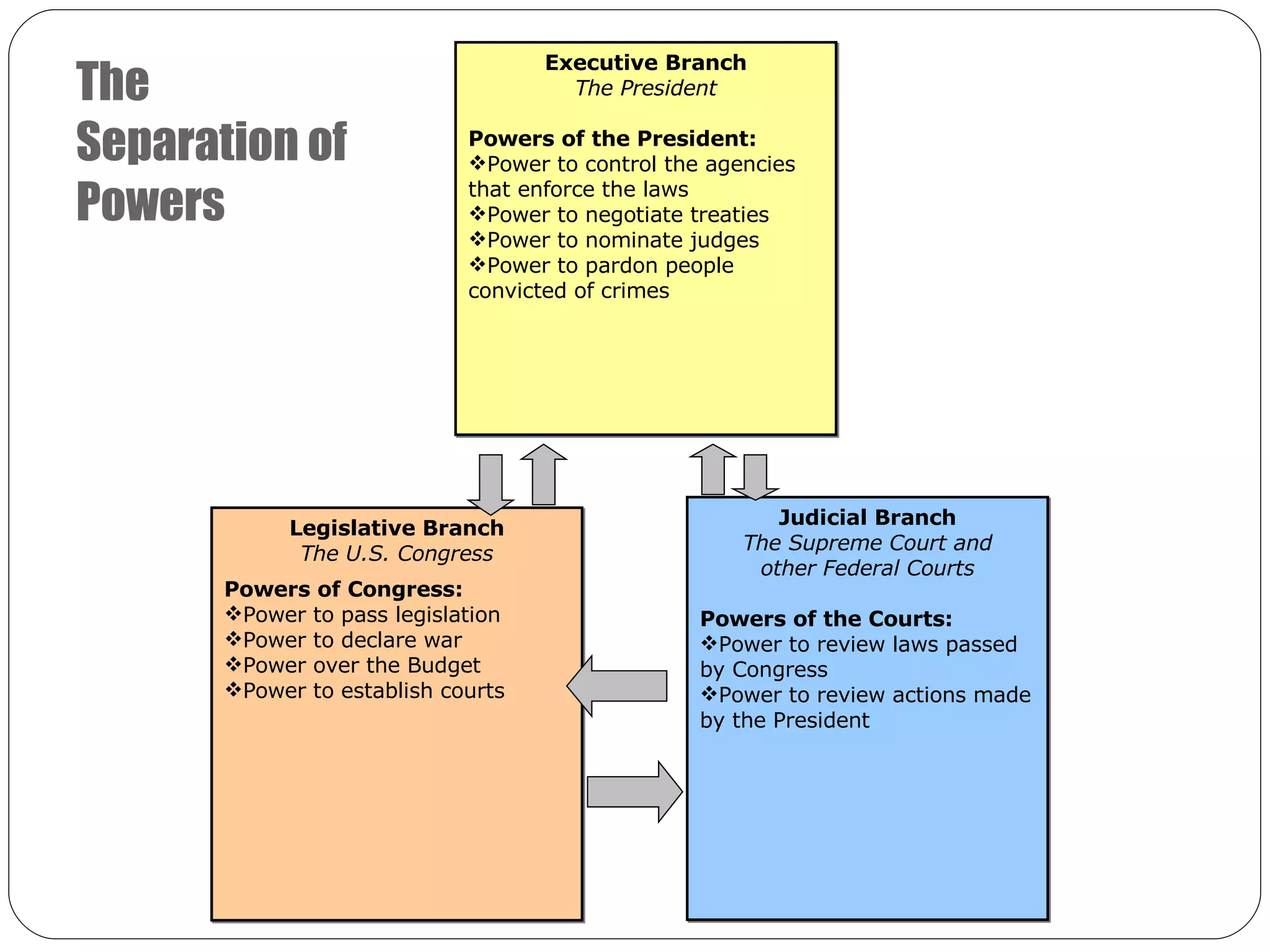
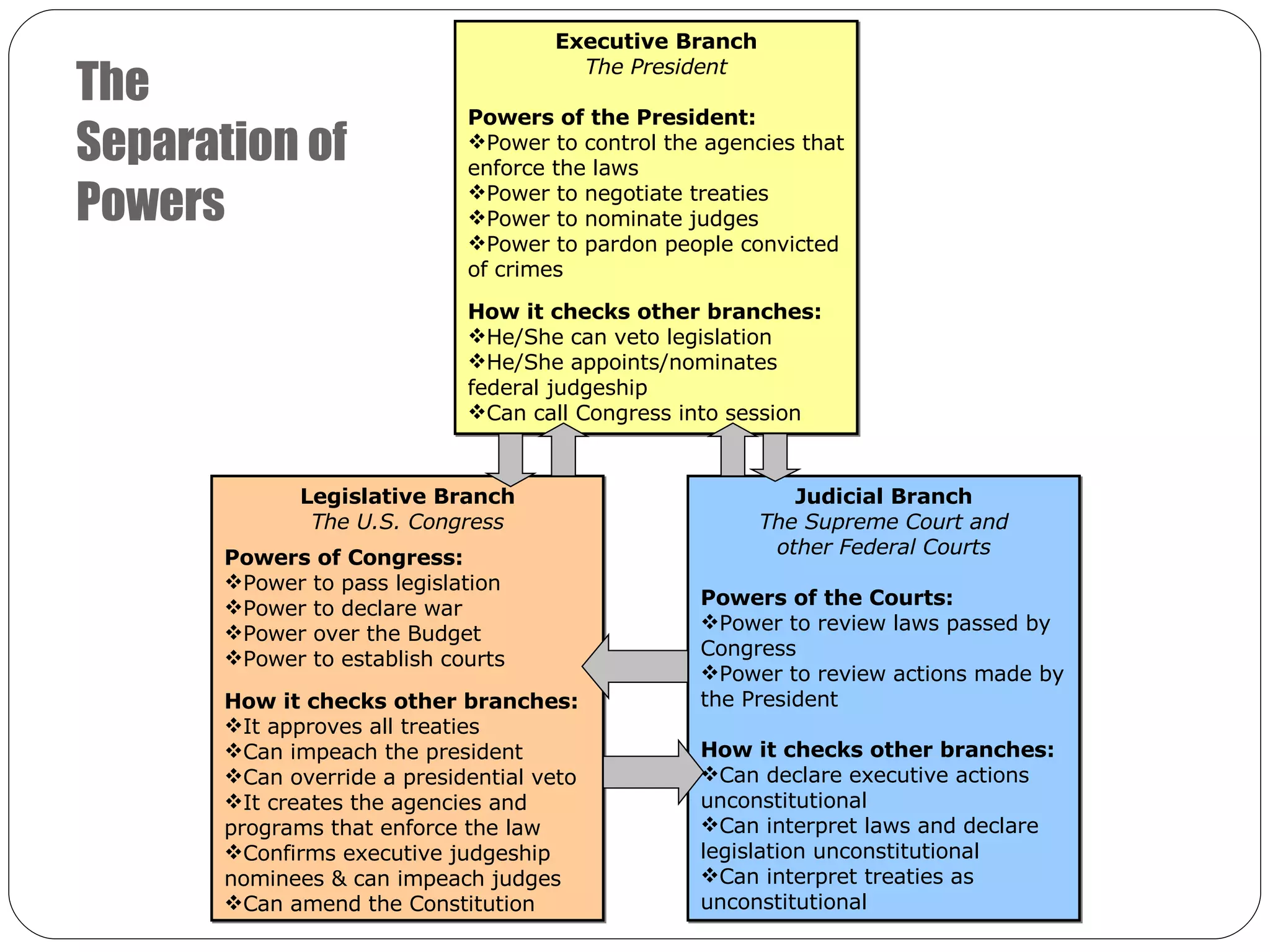
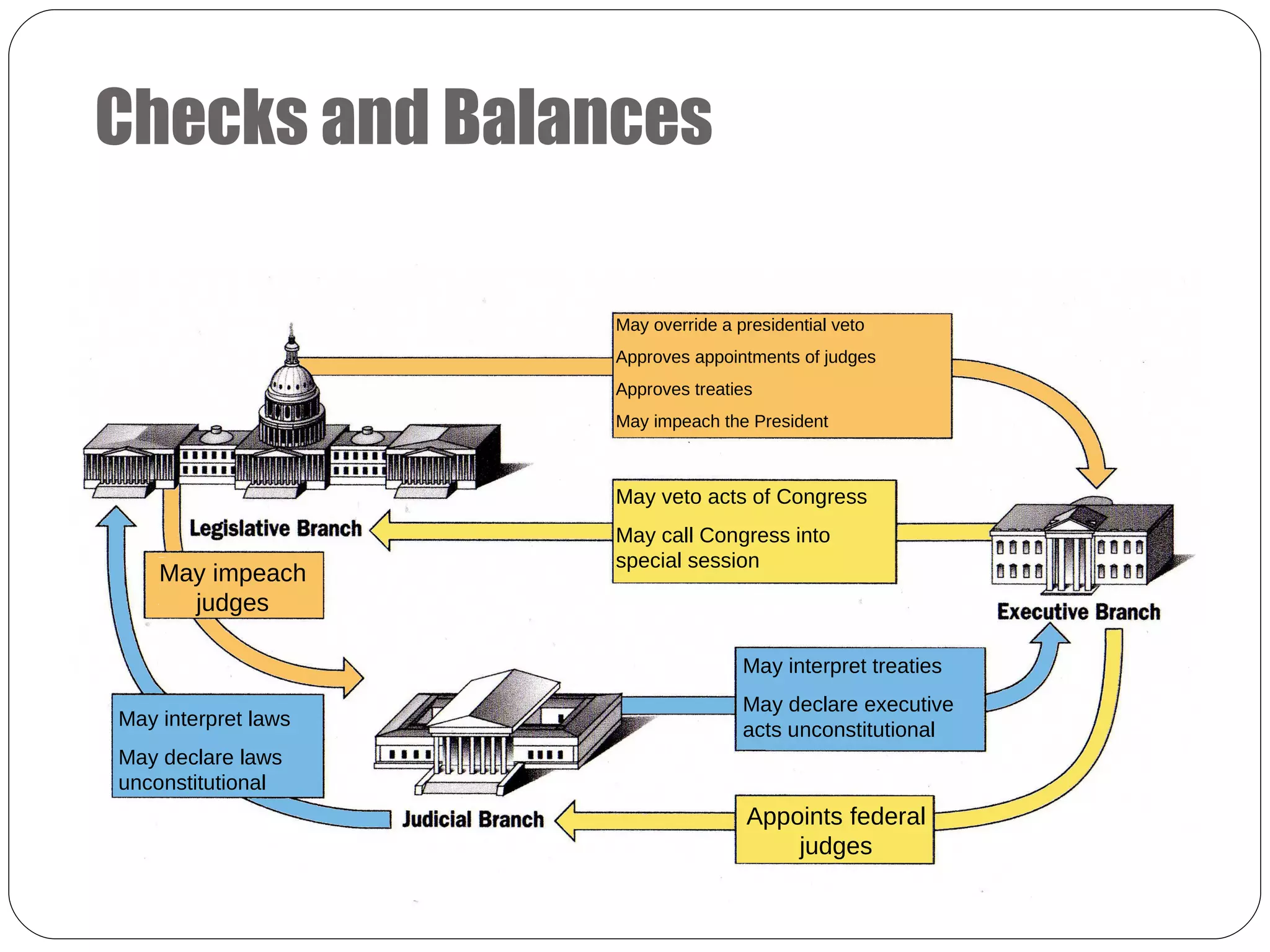
The delegates at the Constitutional Convention divided power between the national and state governments, and also separated the national government into three branches: the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. This created a system of separation of powers. To prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful, the founders established a system of checks and balances, allowing each branch to limit the powers of the others. For example, Congress checks the president through the power to override a veto or impeach, while the president checks Congress through the veto power and ability to call special sessions. This system aimed to prevent tyranny and protect individual liberties.