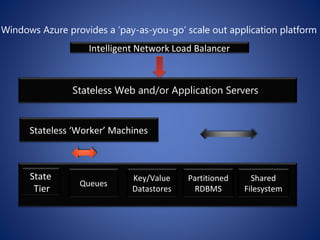
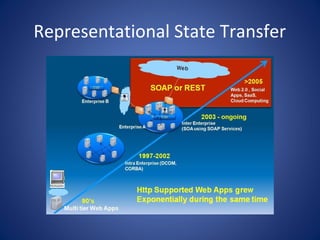
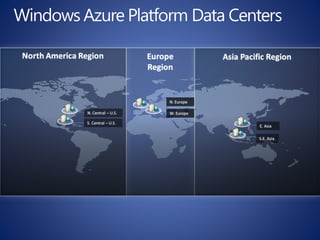
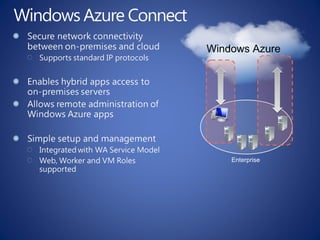
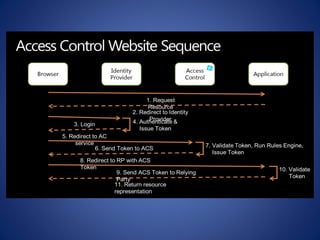
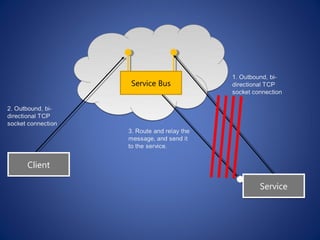
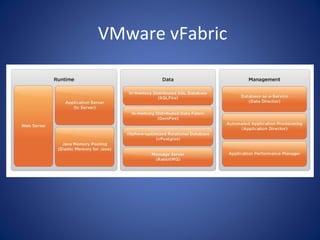
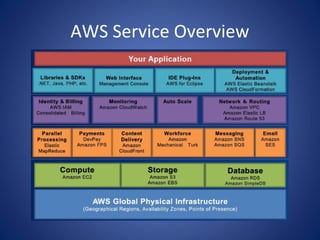
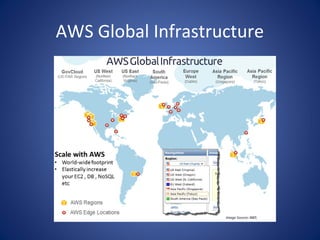
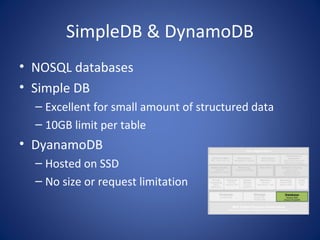
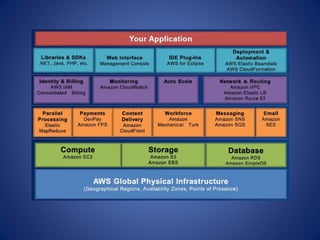
The document discusses cloud computing, defining it as a scalable model that offers various service models like IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, along with deployment options such as private, community, public, and hybrid clouds. It highlights benefits like cost reduction, scalability, and efficiency in scenarios such as mobile backends and financial services, while detailing Amazon Web Services' capabilities including Elastic Compute Cloud, relational databases, and auto-scaling features. The discussion also emphasizes the importance of stateless development and the continuous evolution of cloud platforms.