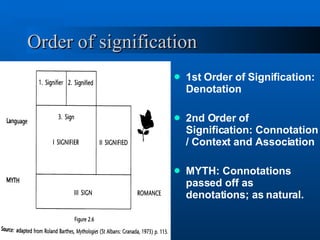
This document provides an introduction and overview of semiotics and communication theory. It defines semiotics as the study of signs and meaning-making processes in communication. Some key concepts discussed include Jakobson's model of communication, codes, anchorage, orders of signification, and myth. Roman Jakobson's model of communication involves an addresser, addressee, message, context, contact, and code. Codes are systems of symbols and meanings agreed upon within a society. Anchorage is the process of affixing meanings to images through denotation and connotation.