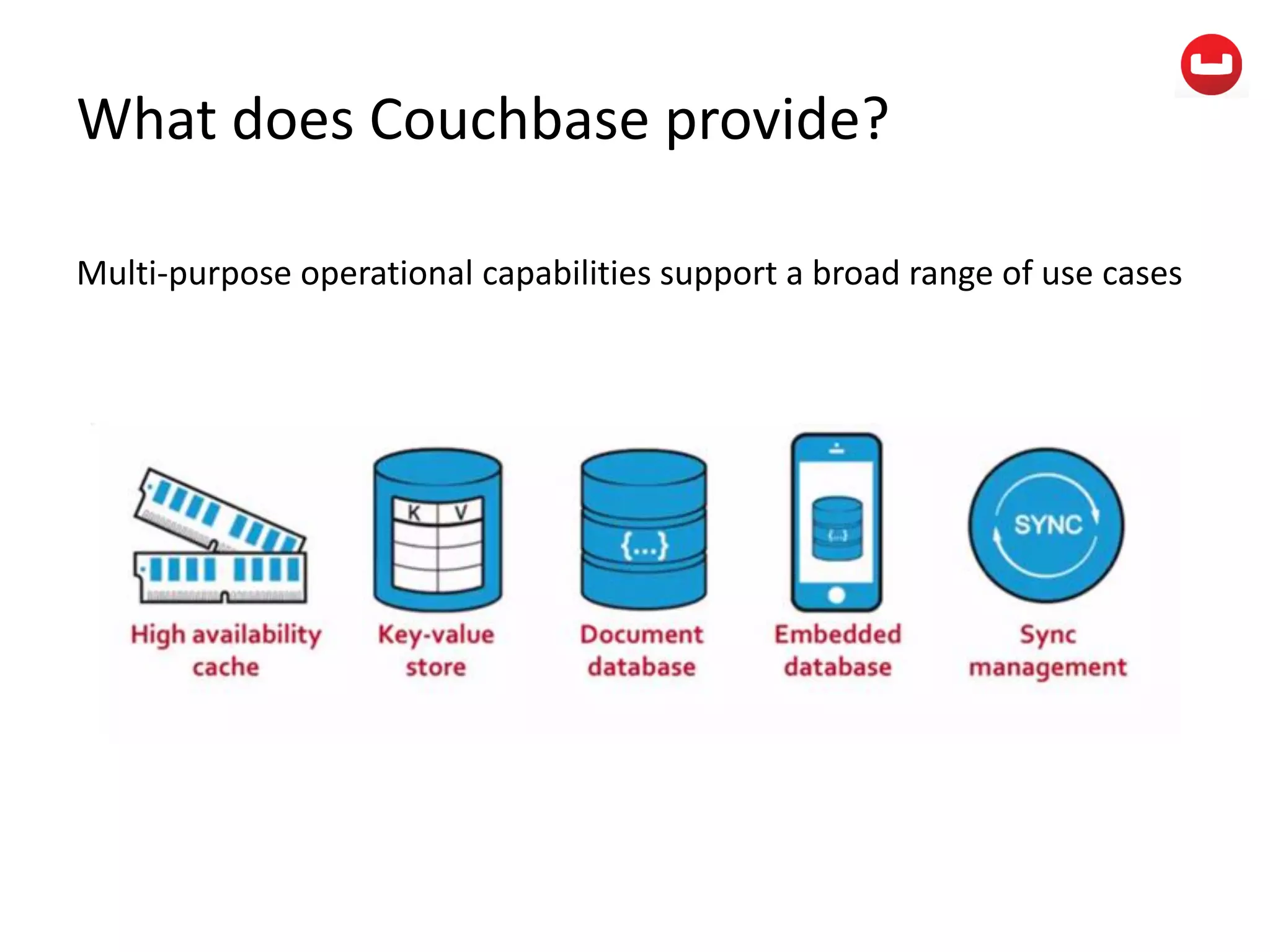
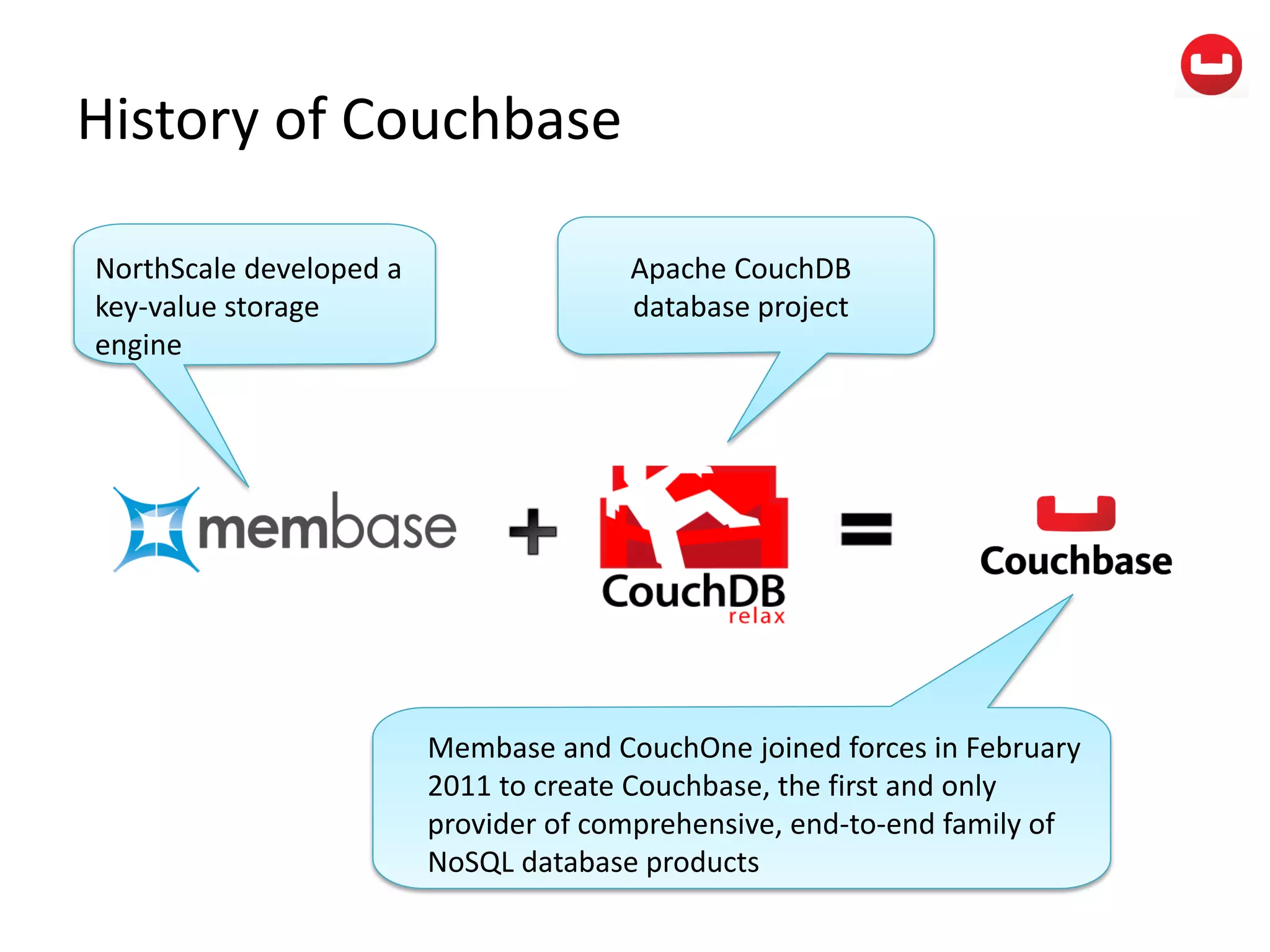
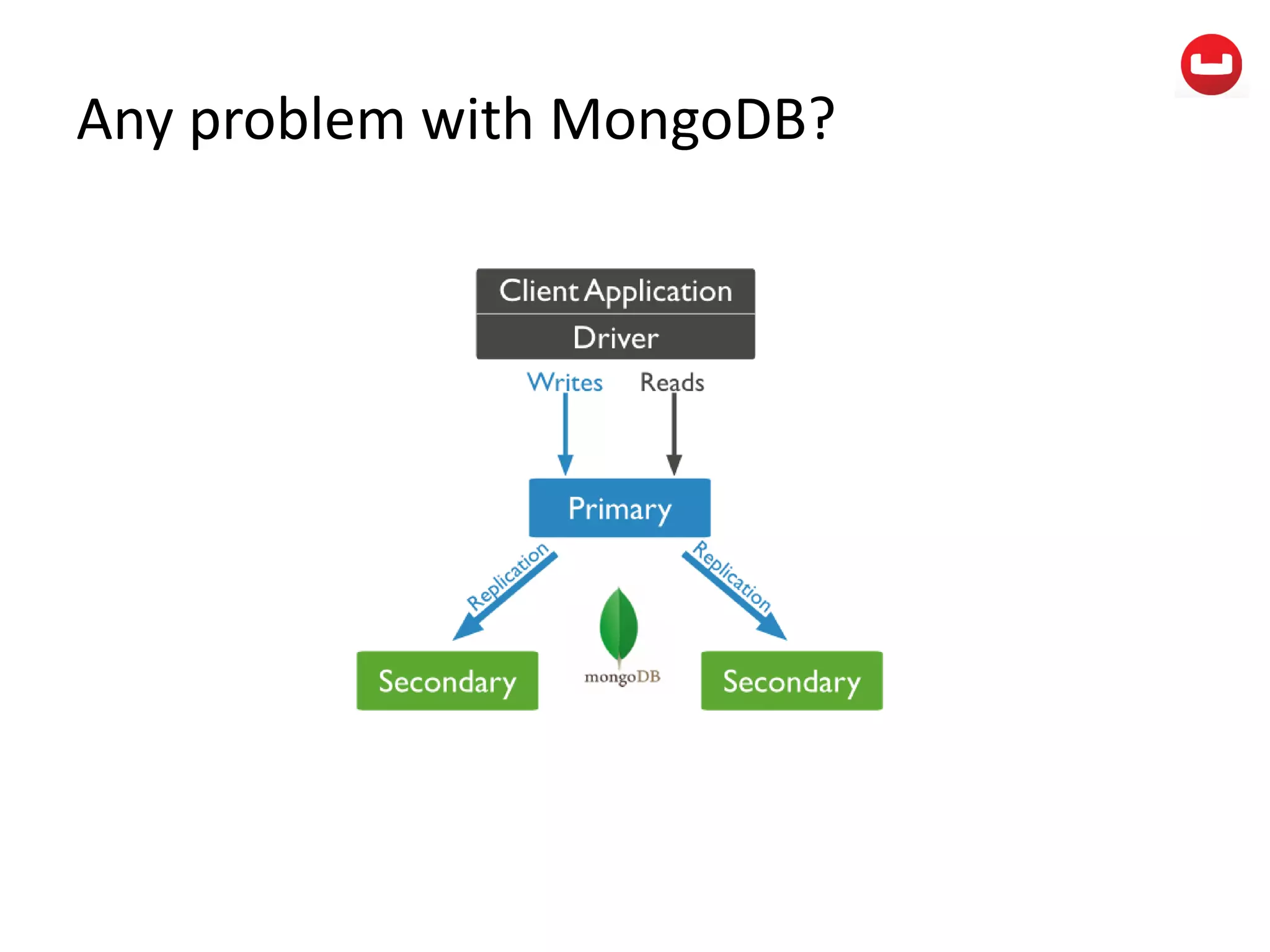
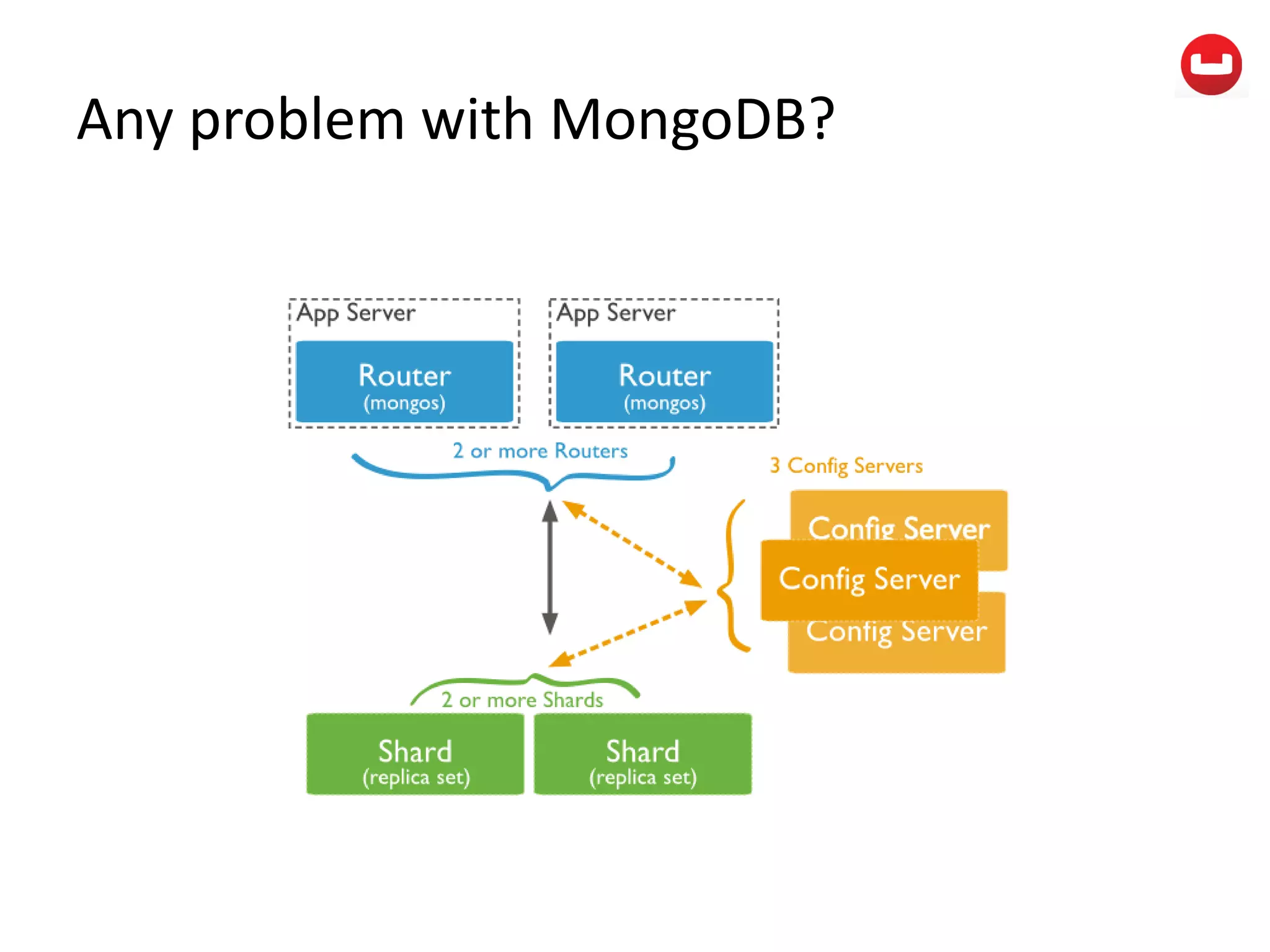
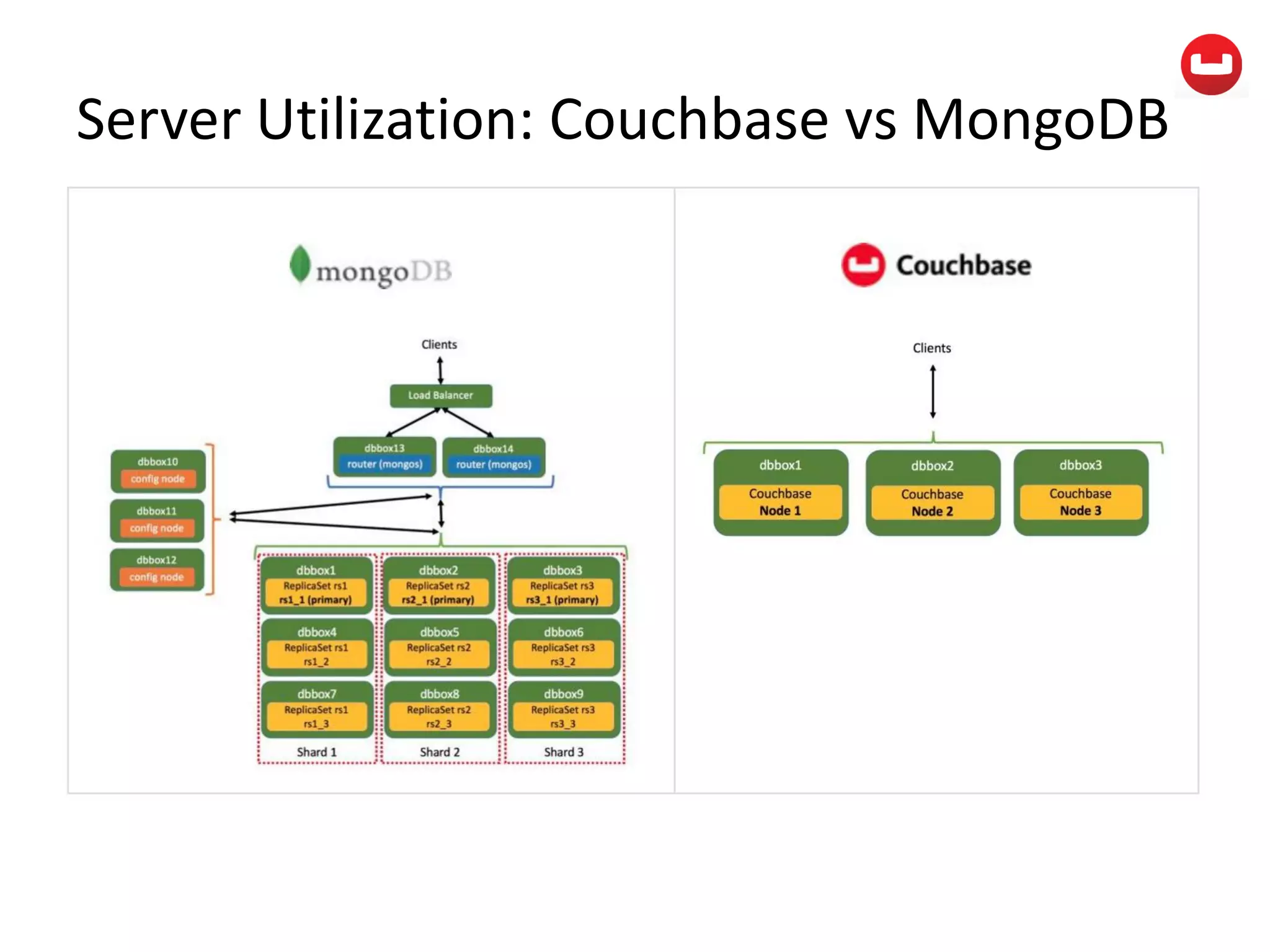
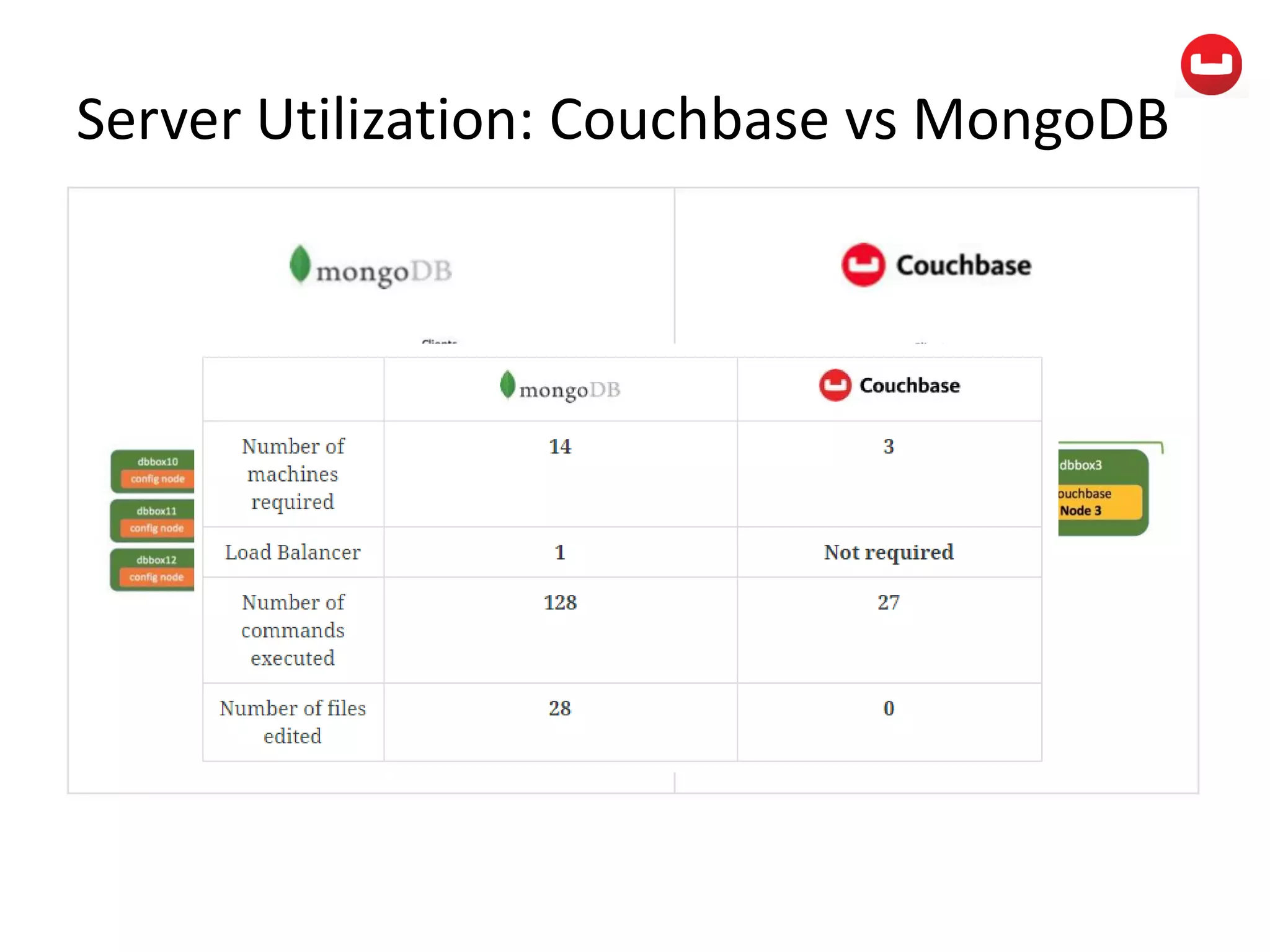
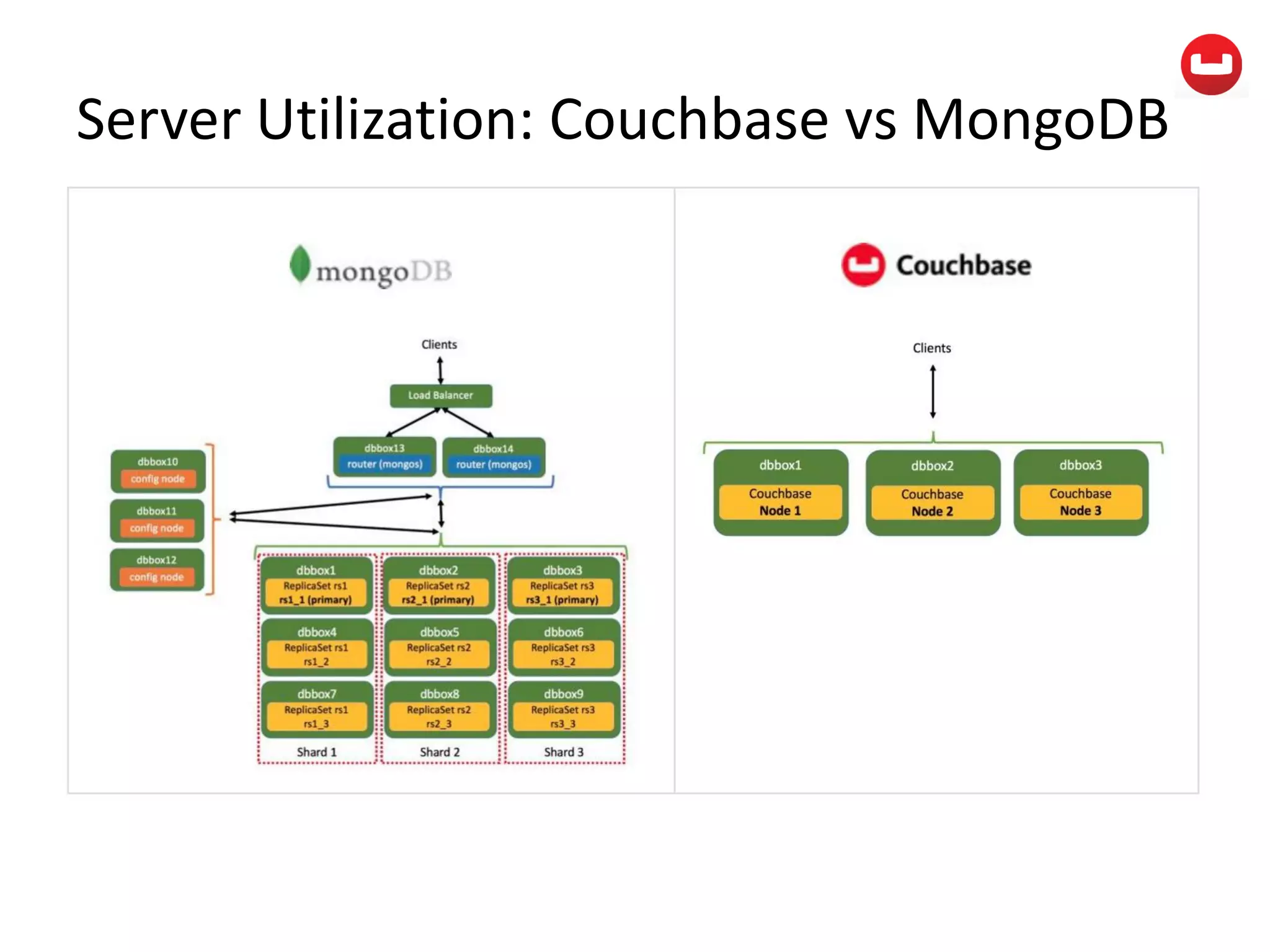
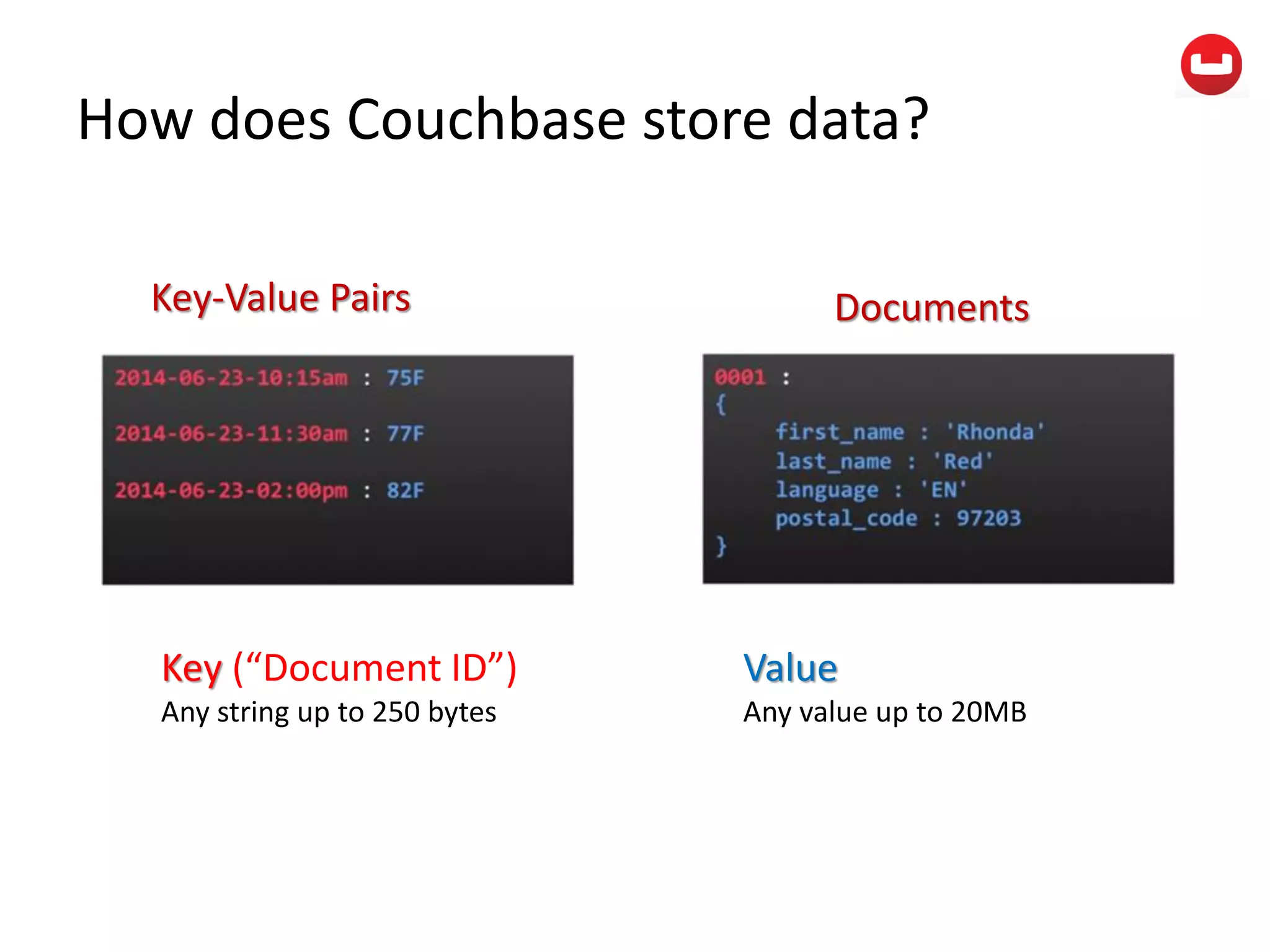
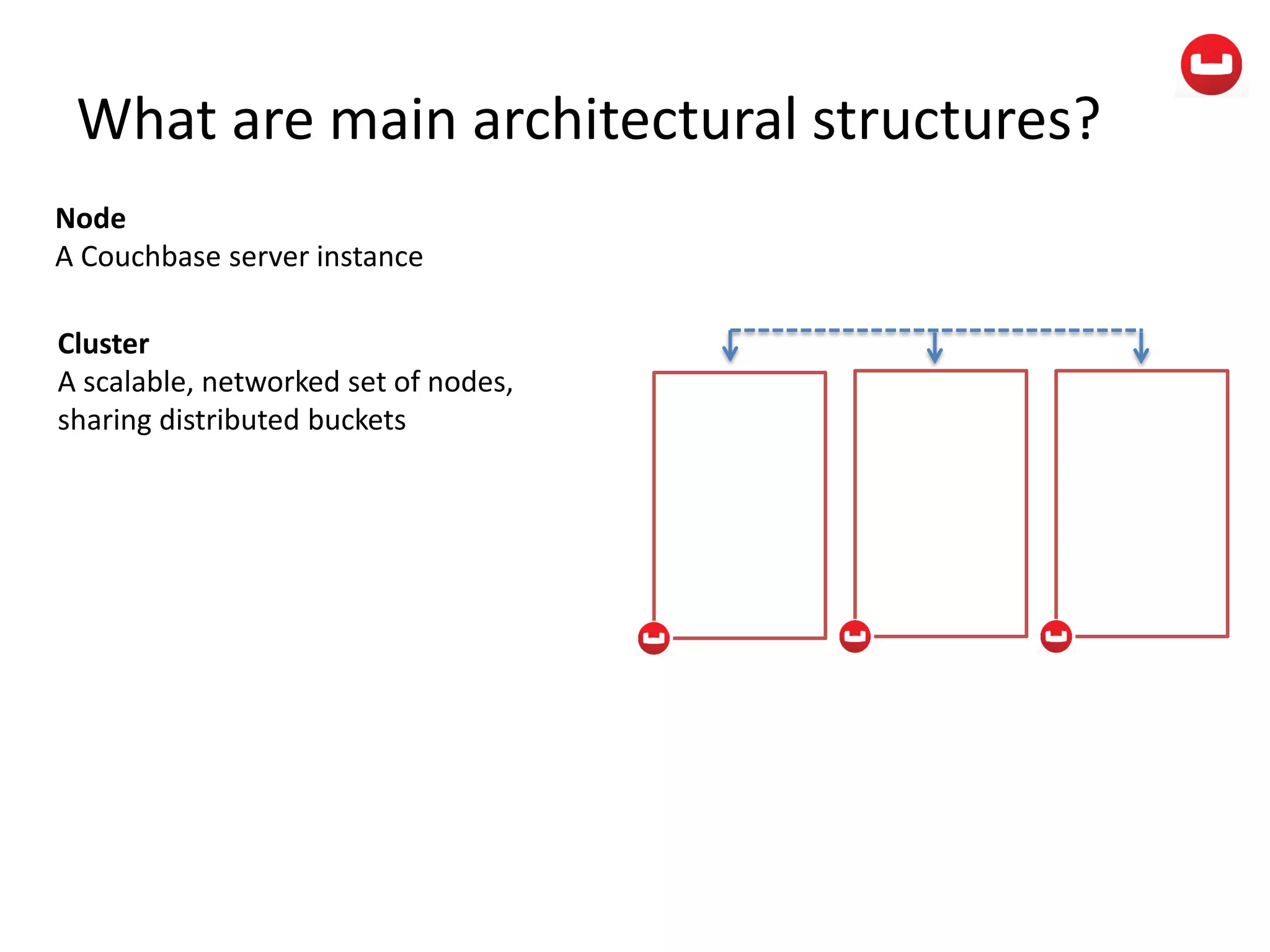
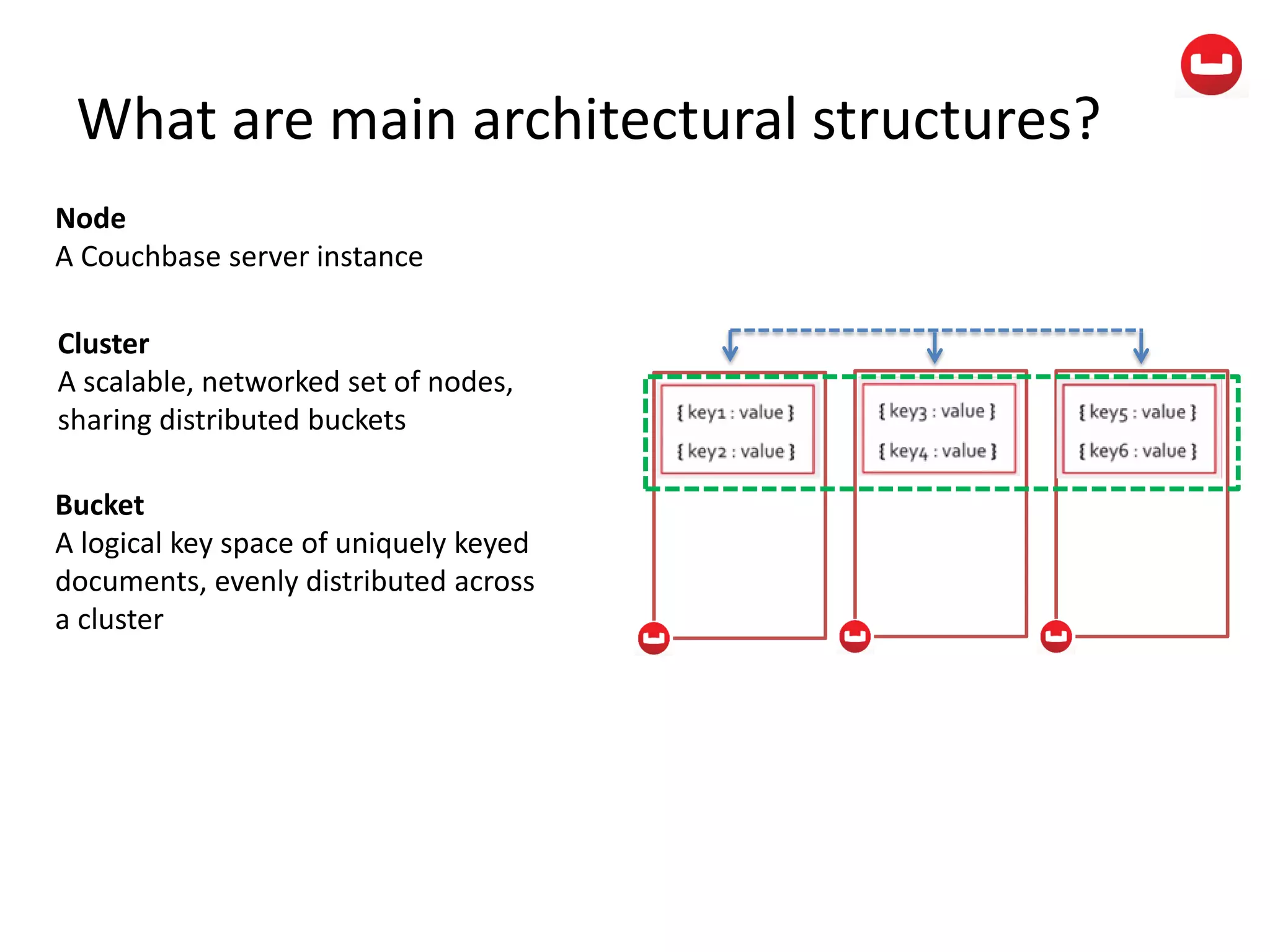
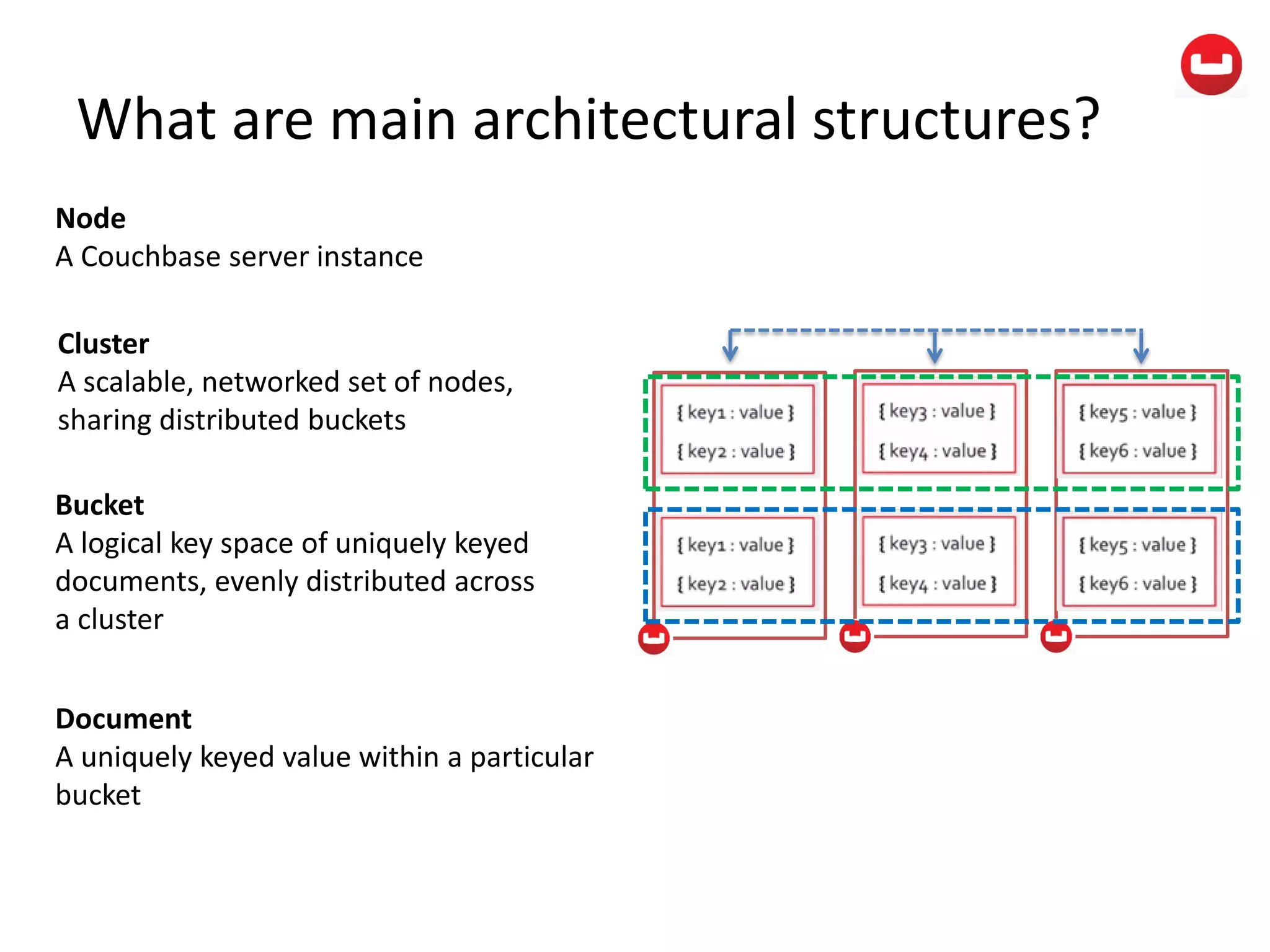
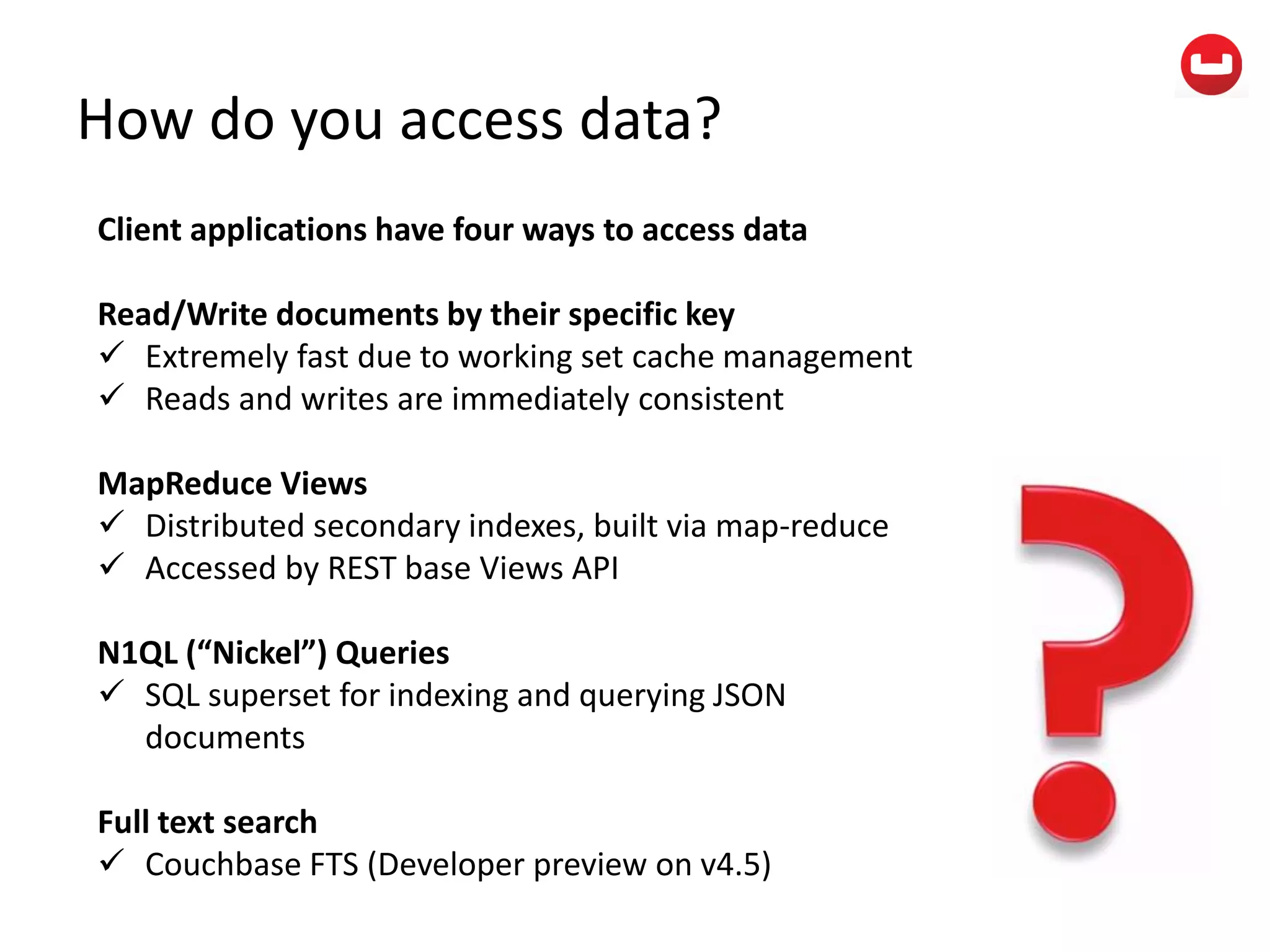
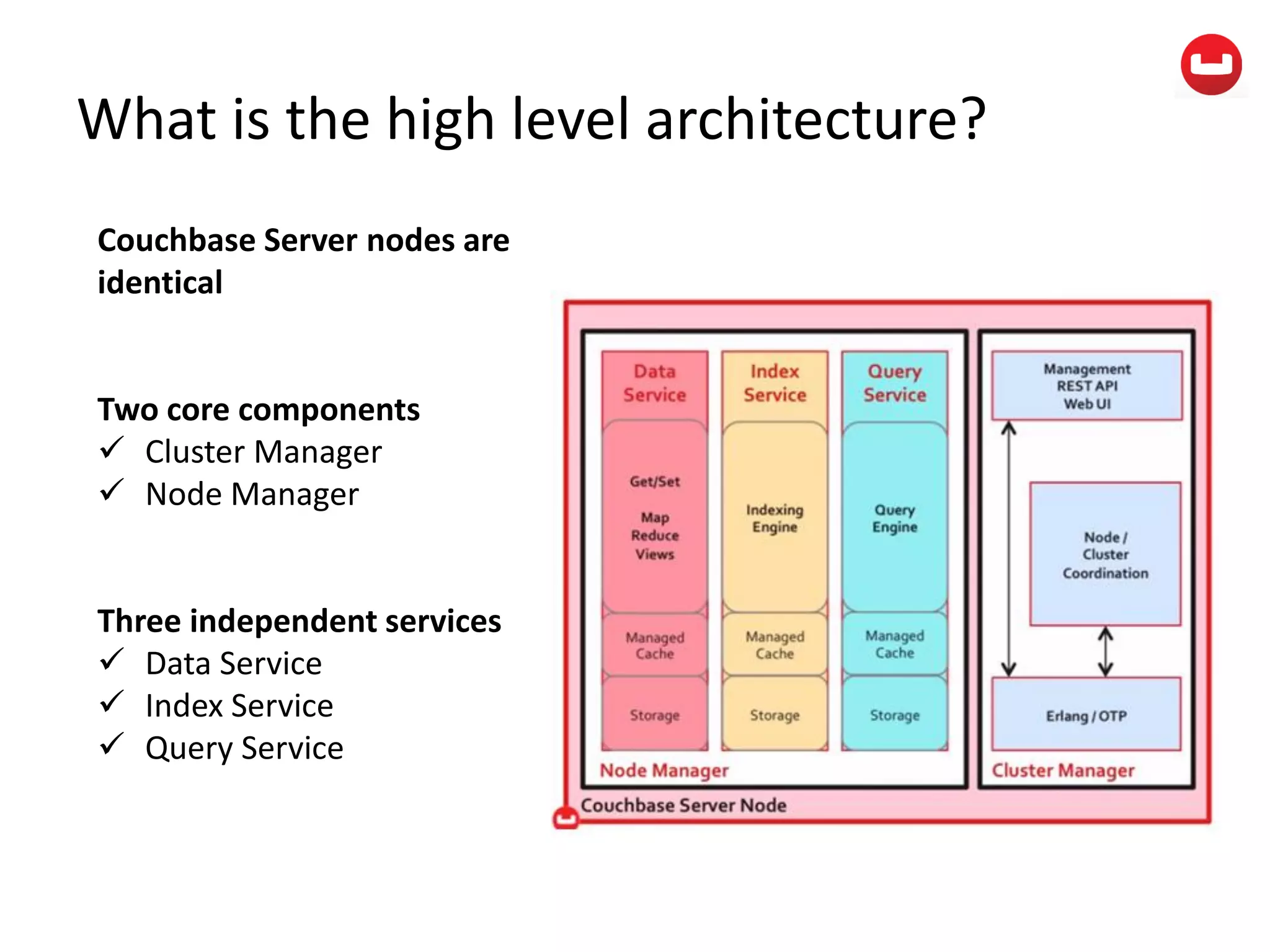
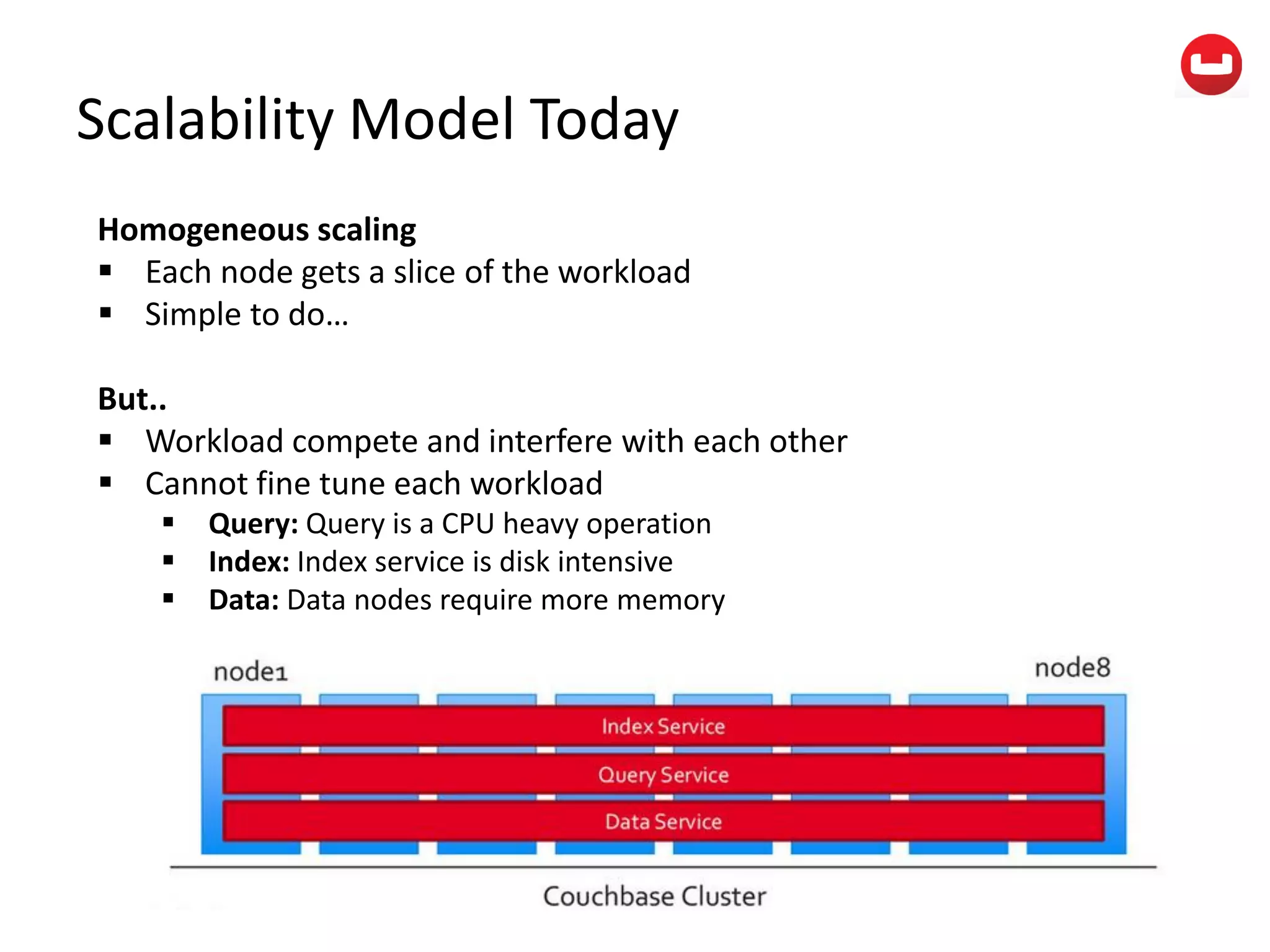
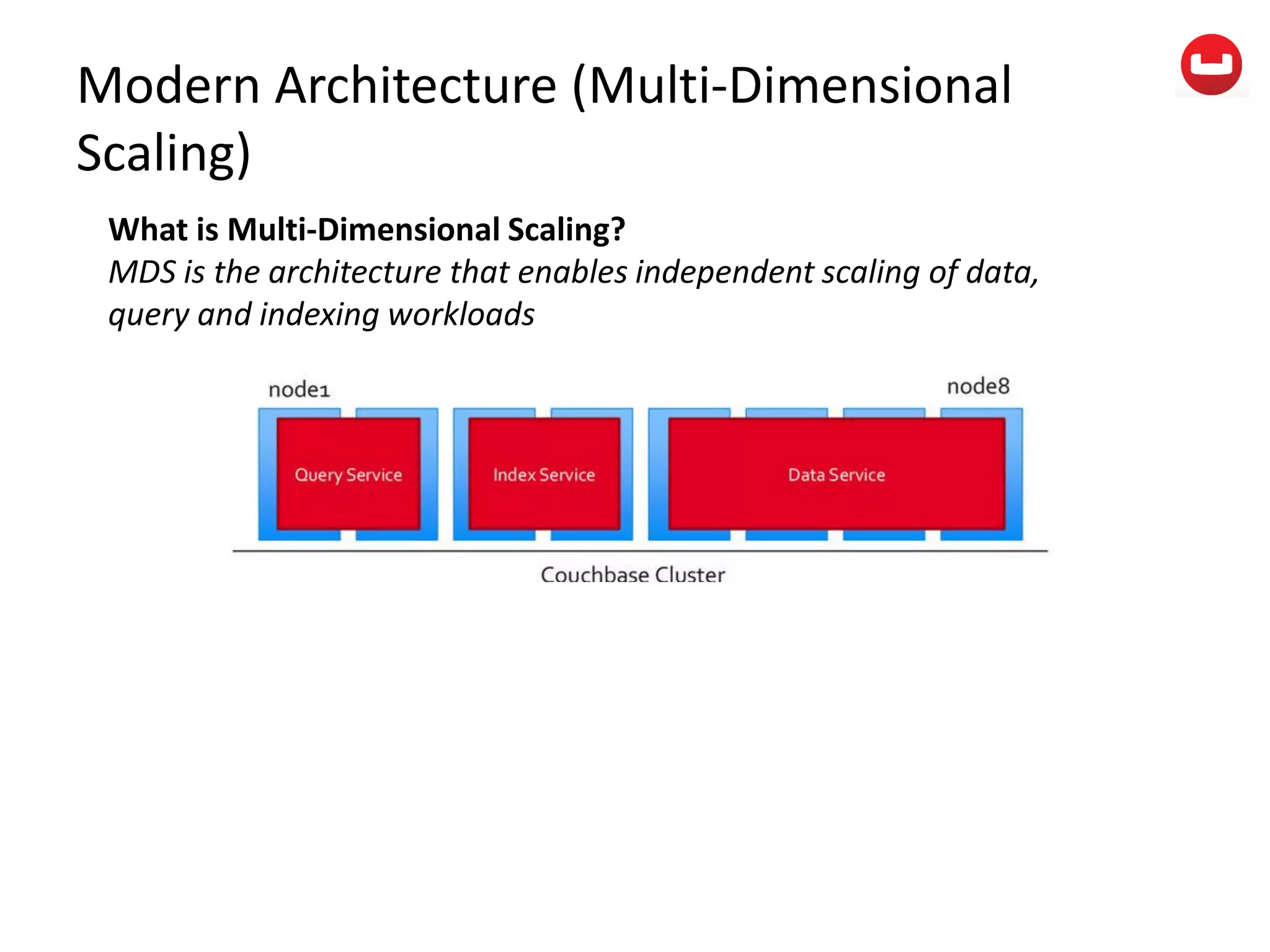
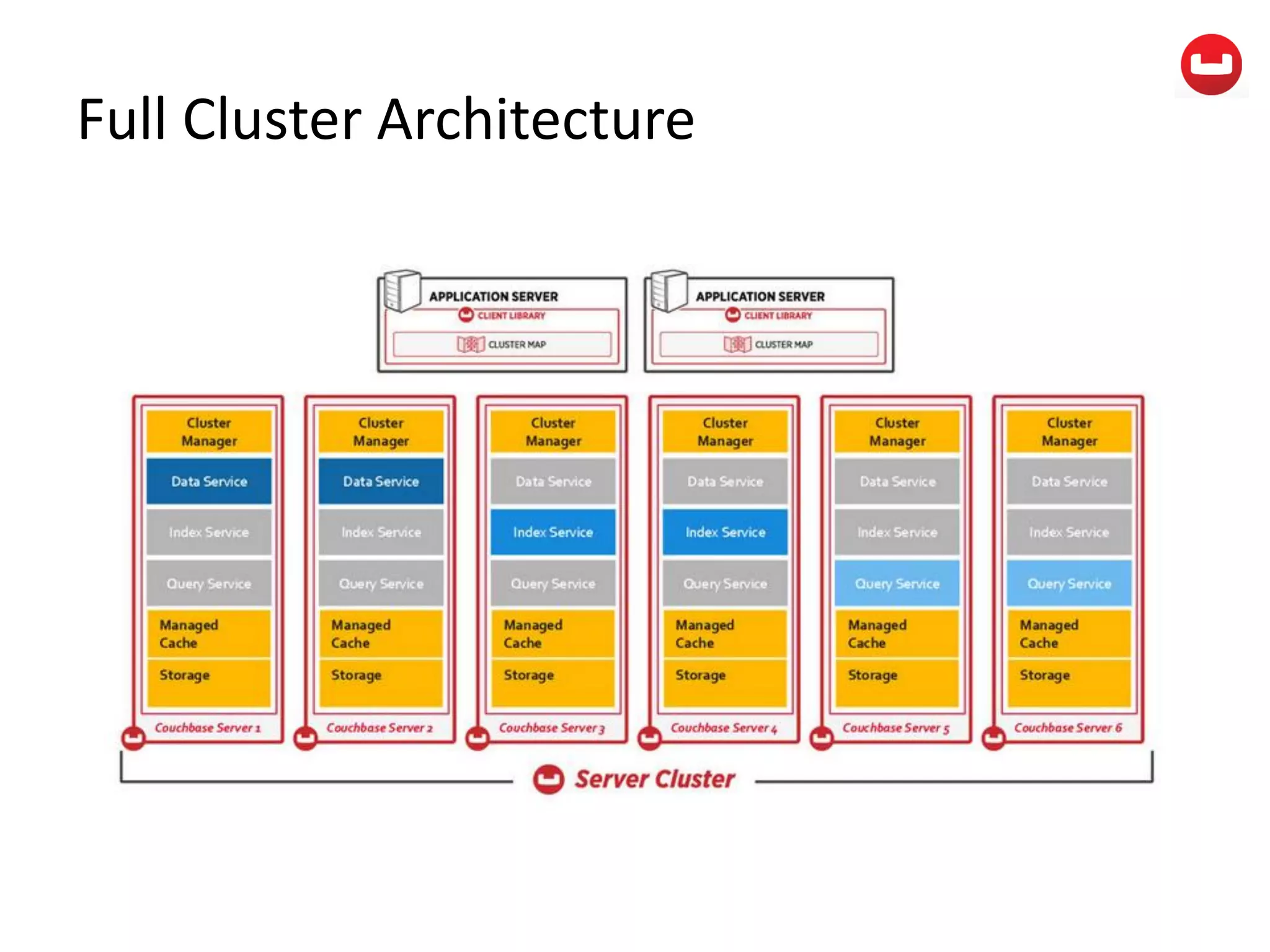
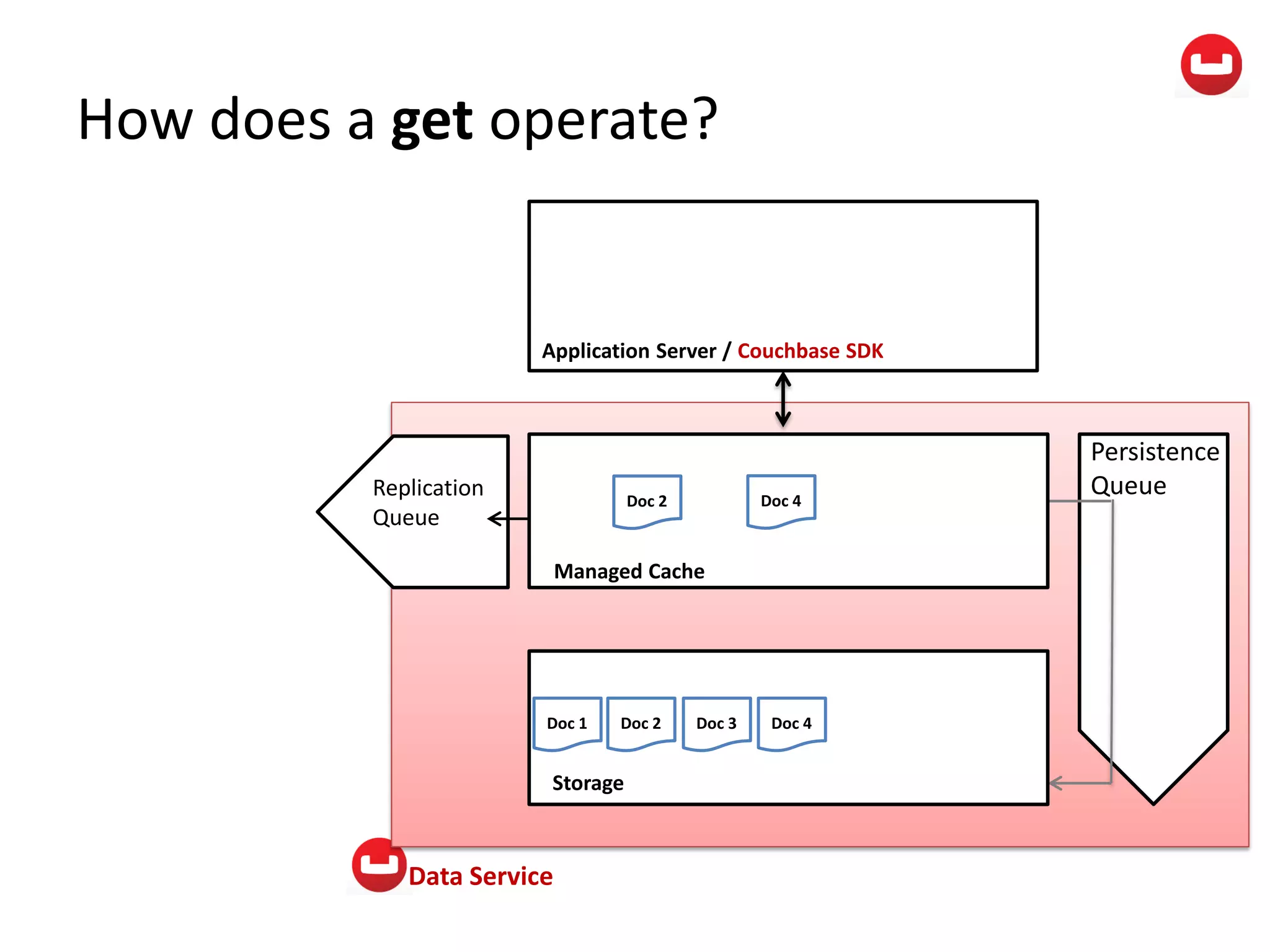
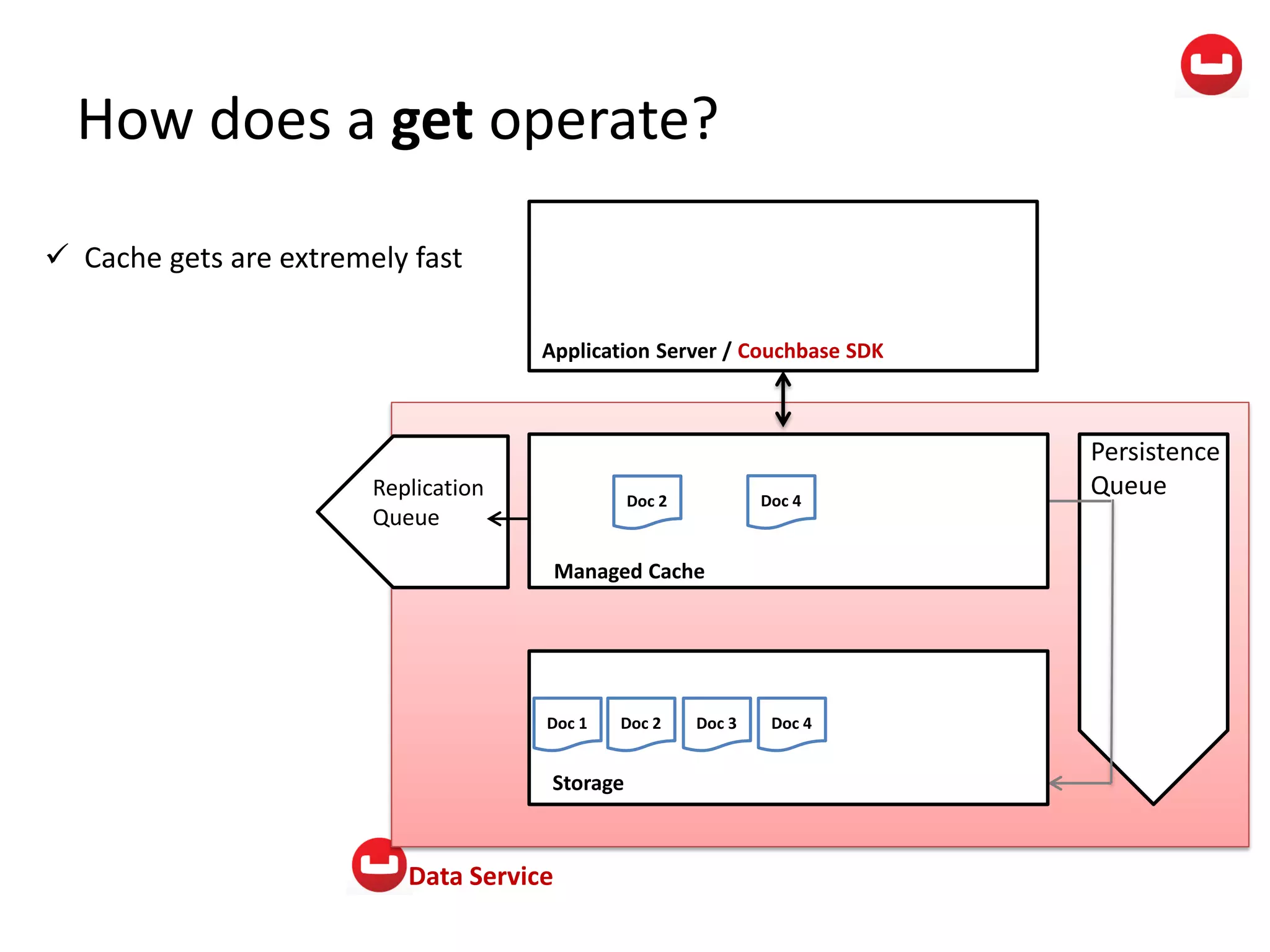
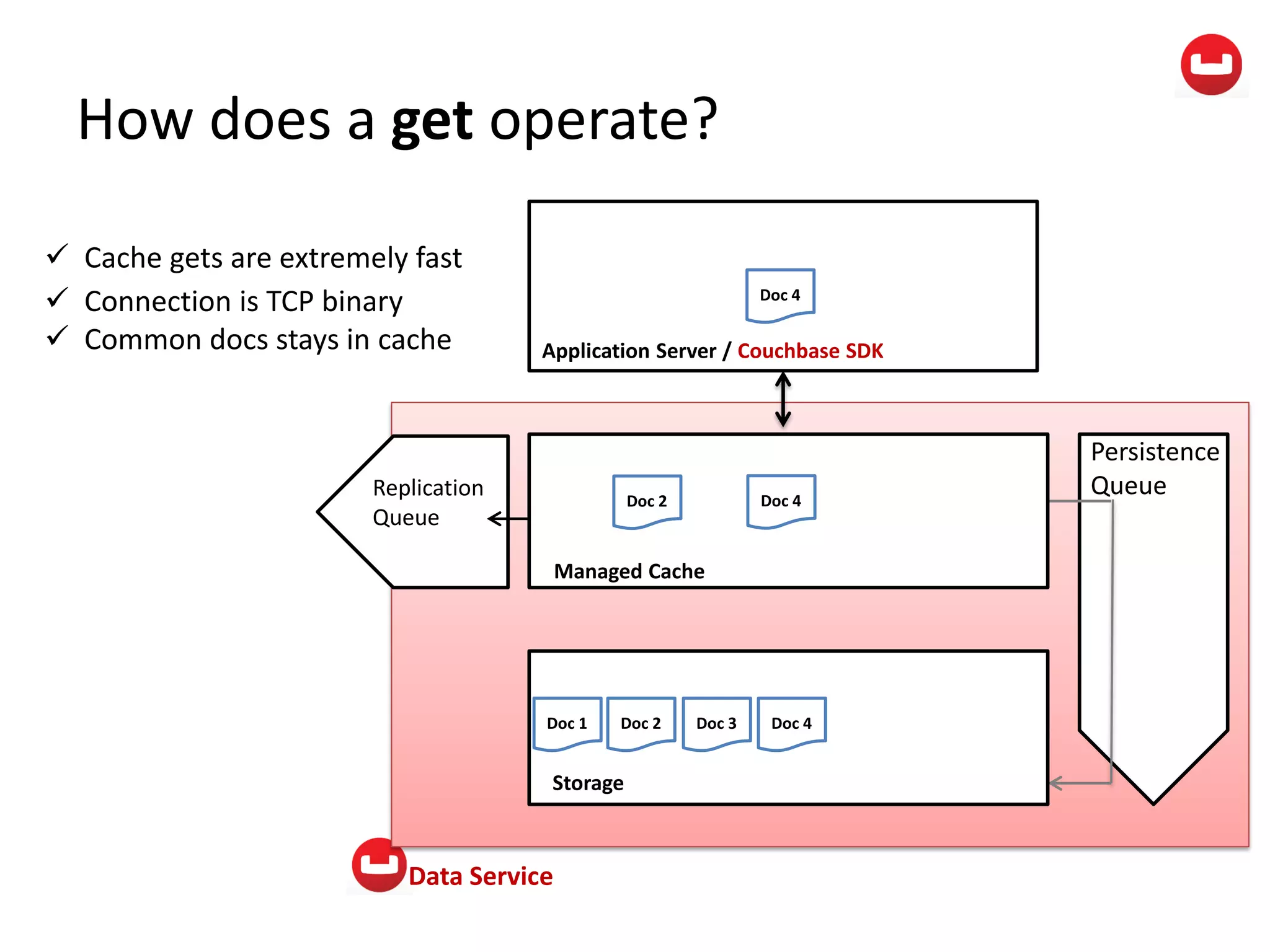
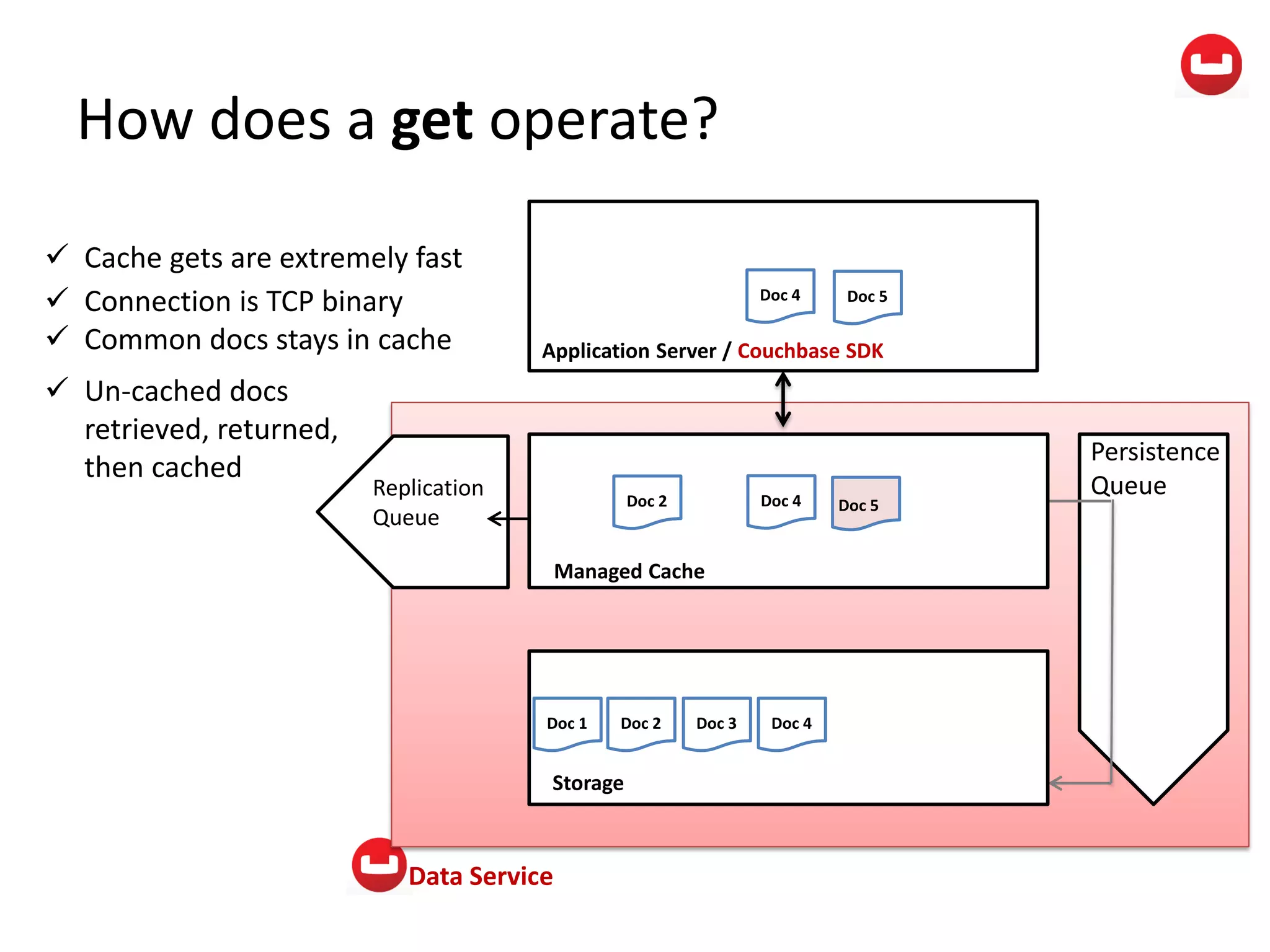
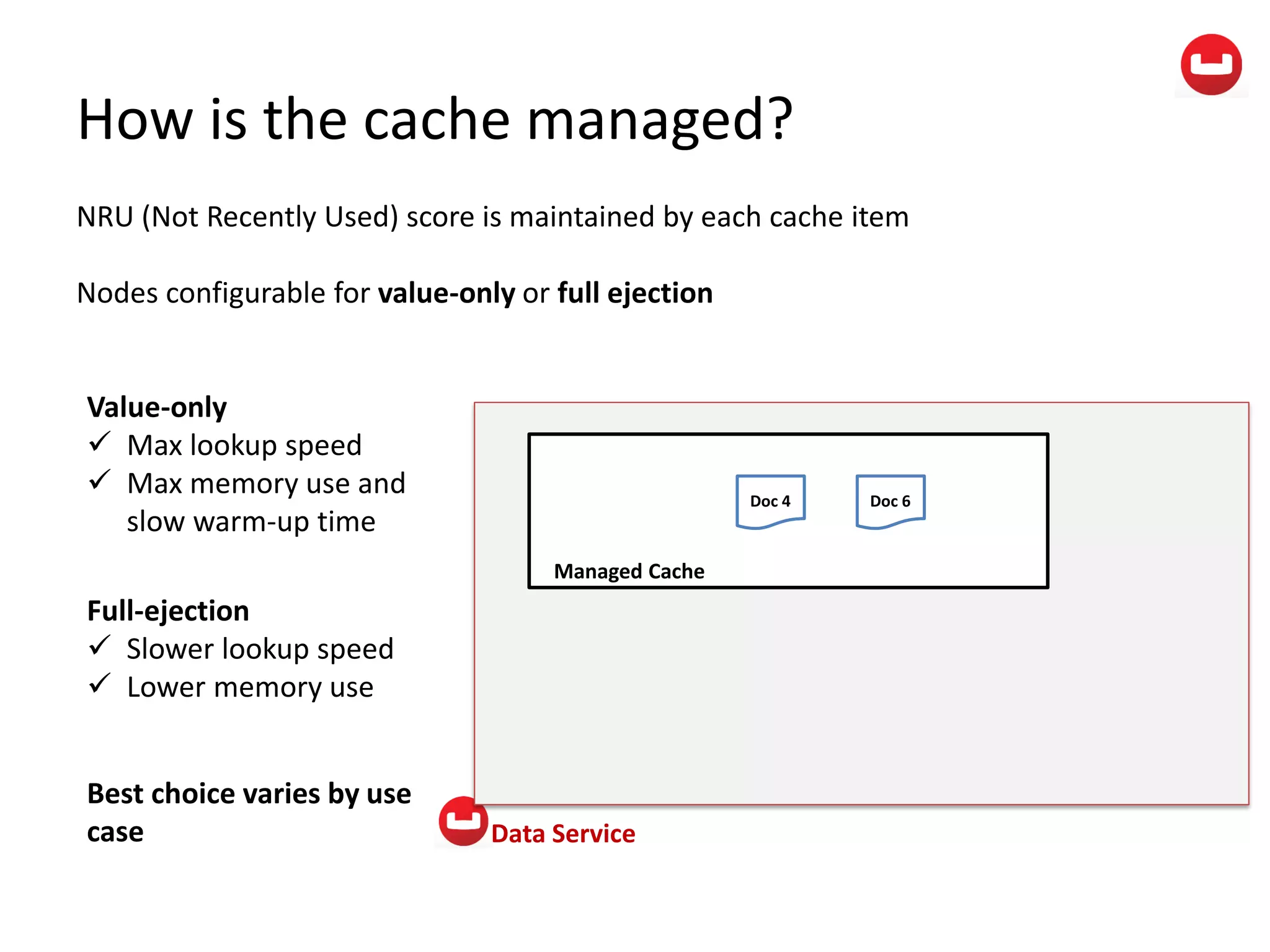
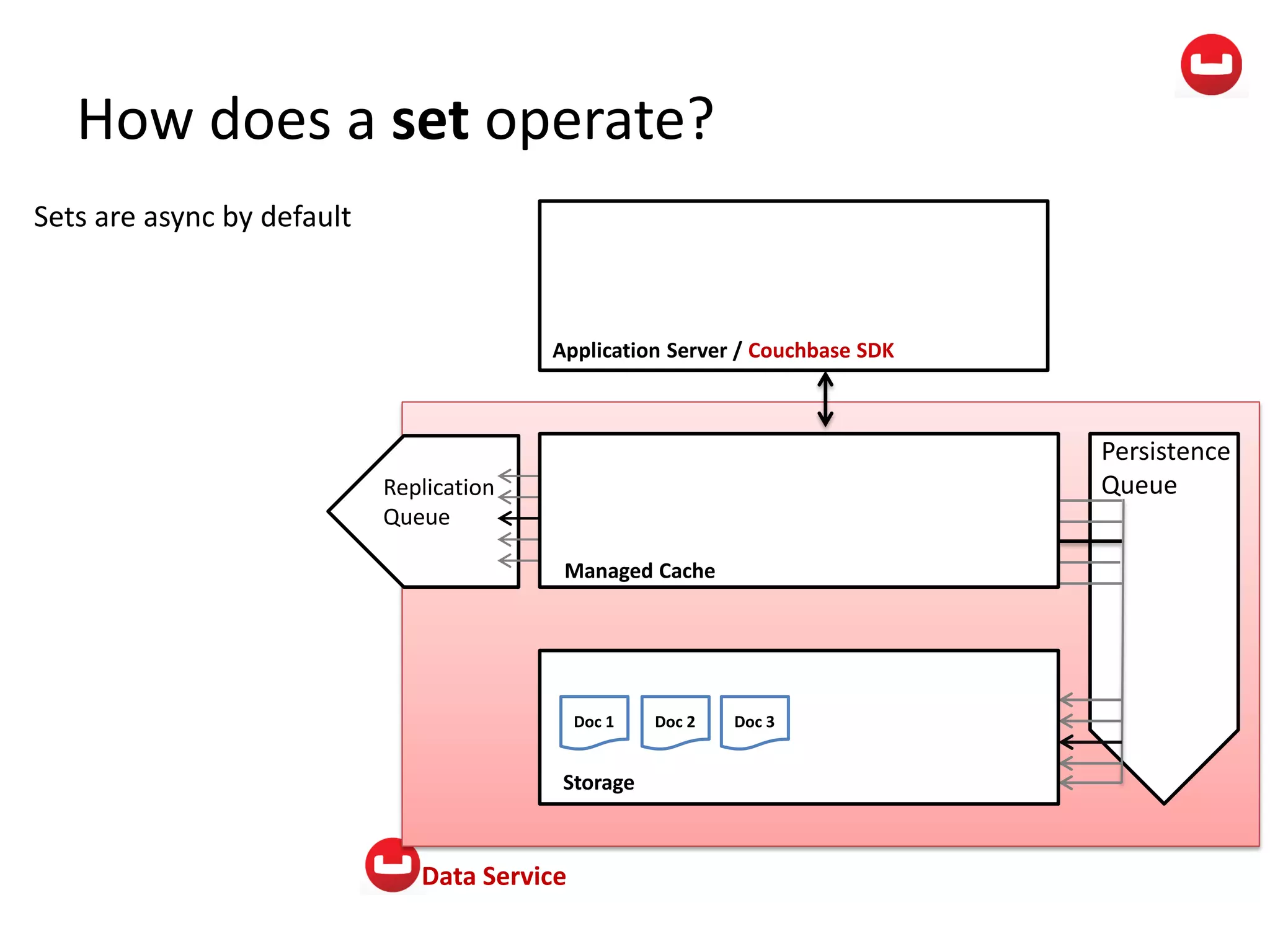
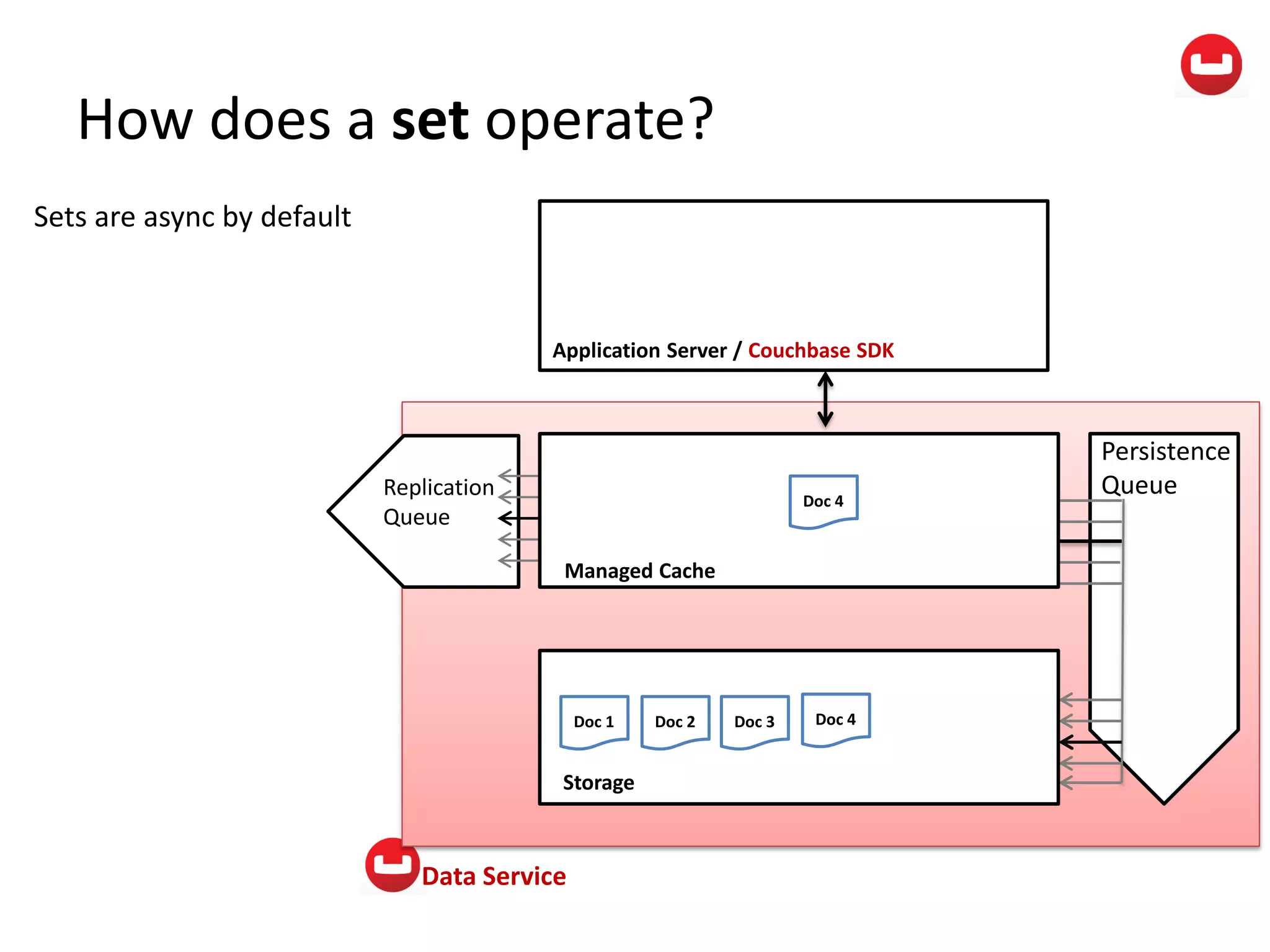
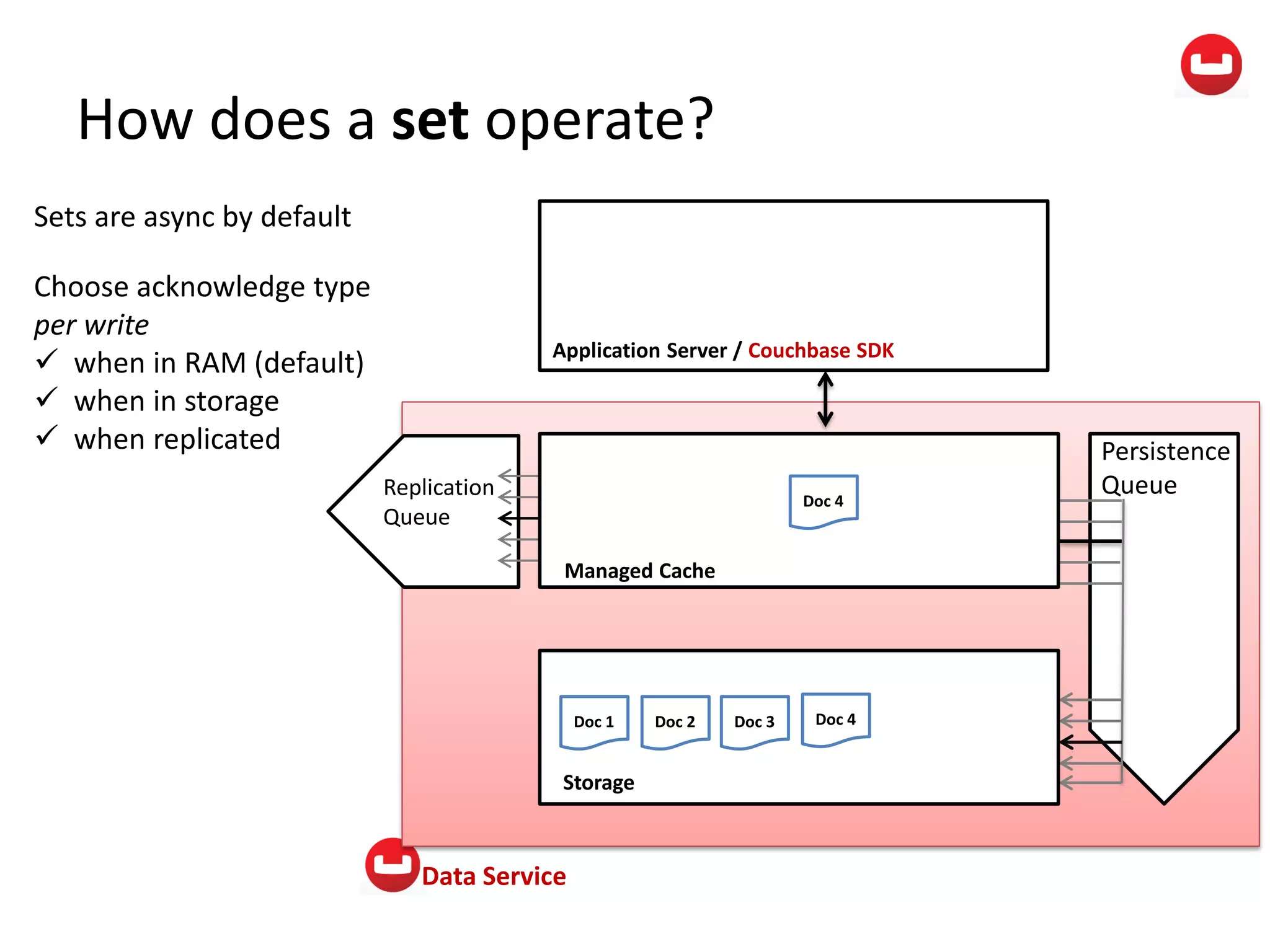
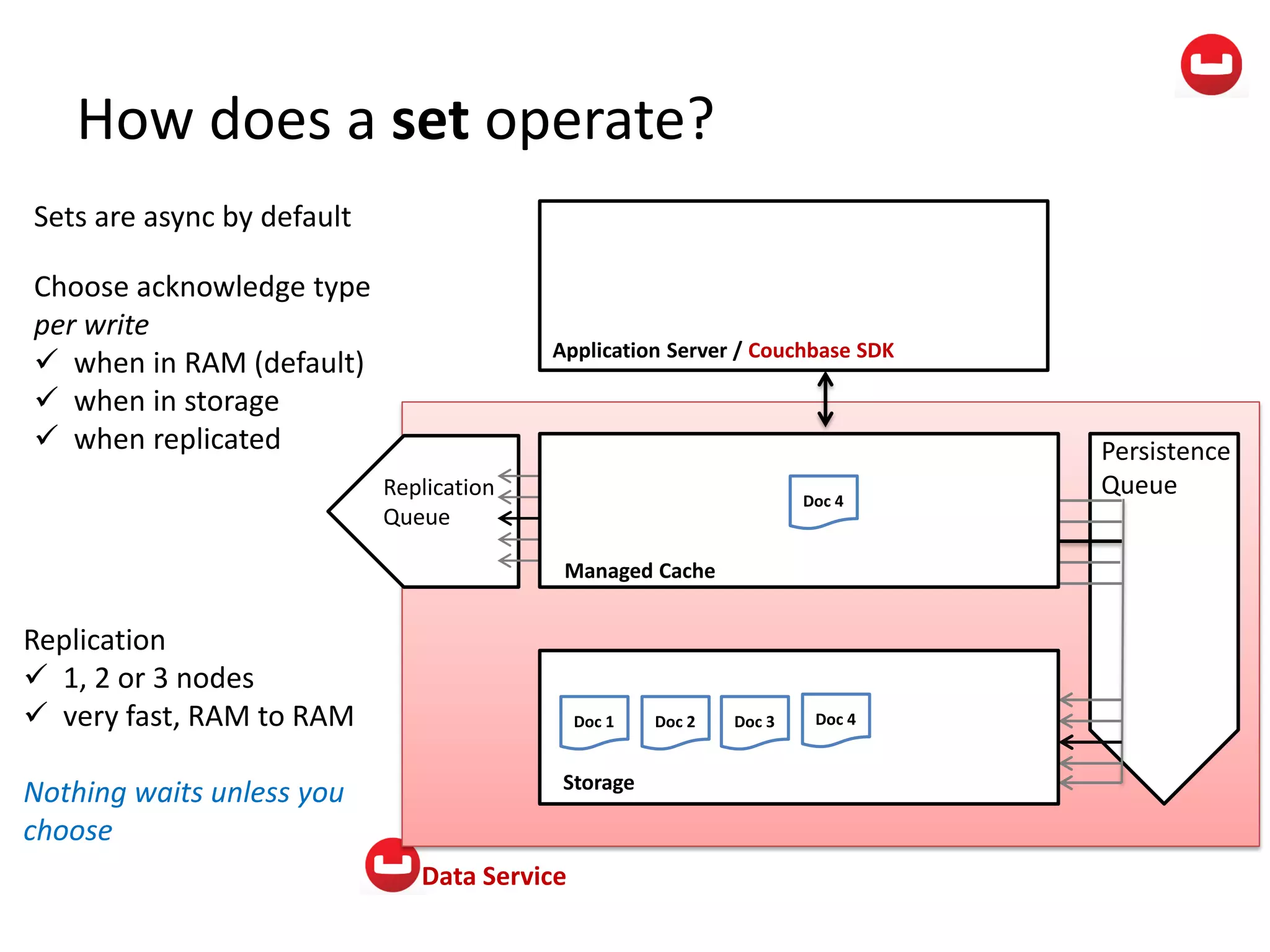
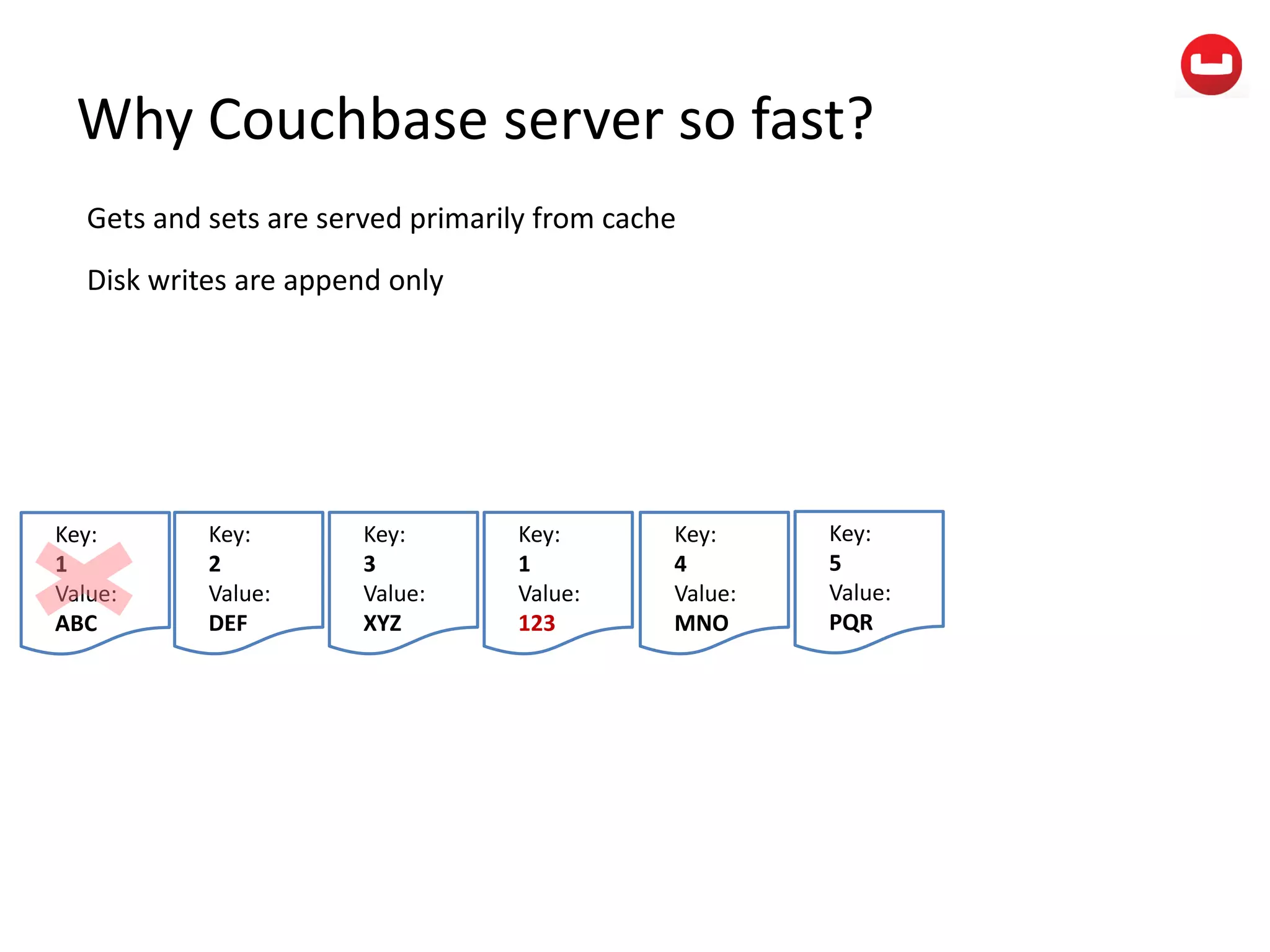
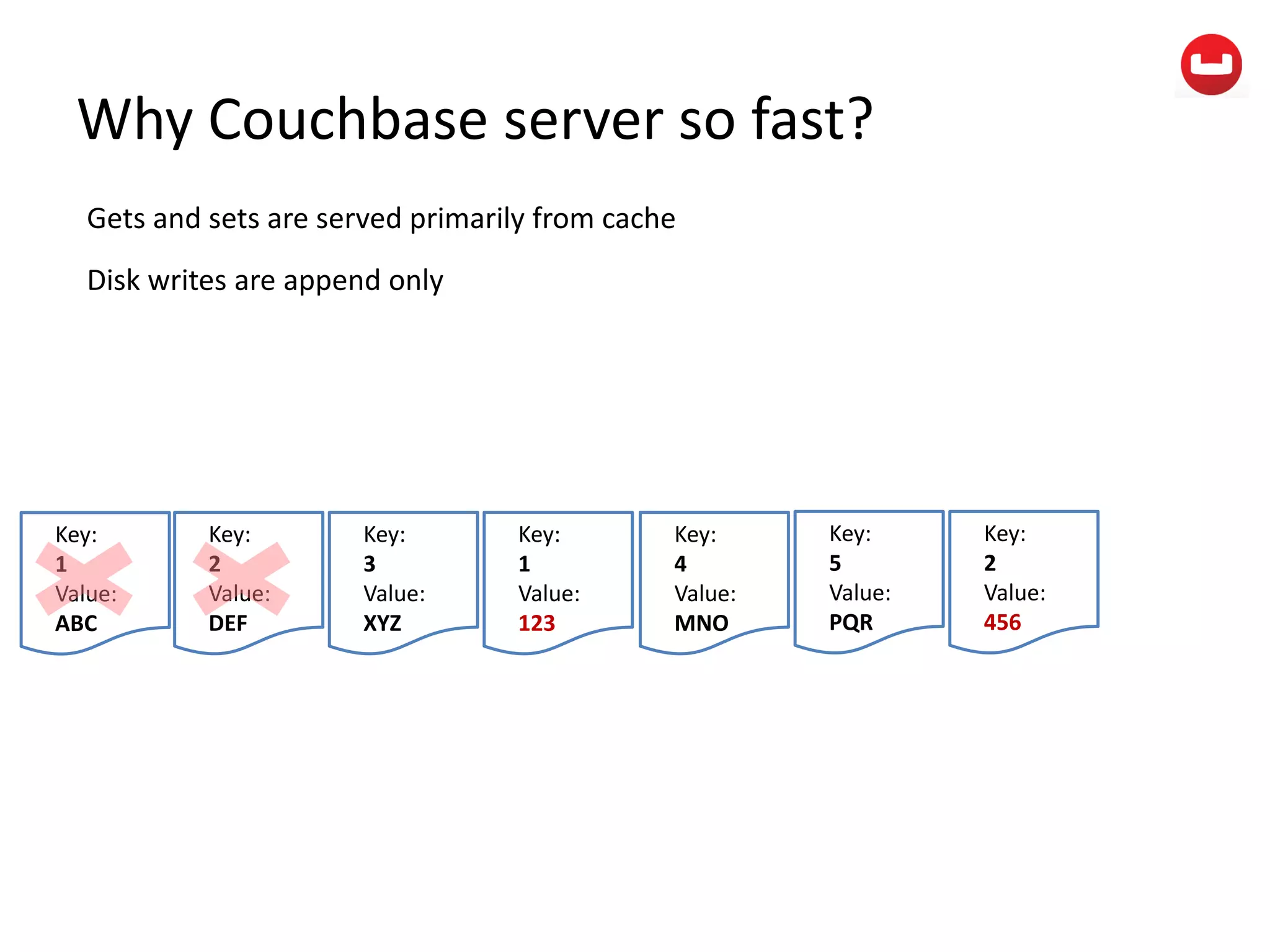
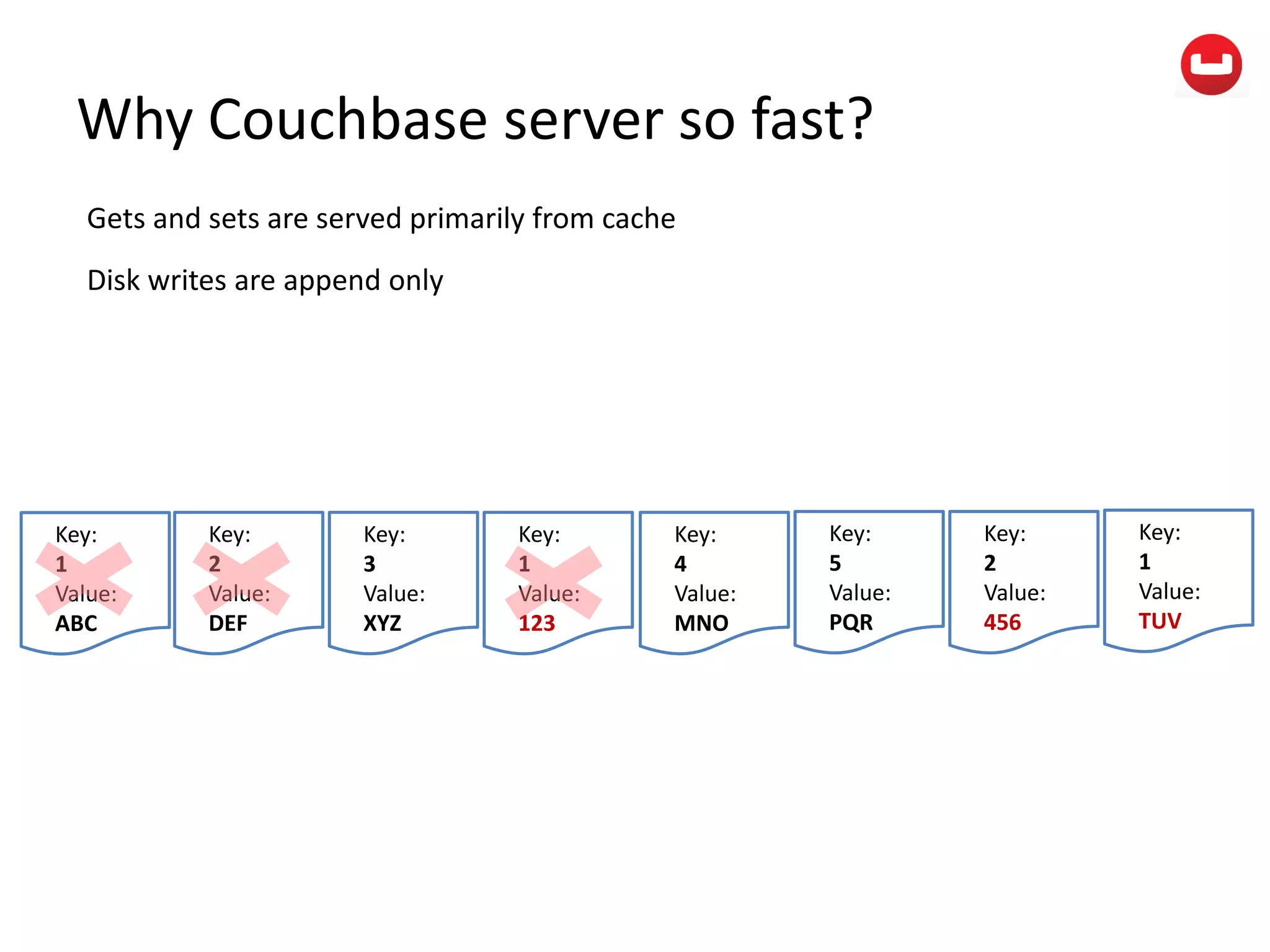
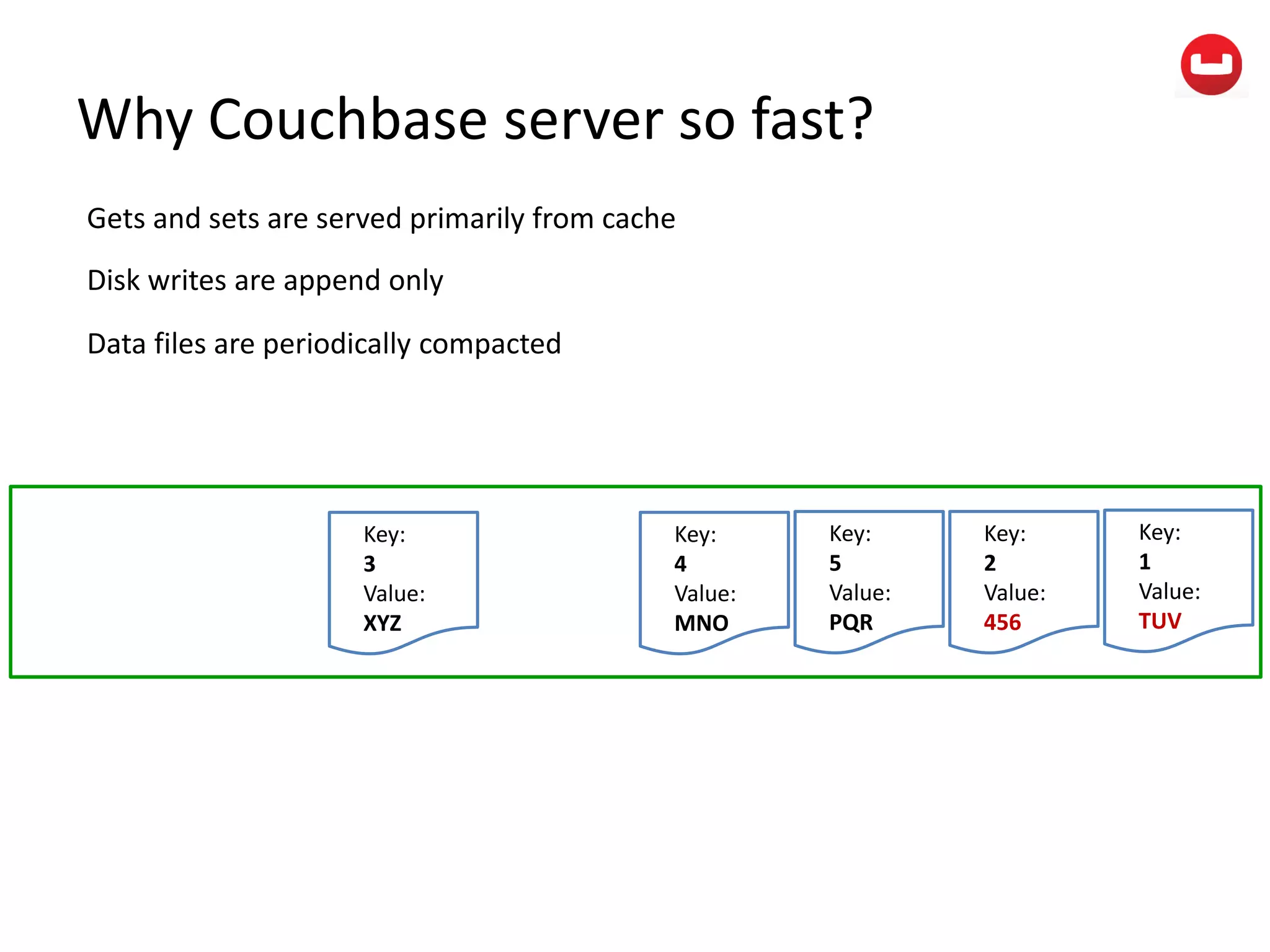
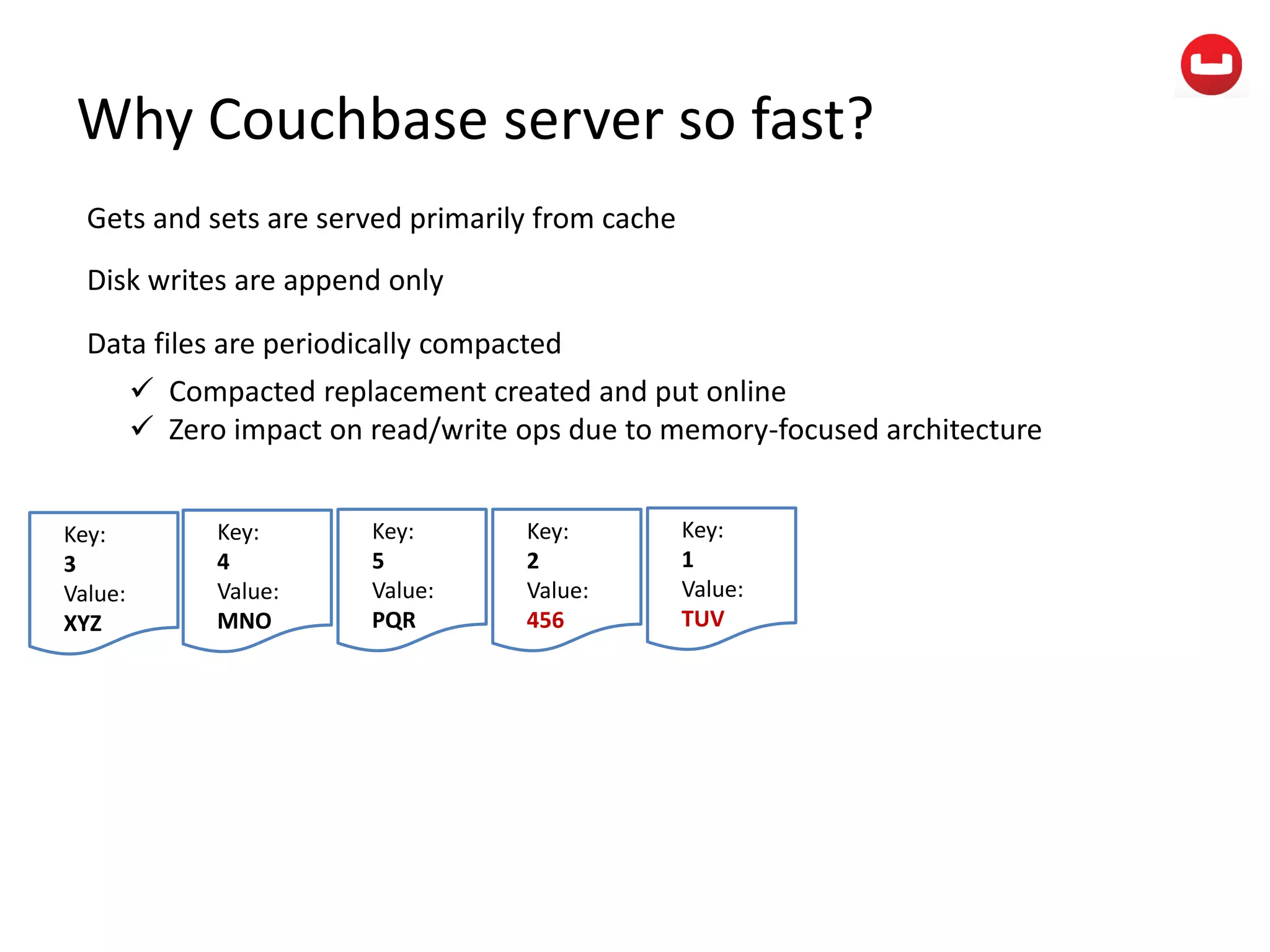
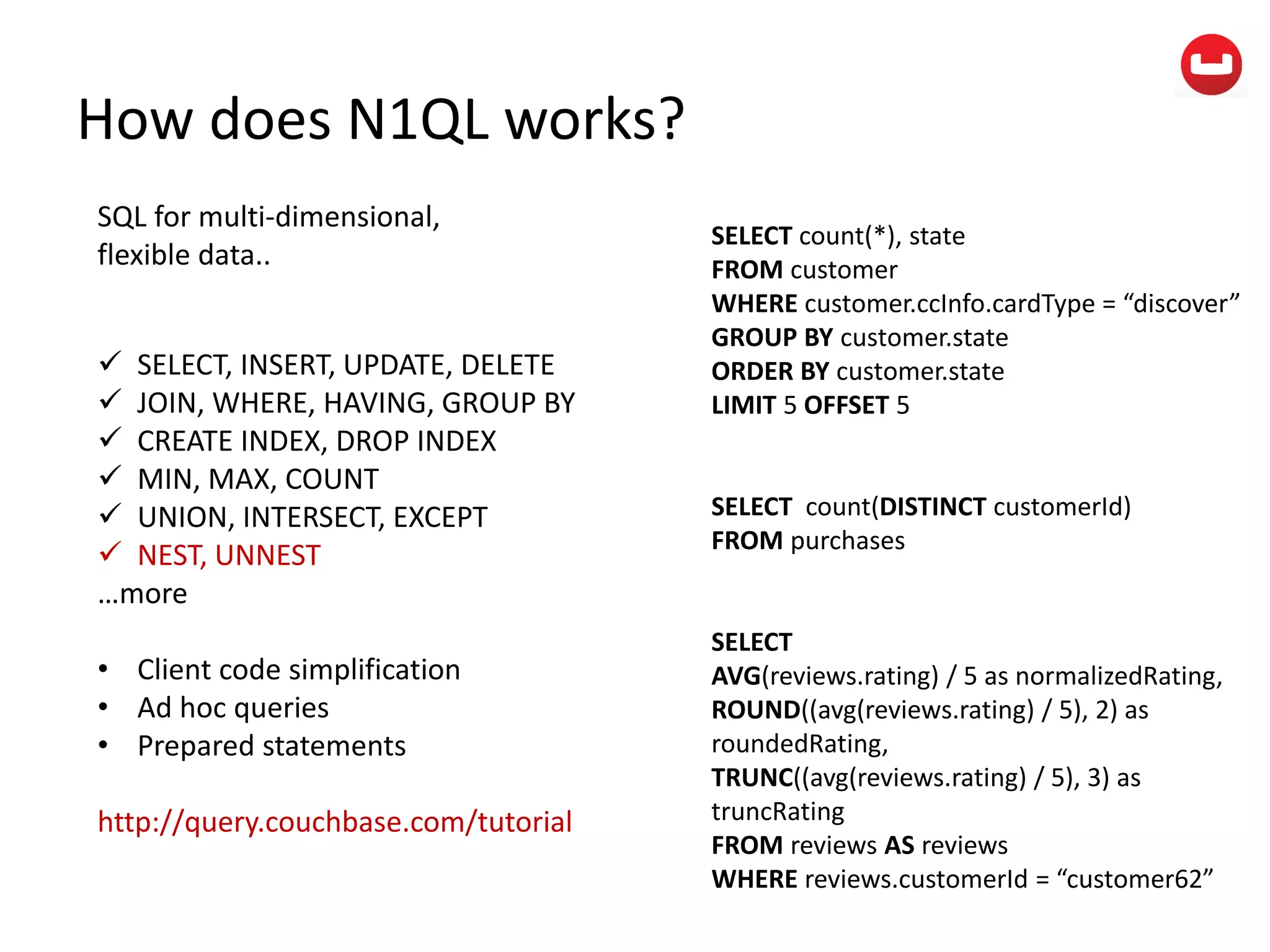
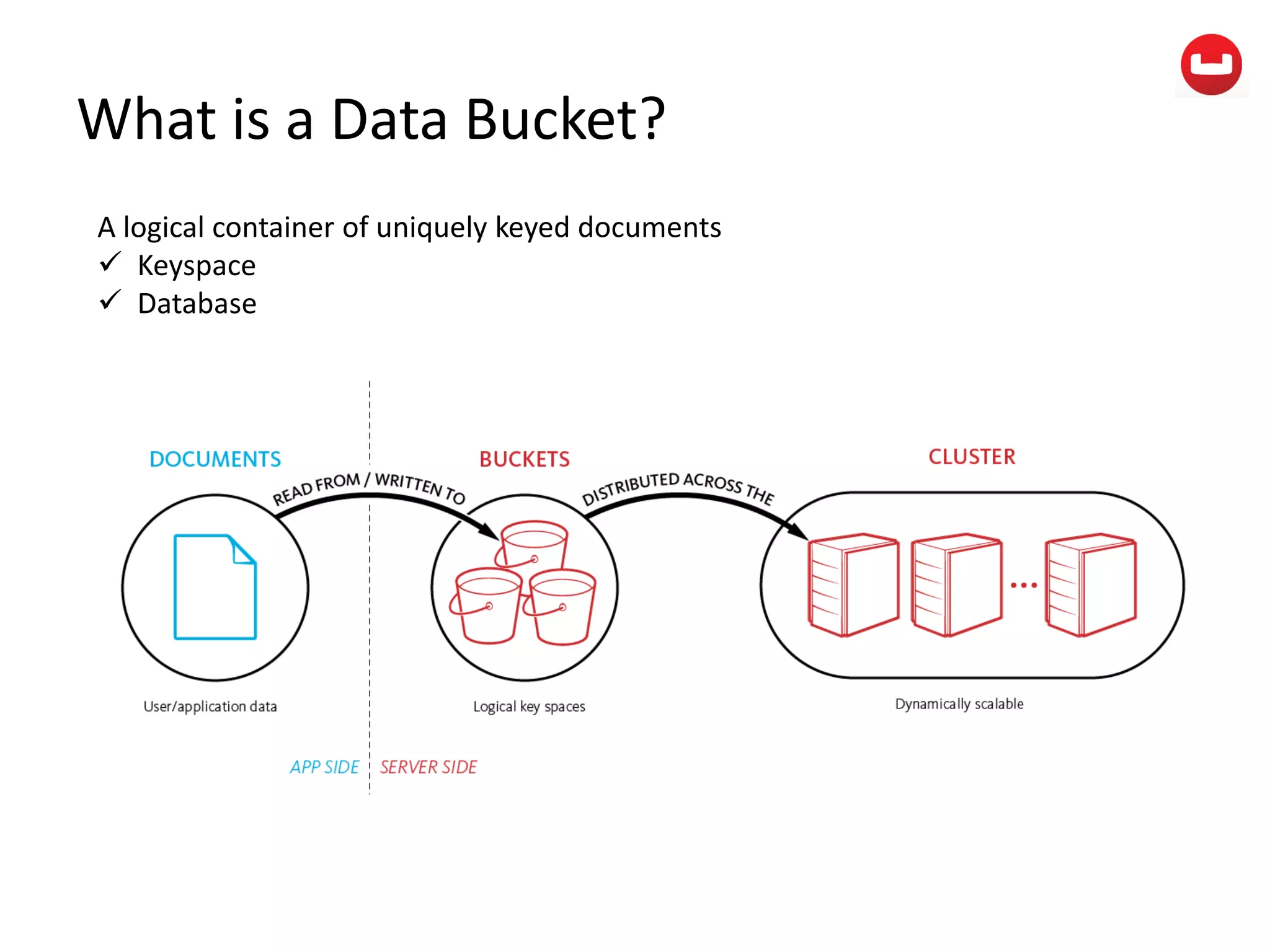
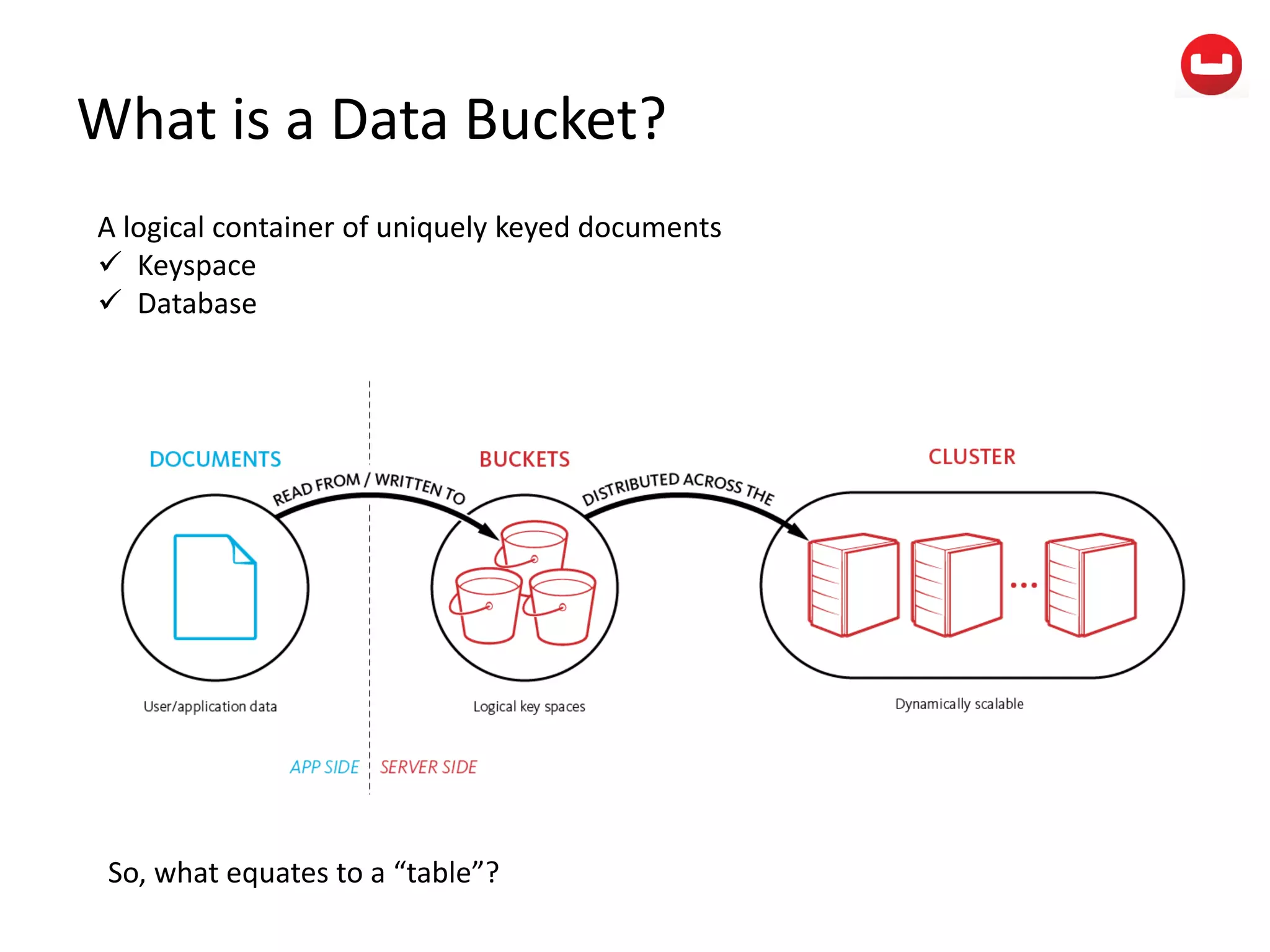
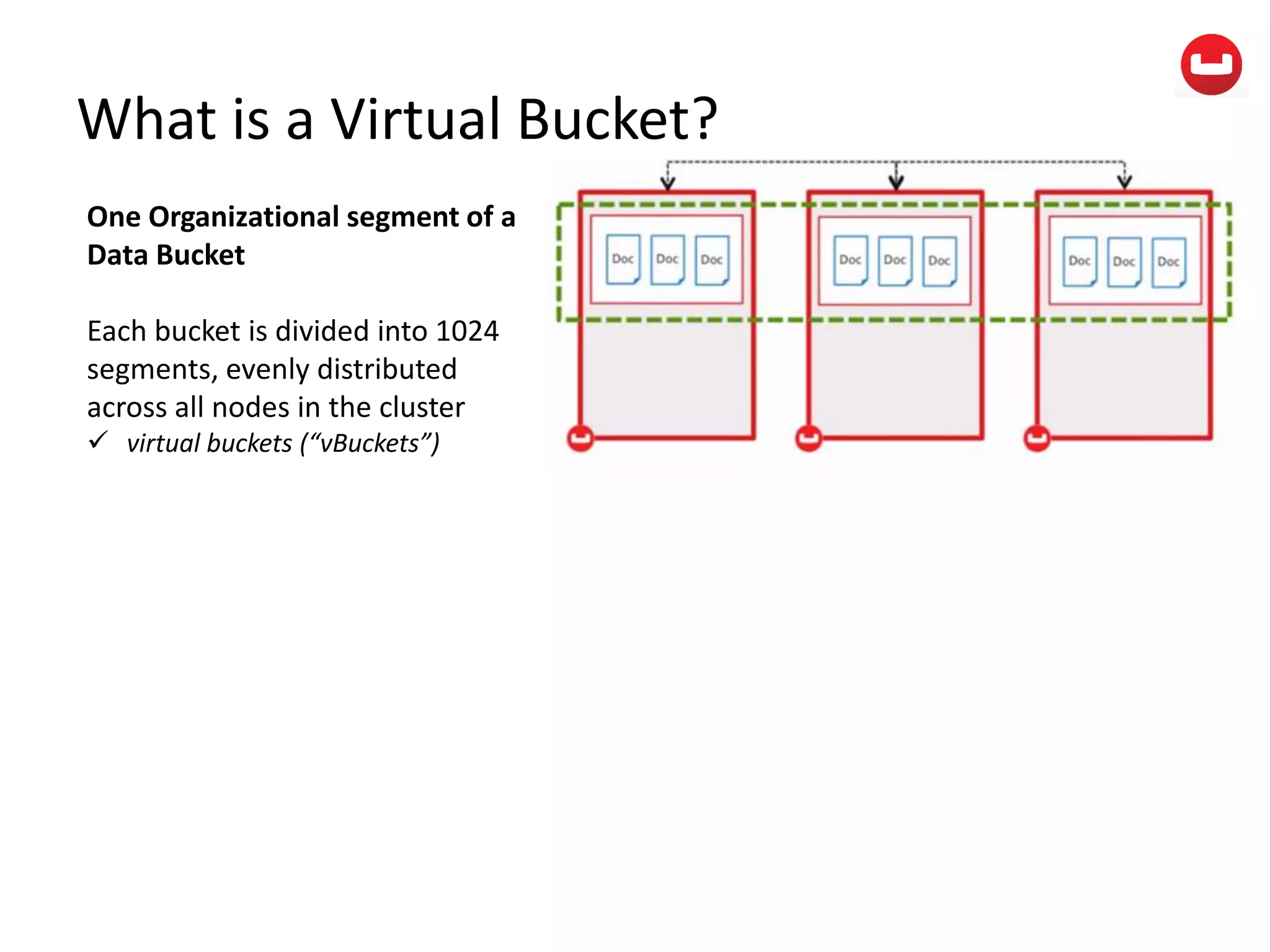
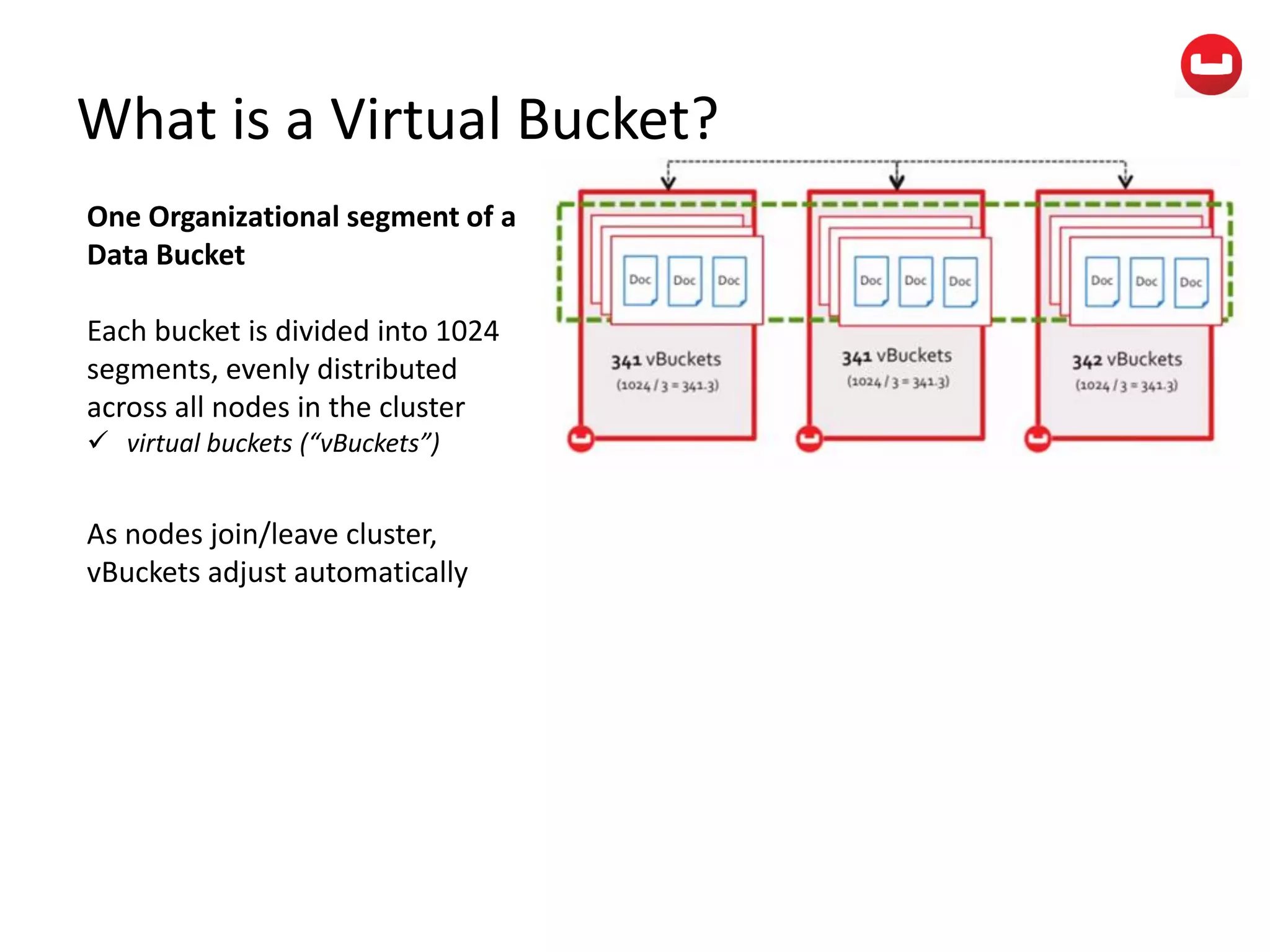
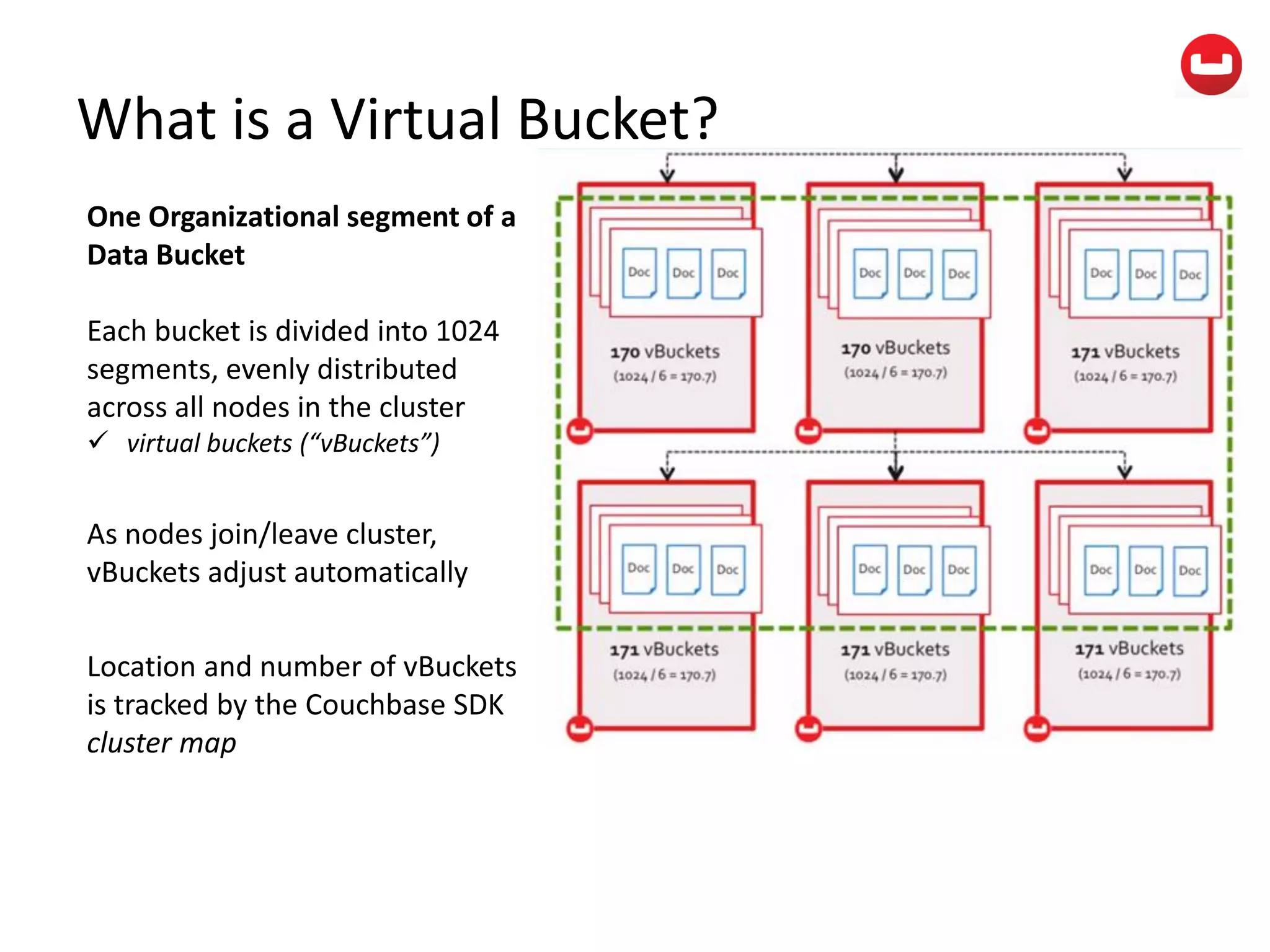
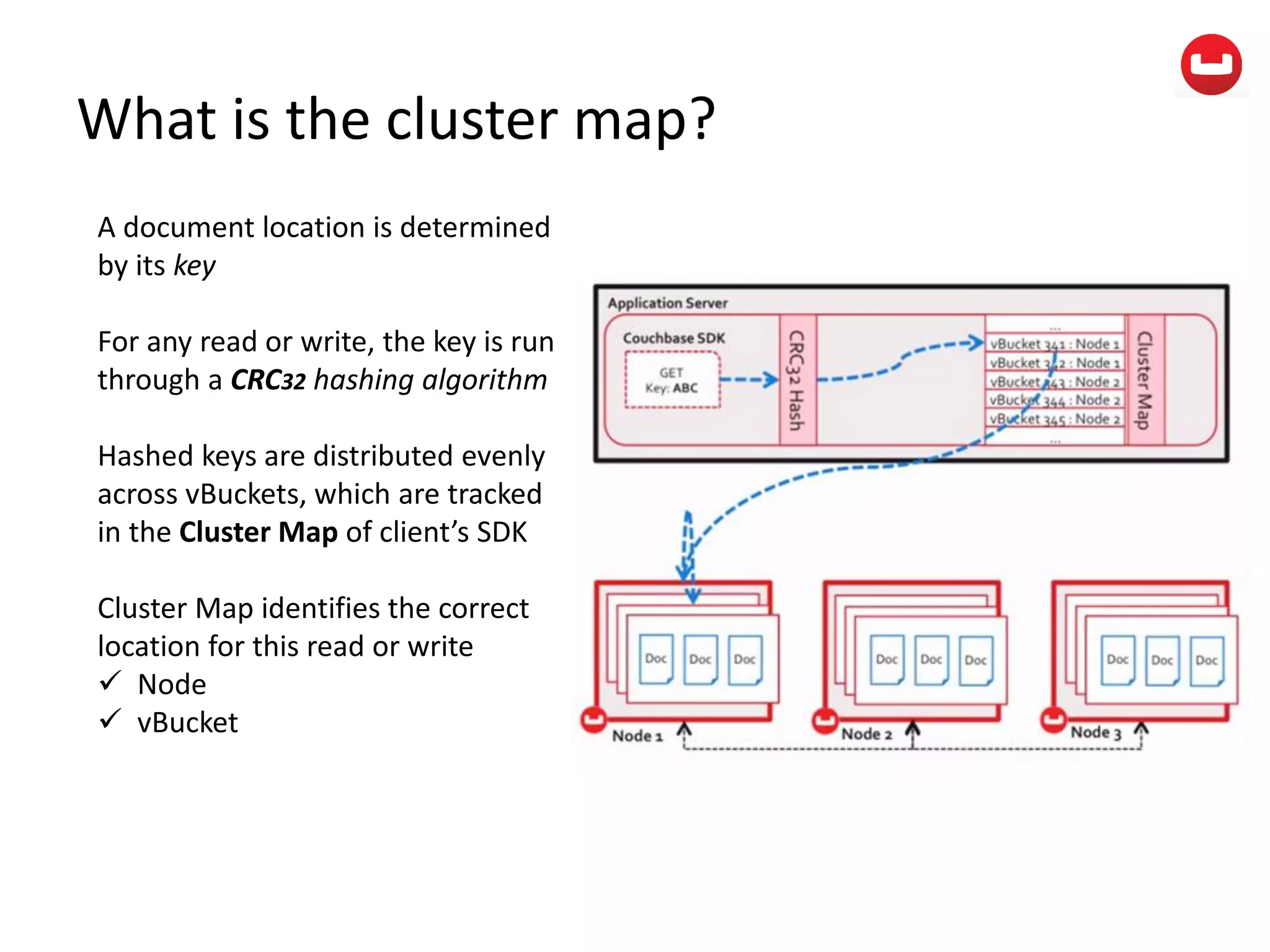
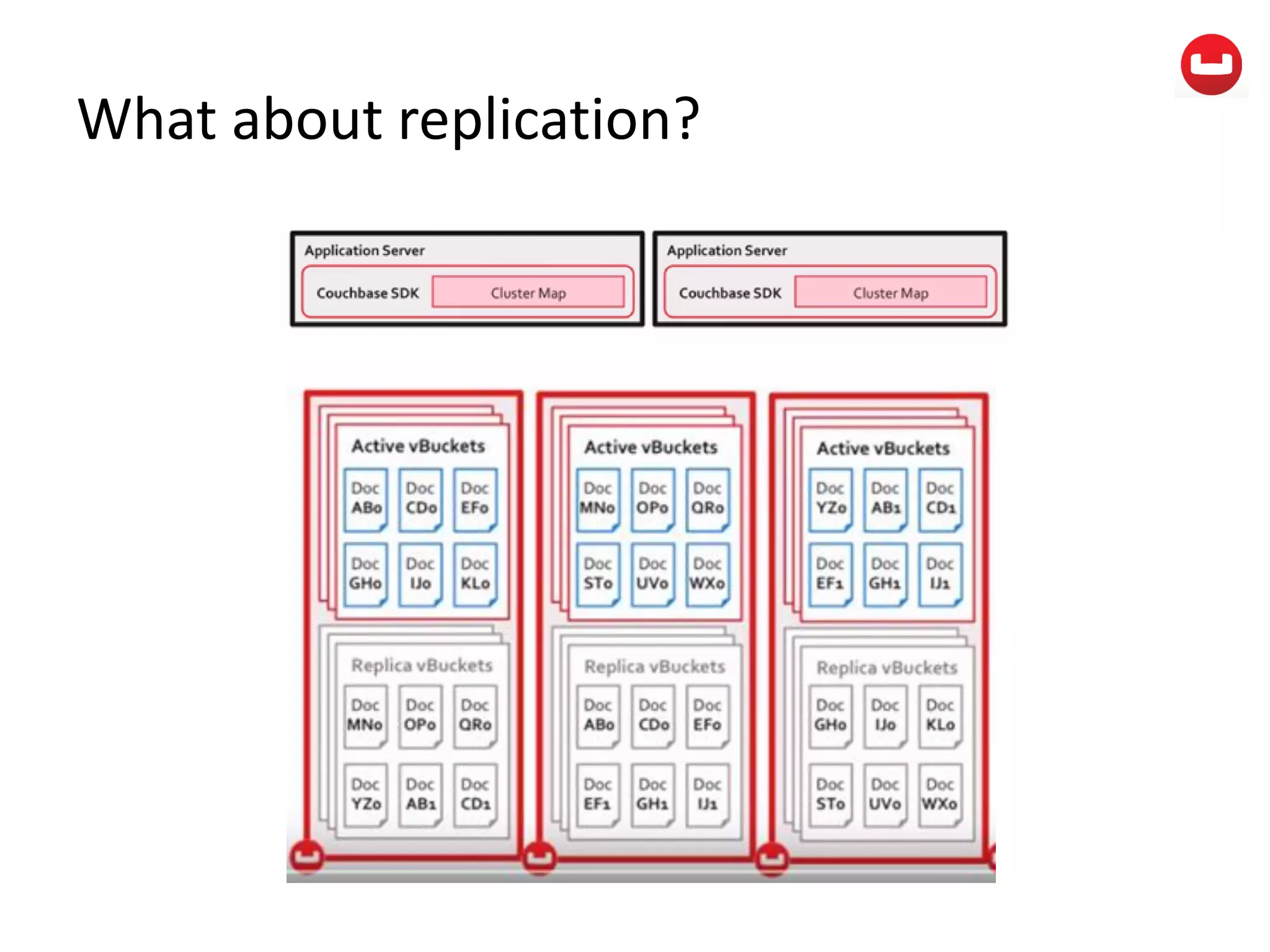
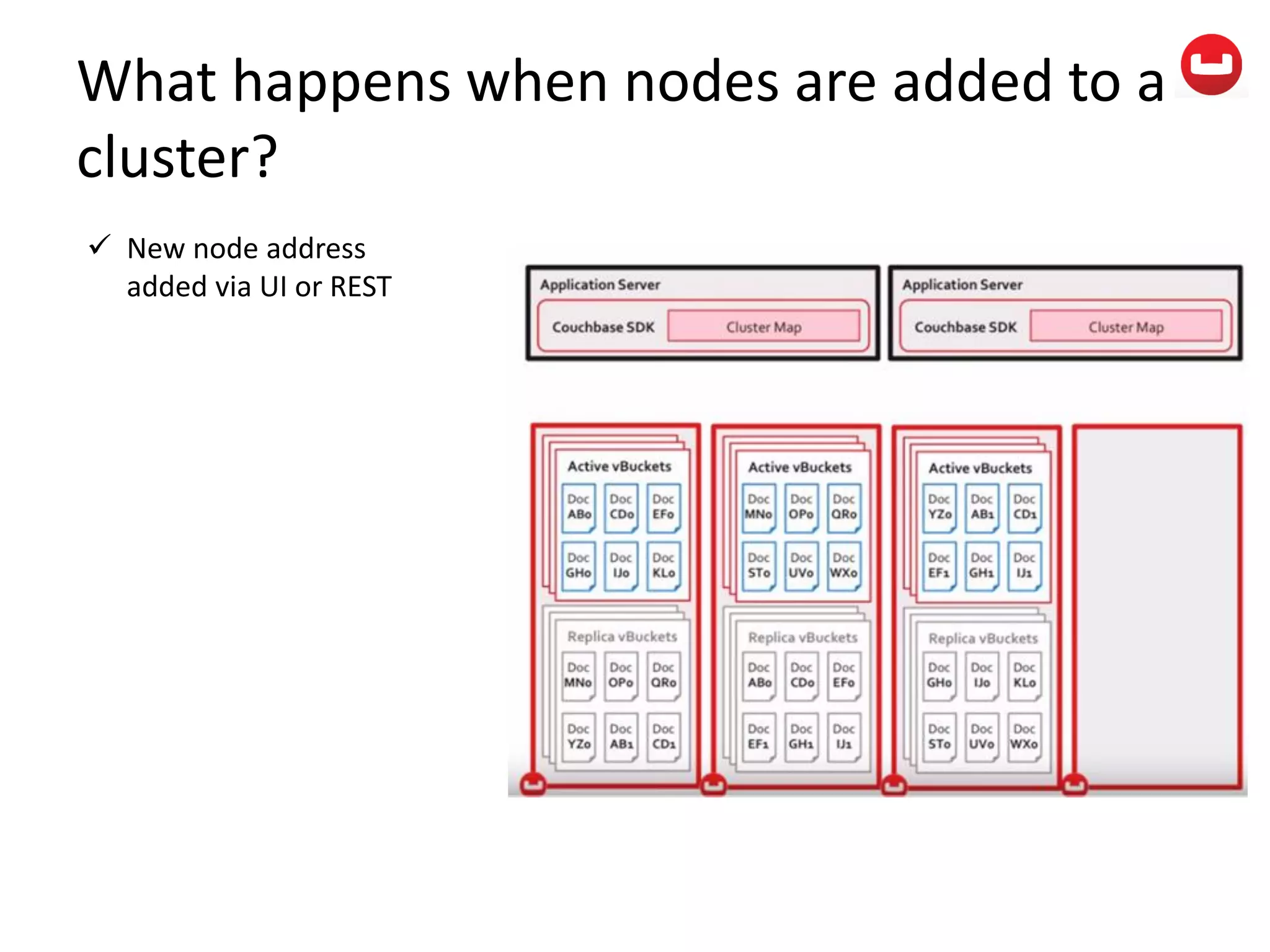
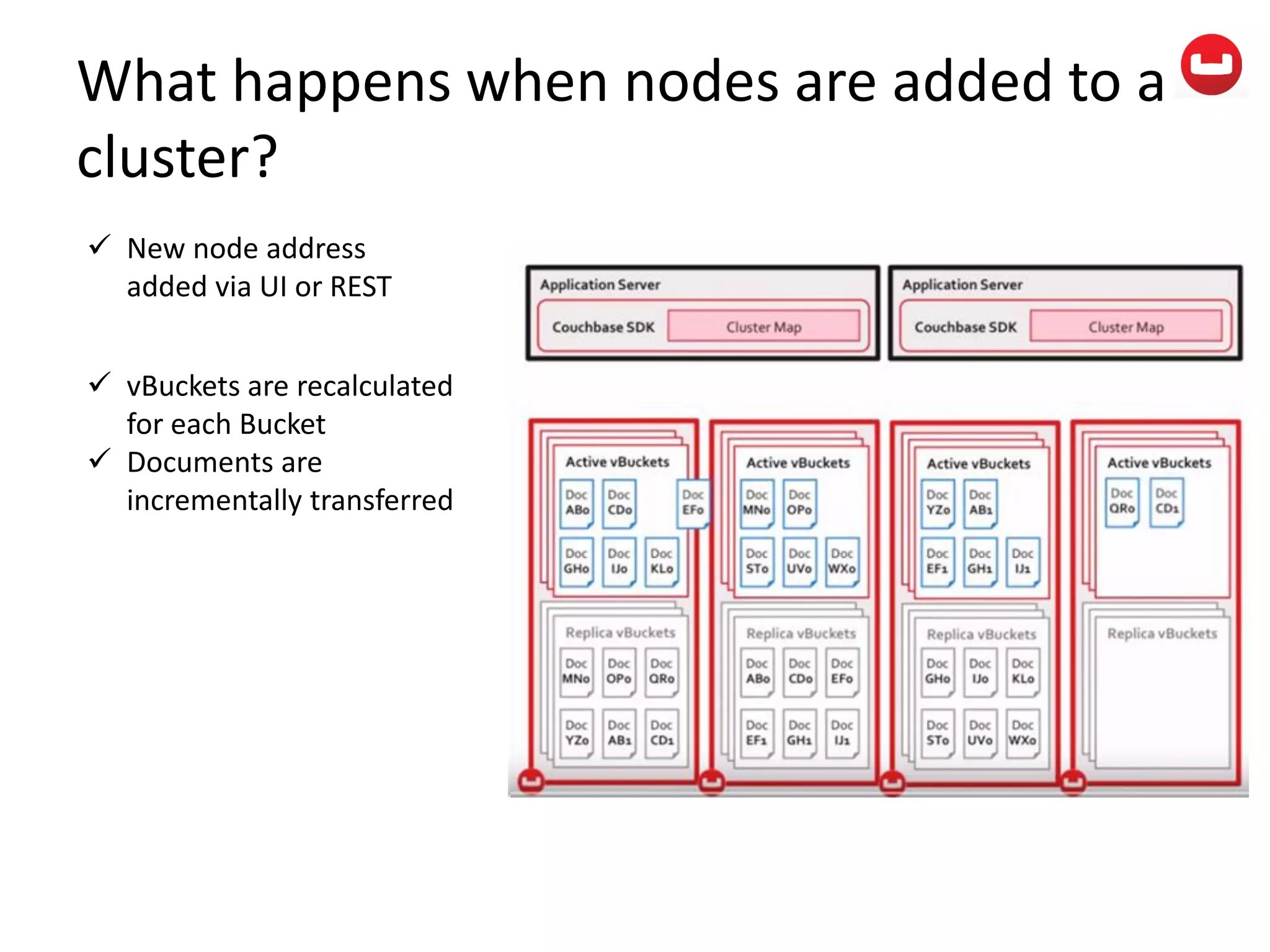
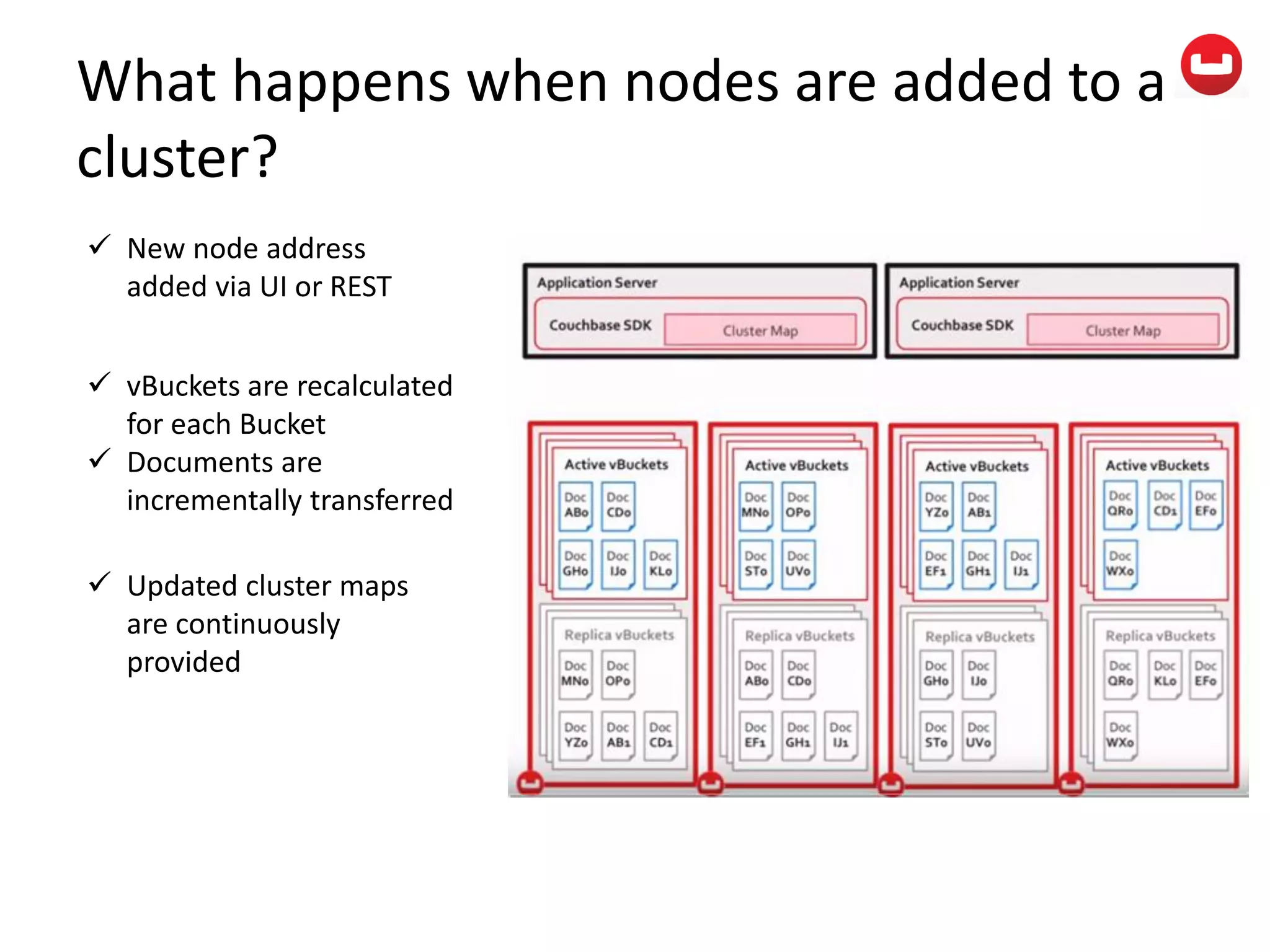
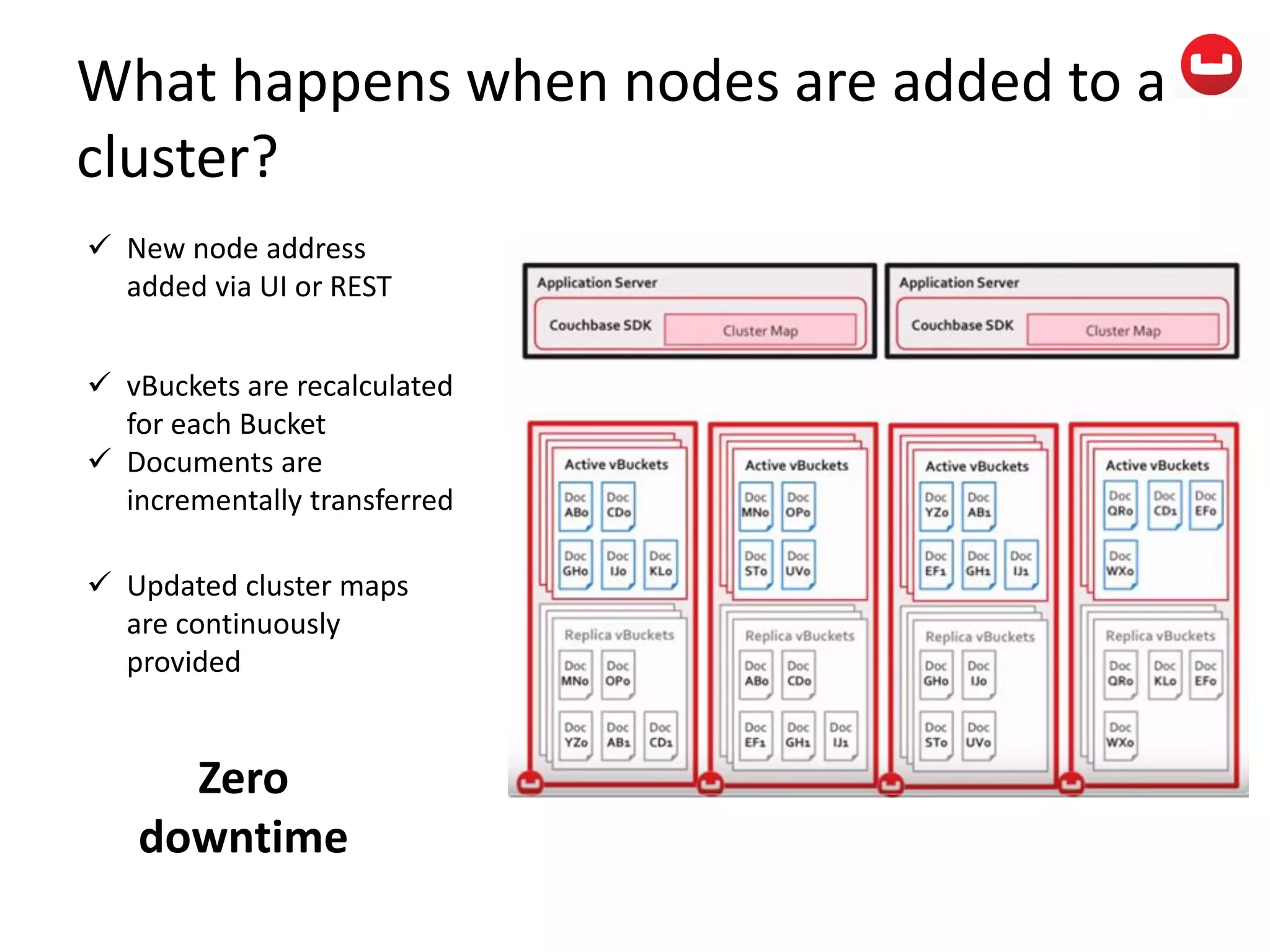
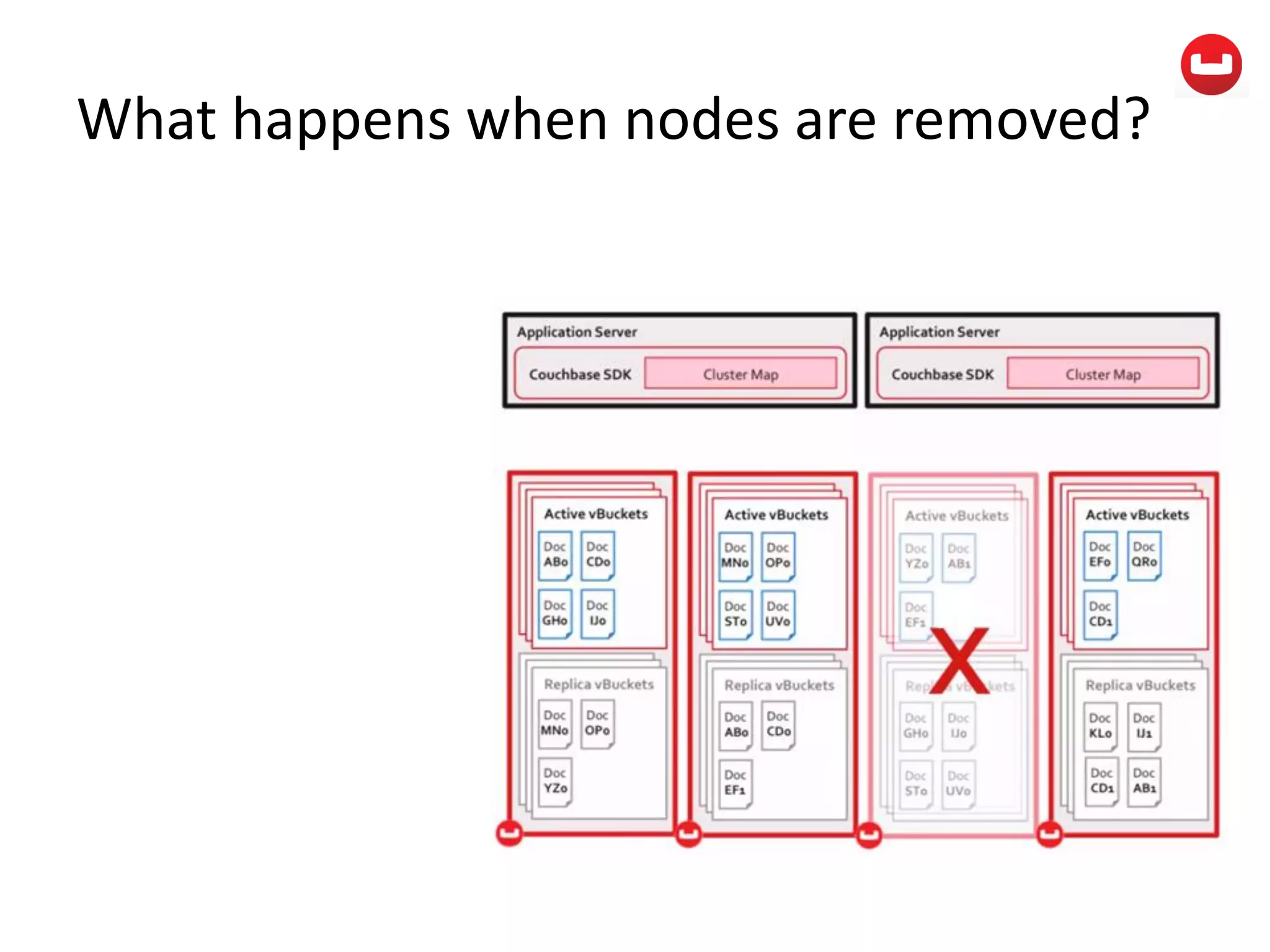
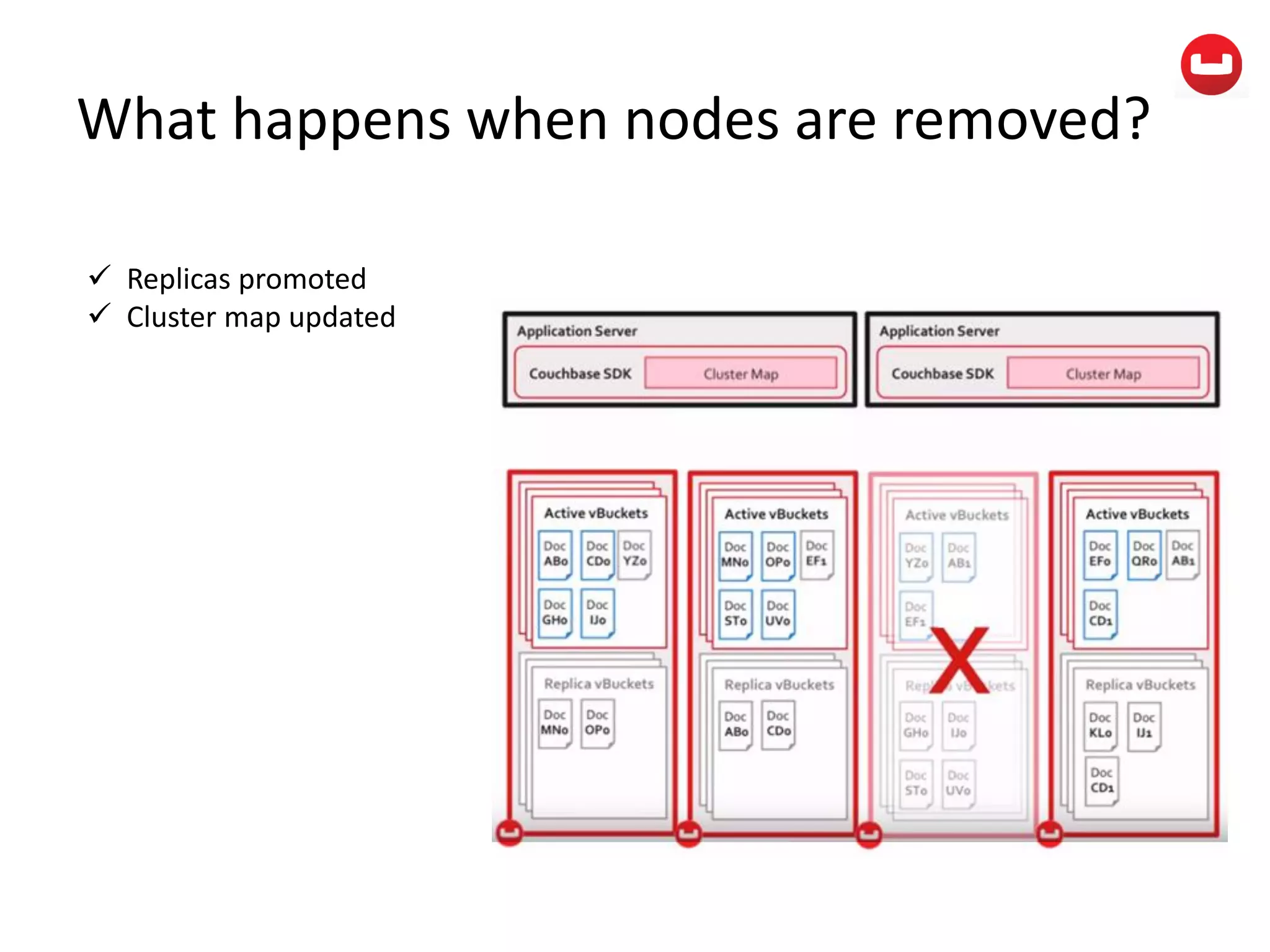
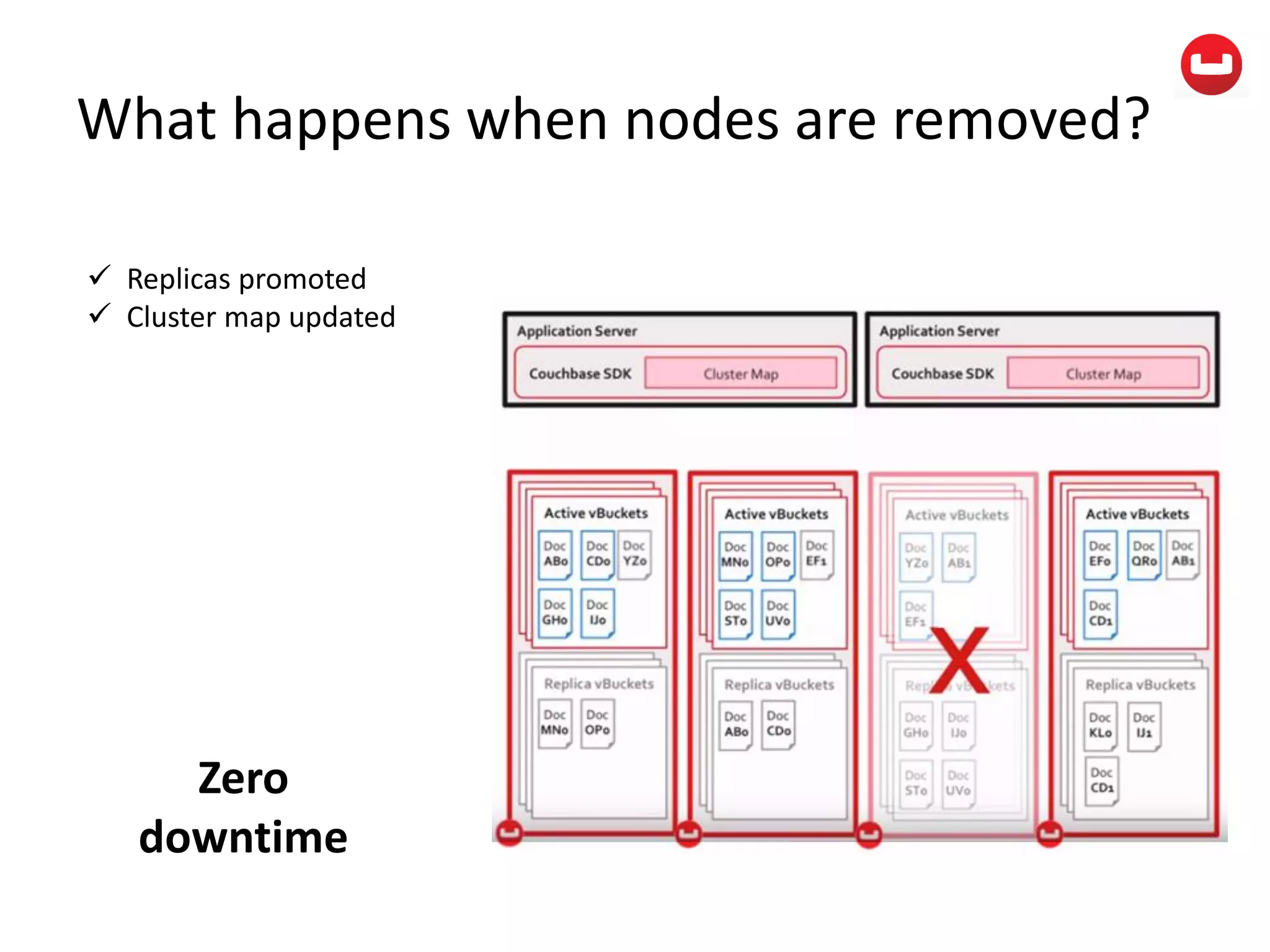
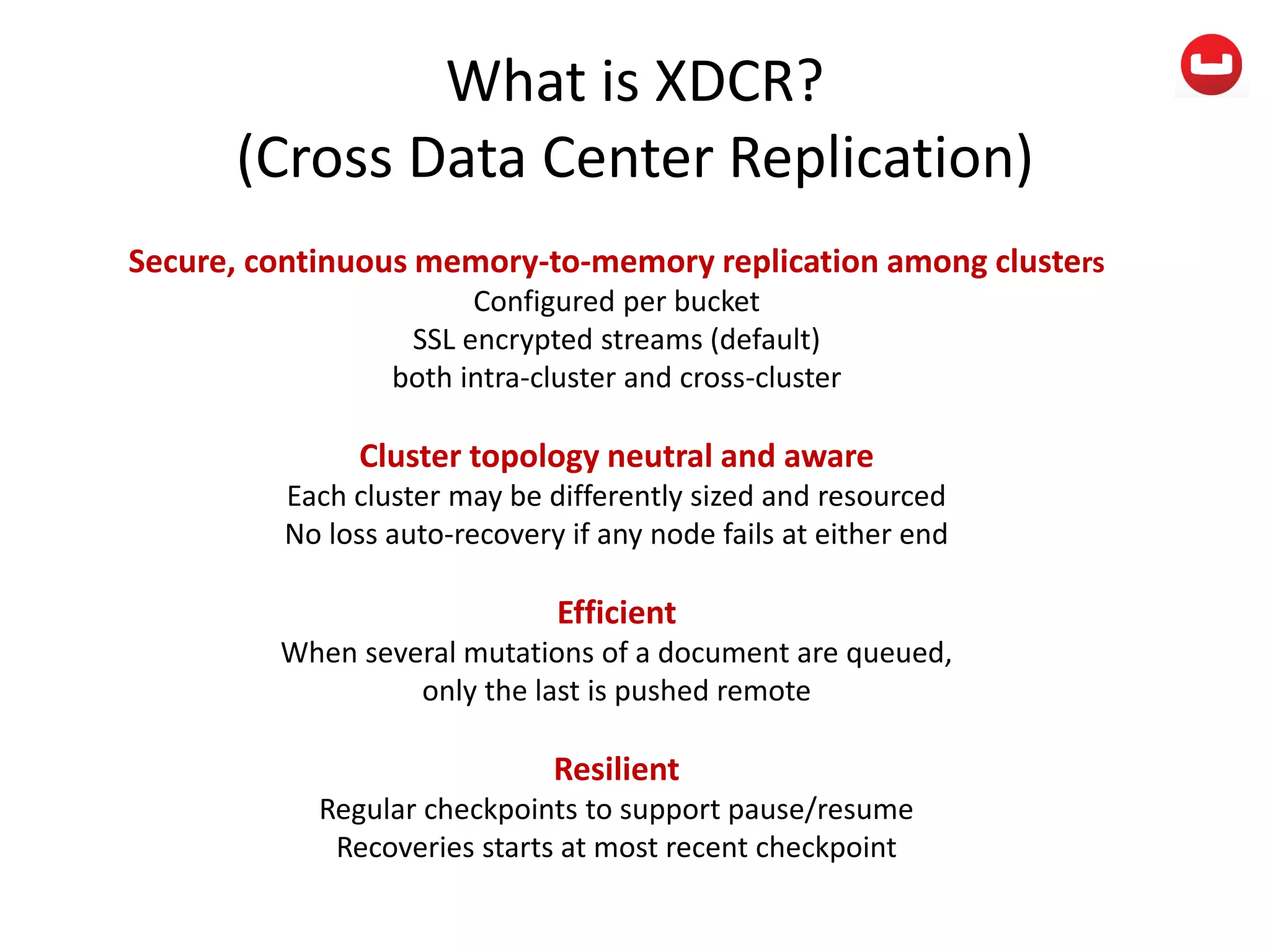
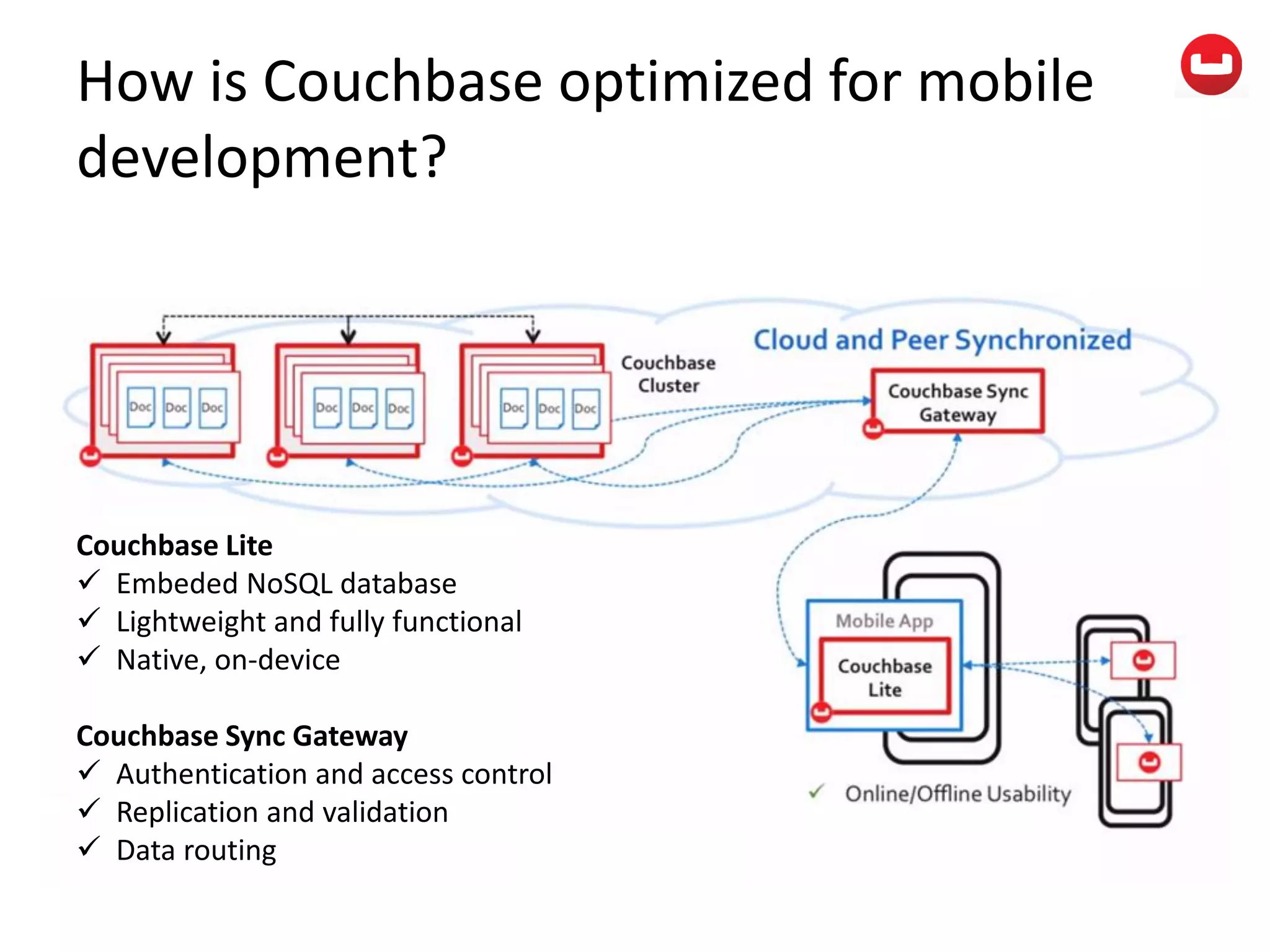
The document provides information about Couchbase, a NoSQL database. It discusses Couchbase's key-value data model and how data is stored and accessed. The main architectural components are nodes, clusters, buckets, and documents. Data is accessed via reads, writes, views, and N1QL queries. Couchbase provides scalability and high performance through its caching architecture and append-only disk writes.














![References
• [1] “CB030 Essentials of Couchbase NoSQL
Technology” [Online]. Available :
https://training.couchbase.com/online](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/couchbase-160429030813/75/Couchbase-Yet-Another-Introduction-63-2048.jpg)