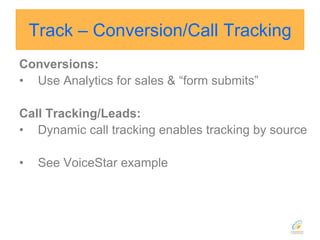
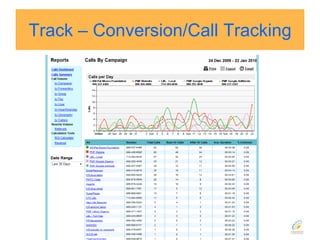
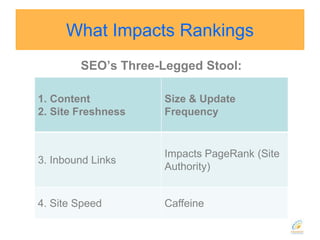
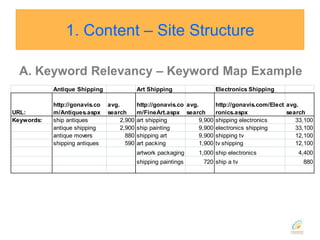
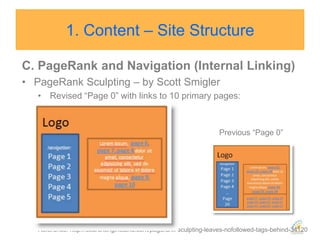
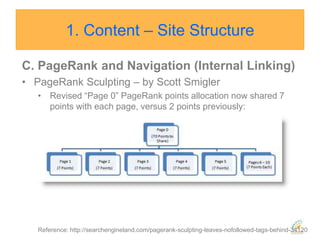
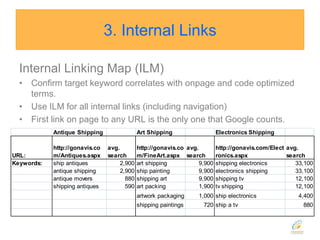
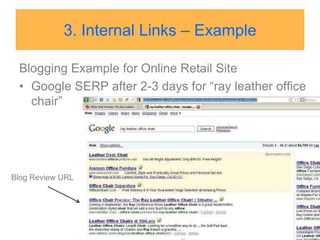
This document discusses strategies for search engine optimization (SEO). It emphasizes the importance of tracking key metrics like keyword rankings, site traffic, and conversions. Content and site structure are also important factors for SEO success. Content should be relevant to target keywords and the site structure should be optimized for both users and search engines through internal linking. Regularly adding fresh content is important to keep search engine bots crawling and indexing the site. Building high-quality inbound and internal links also impacts search engine rankings.












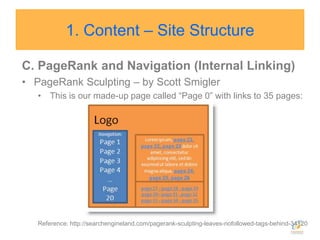
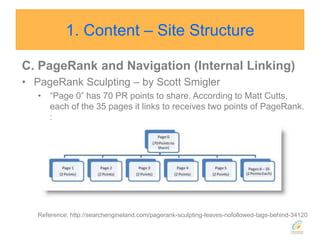
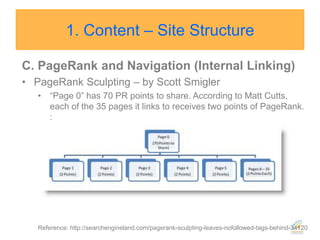

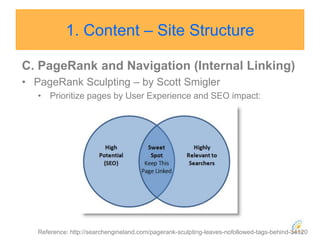










![Google introduced rel=nofollow in 2005 so that NoFollowed links “won’t get any credit when we [Google] rank websites in our search results.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seo2010-100821192655-phpapp01/85/Seo-2010-39-320.jpg)