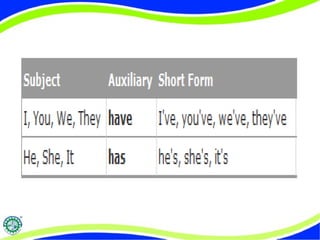
The document compares and contrasts the simple past and present perfect tenses in British English. It provides examples of how the present perfect is used to refer to past events that have relevance to the present, recent experiences, changes over time, successful situations, and situations that have not occurred yet. It also discusses the structure and use of the present perfect in questions and negatives.