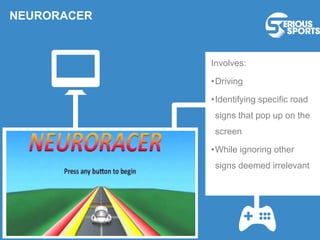
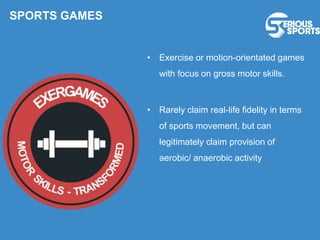
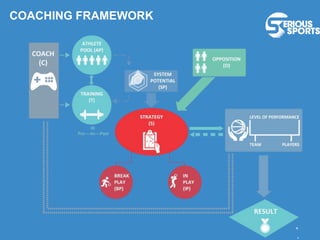
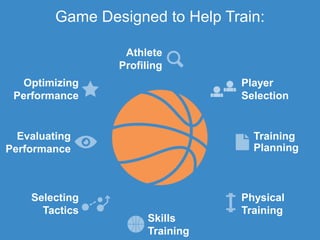
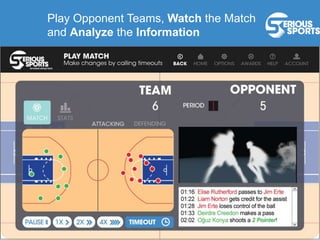
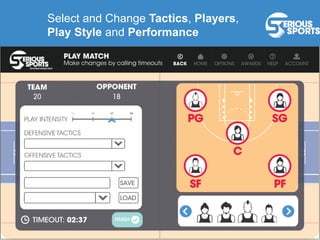
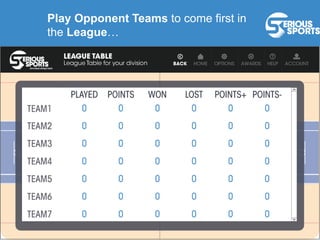
The document discusses the evolution of digital games, highlighting their use in therapy for mild to moderate depression through initiatives like Sparx, and in developing cognitive skills with games like Neuroracer. It further explores the impact of exergames on physical health and social skills, and emphasizes game-based learning principles that enhance educational outcomes. Lastly, it introduces a serious sports project framework for coaching that incorporates game-based training for athlete development, acknowledging the limitations of games compared to traditional training methods.