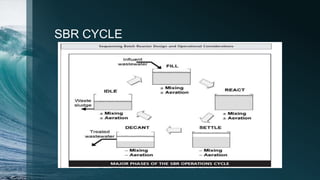
This document provides information on sequencing batch reactors (SBRs), a type of activated sludge wastewater treatment process. SBRs combine treatment steps into a single basin and operate in time-based cycles rather than with separate tanks. The basic SBR treatment process involves five sequential steps - fill, react, settle, decant, and idle. SBRs offer advantages like a smaller footprint and ability to adjust treatment cycles for nutrient removal. Key factors to monitor for effective SBR operation include pH, alkalinity, and effluent quality parameters. The document also outlines best practices for plant operation and provides guidance on products to avoid discharging to the system.