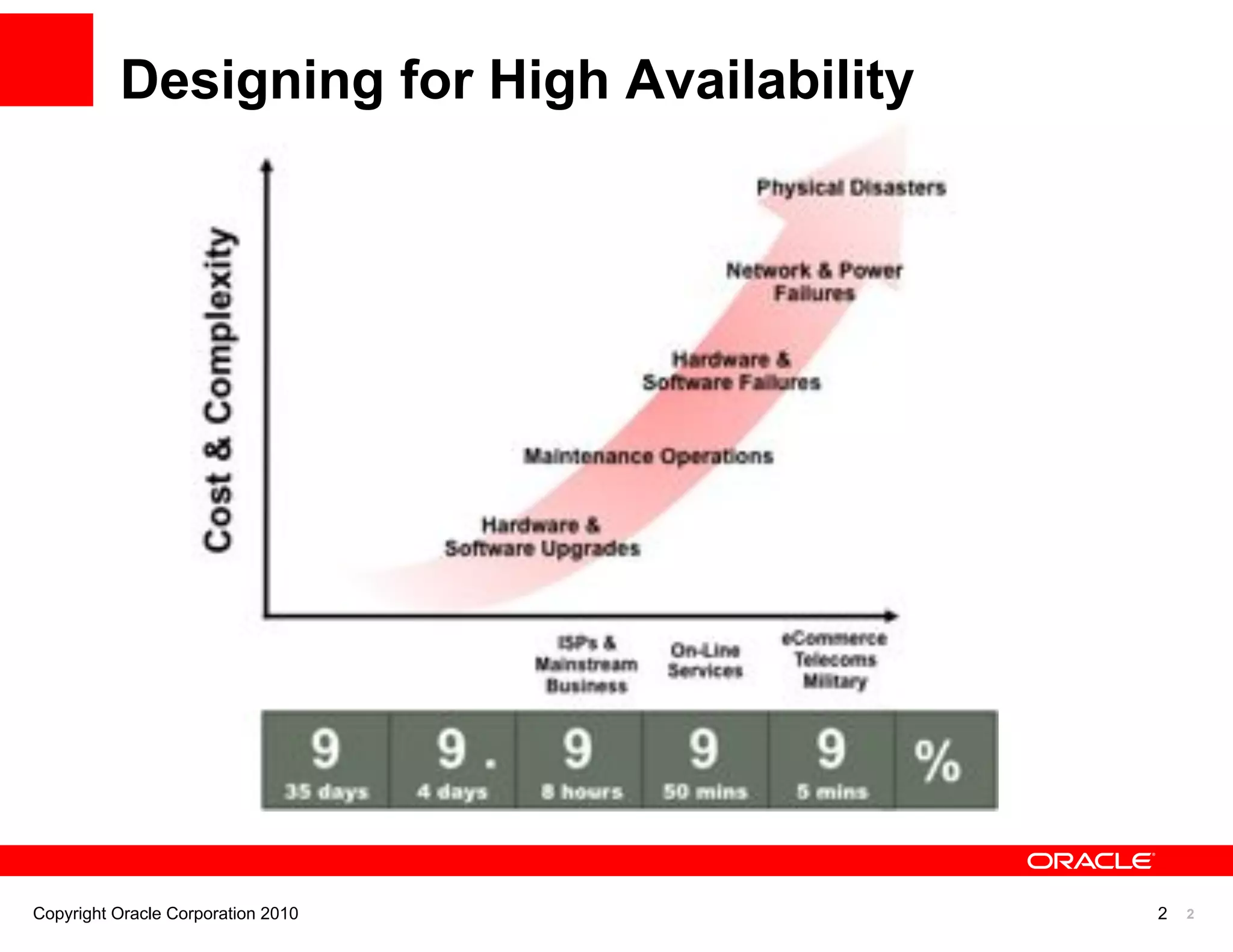
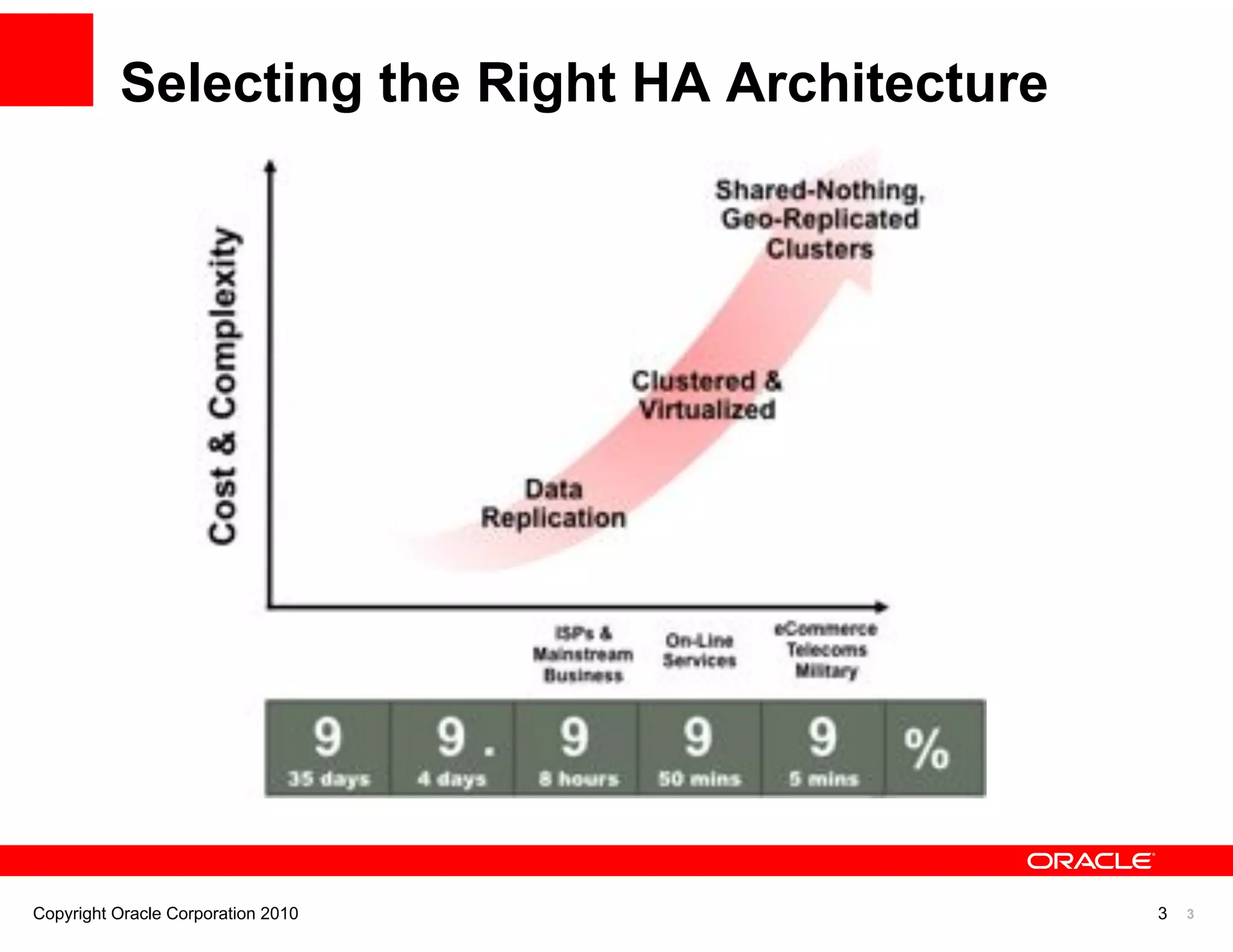
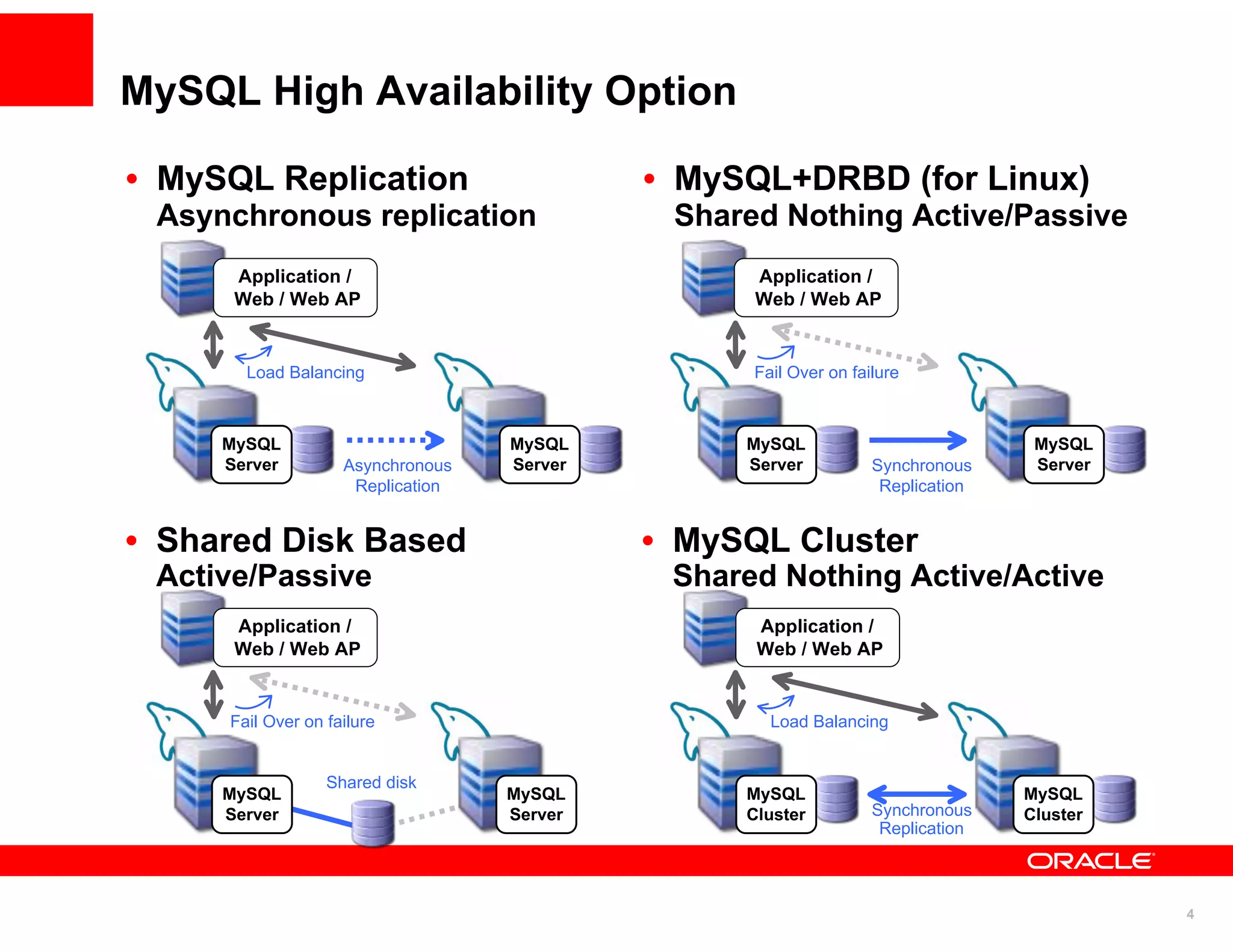
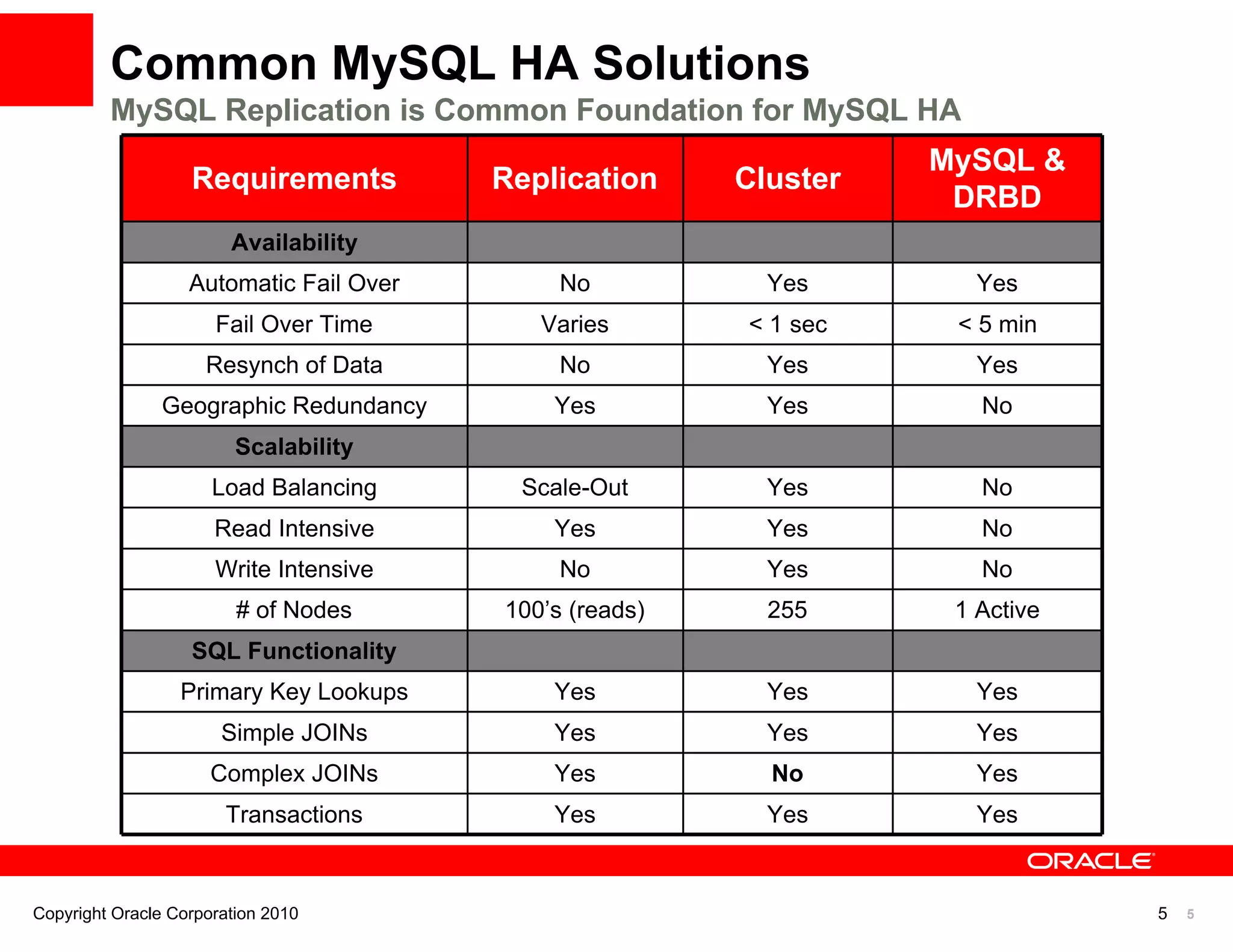
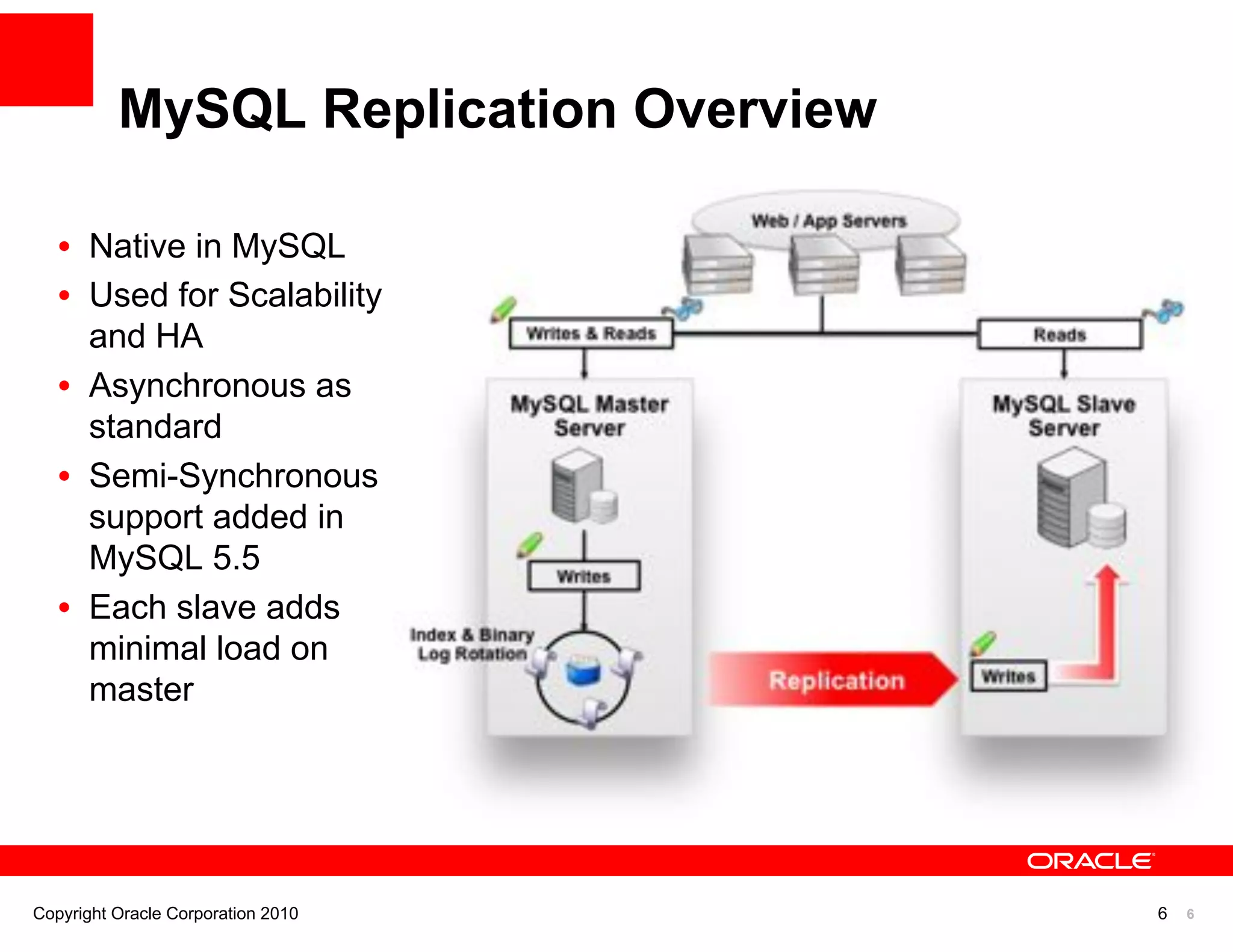
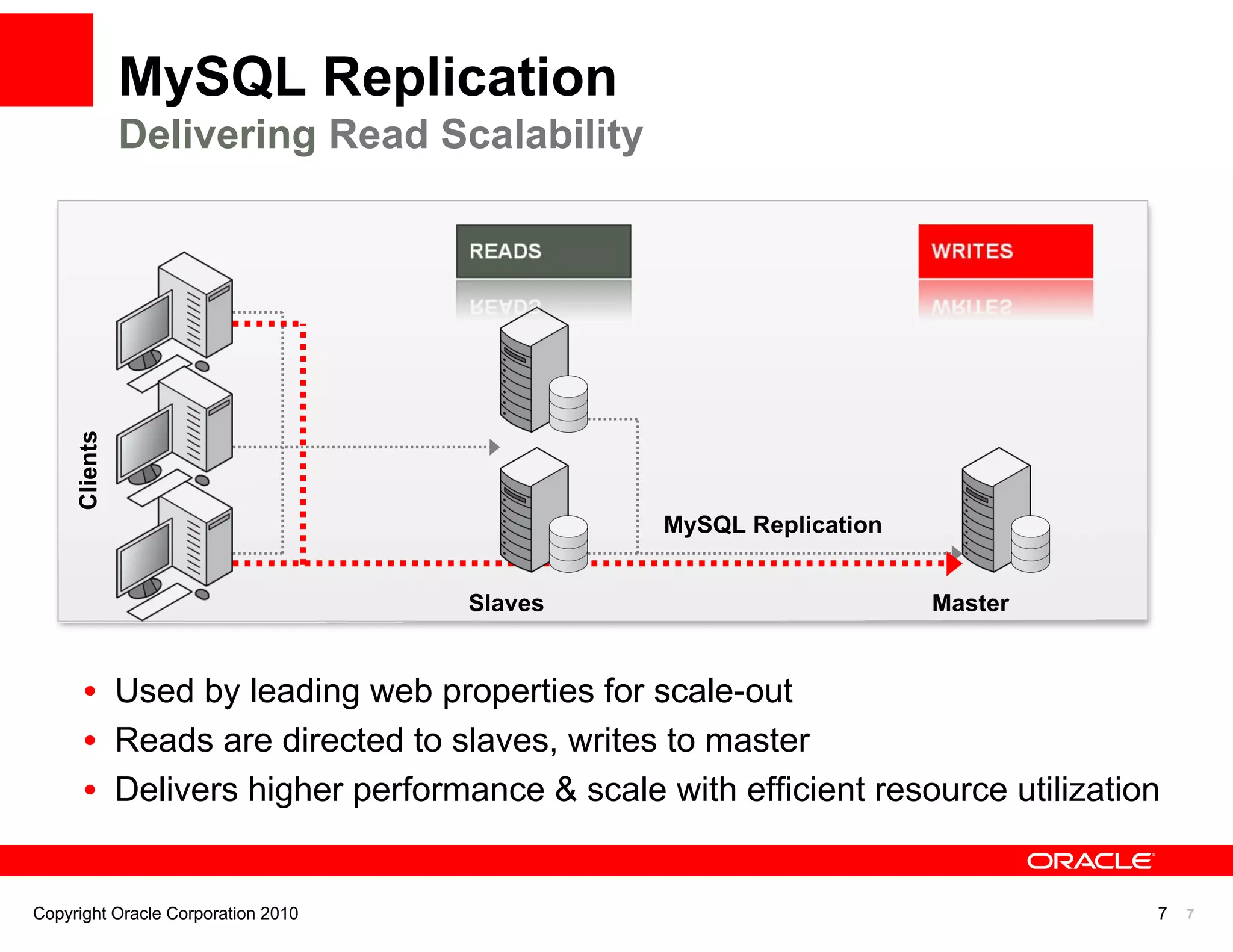
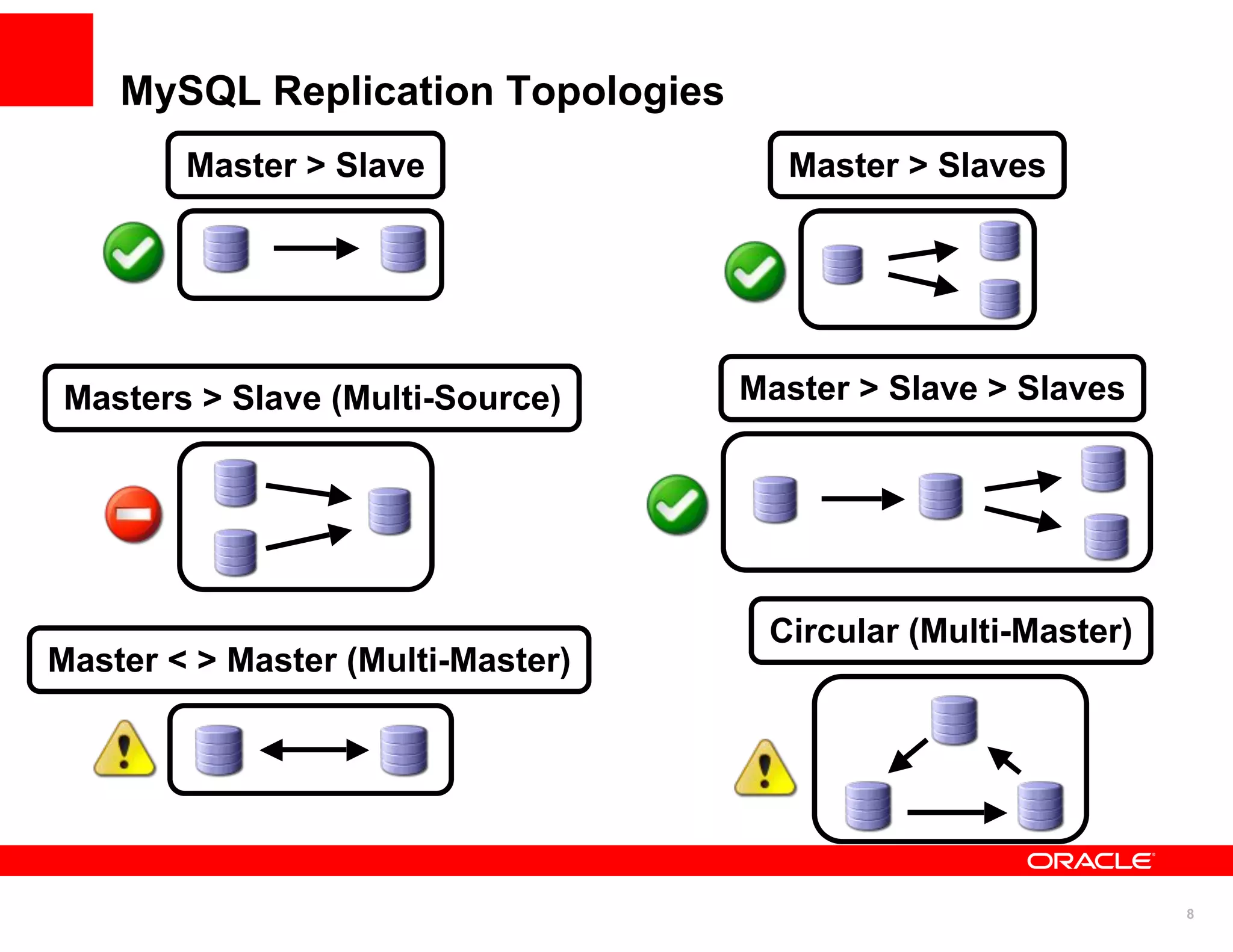
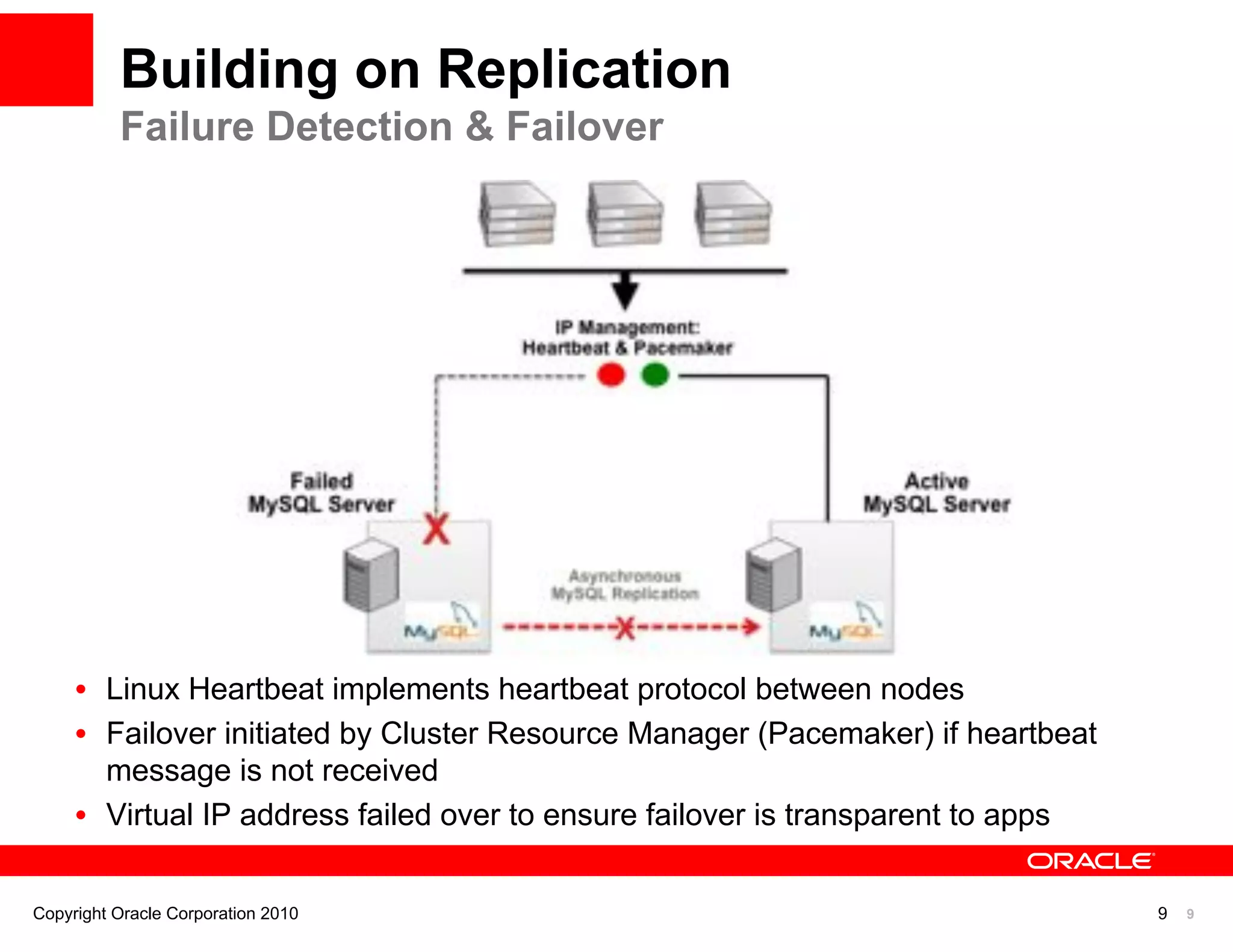
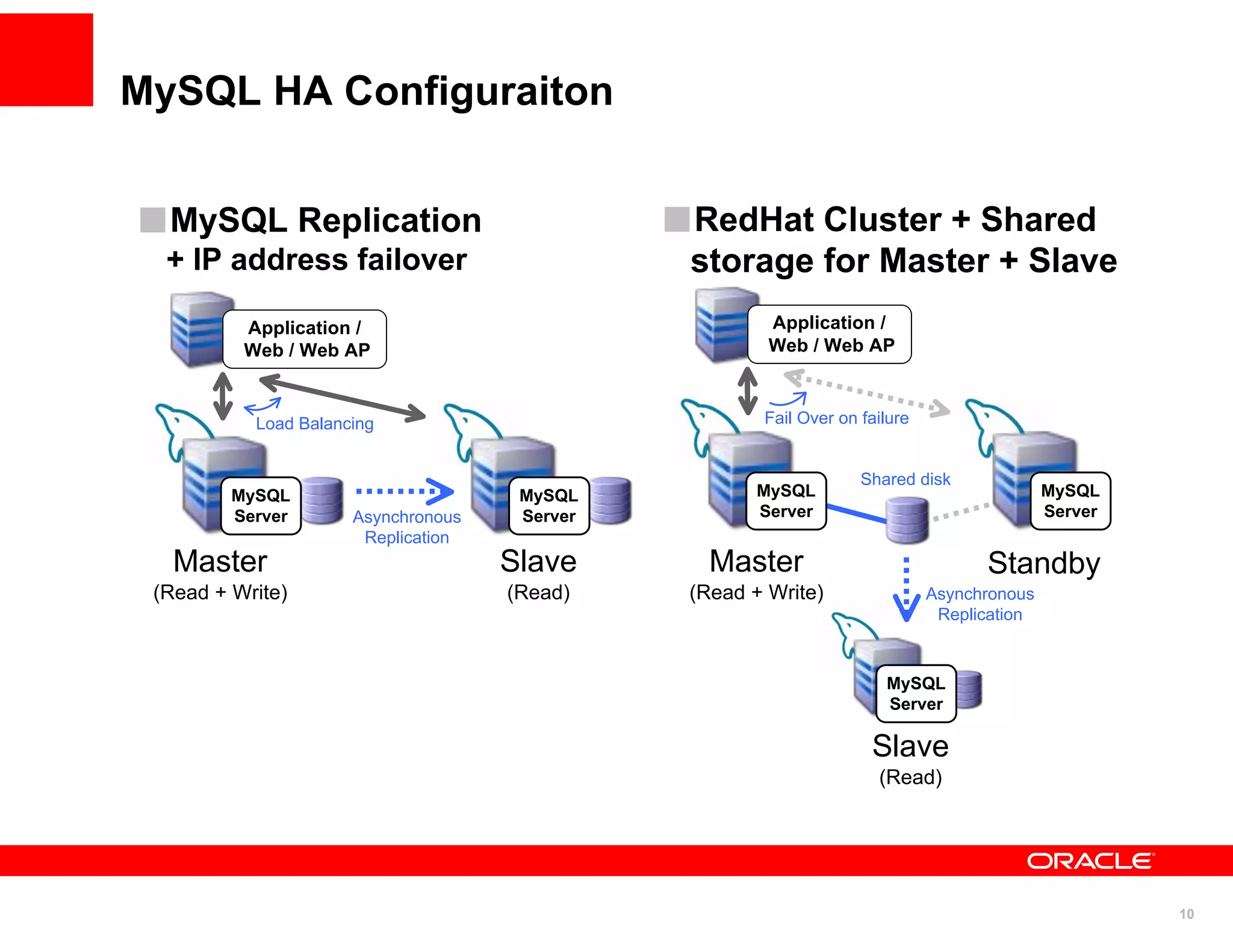
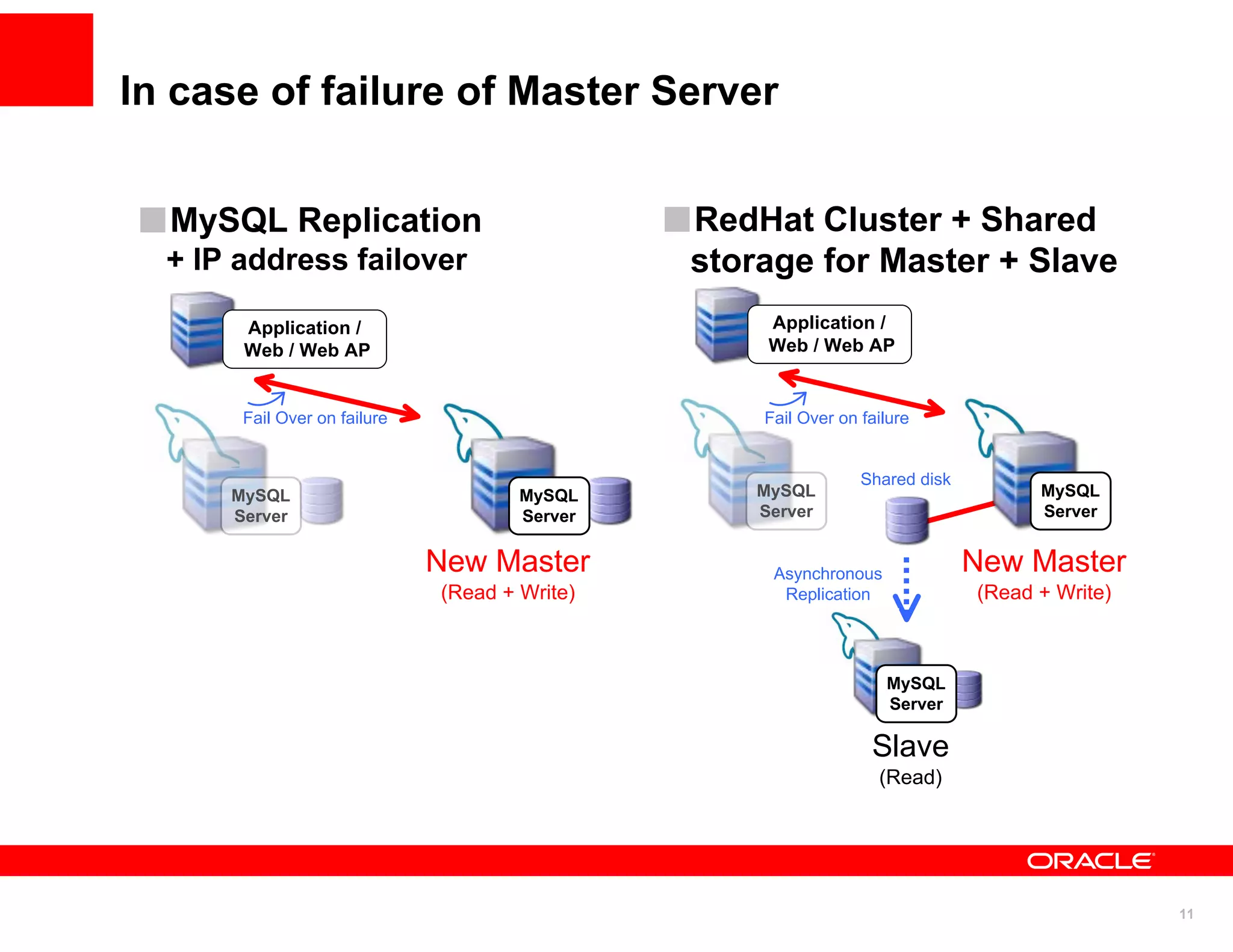
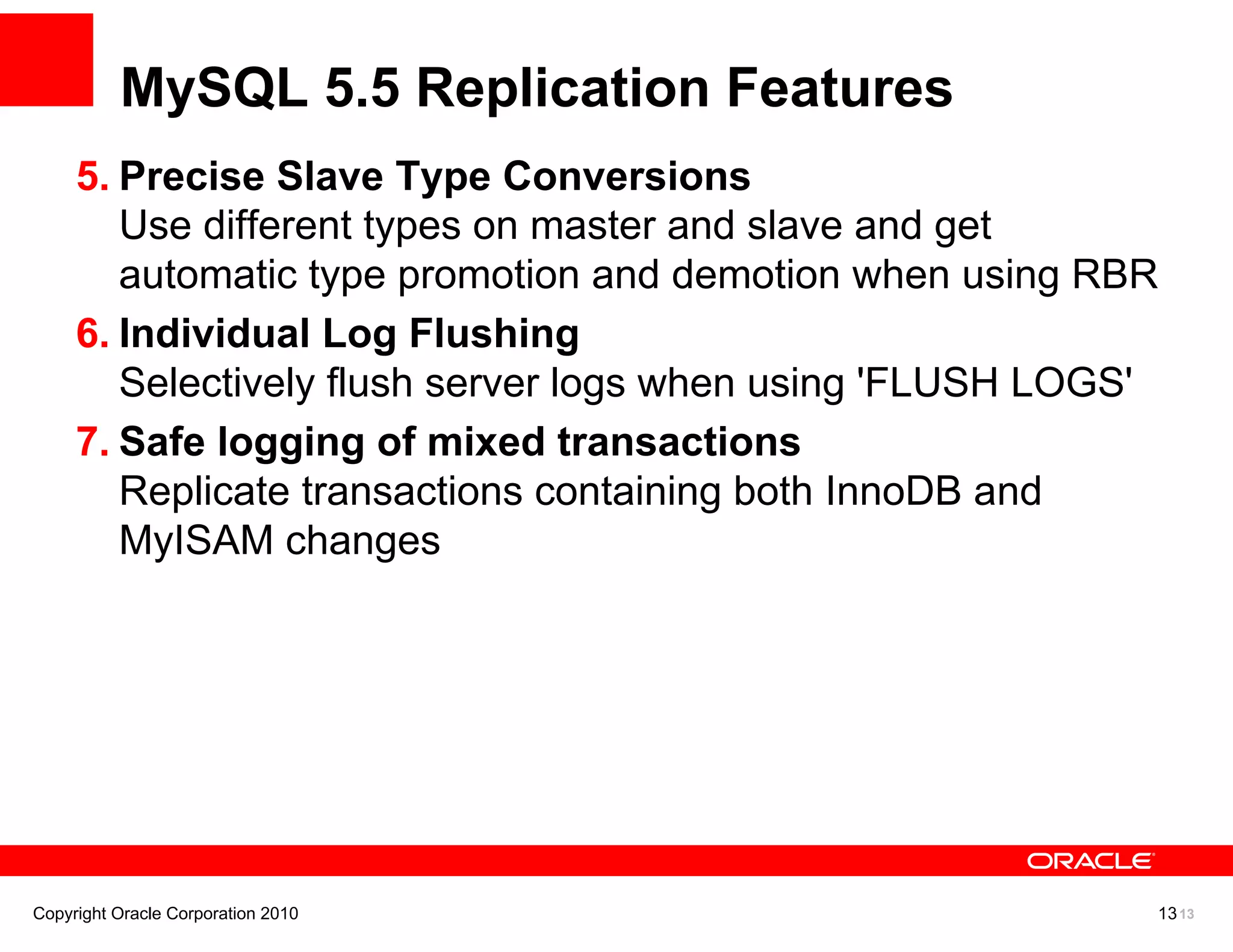
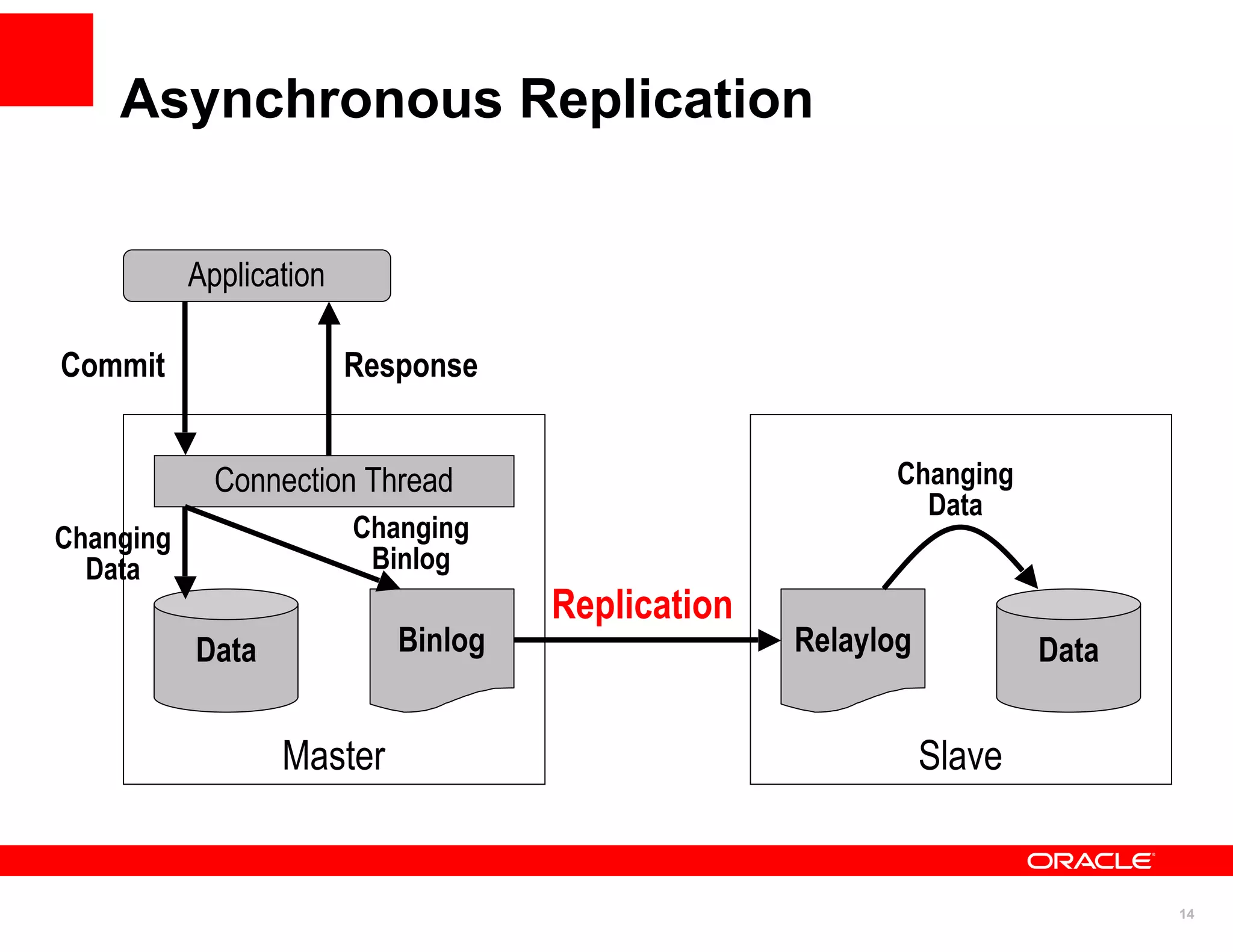
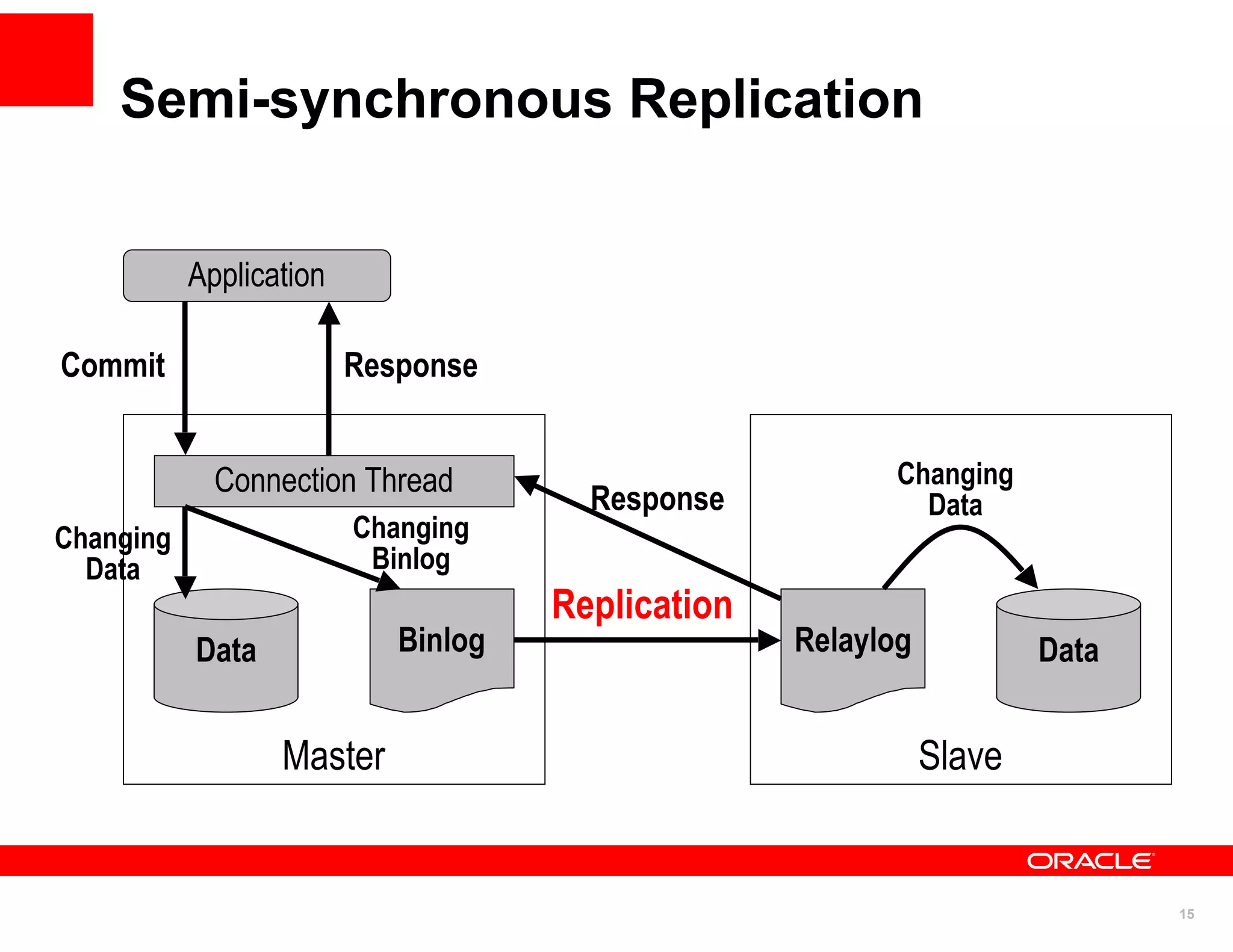
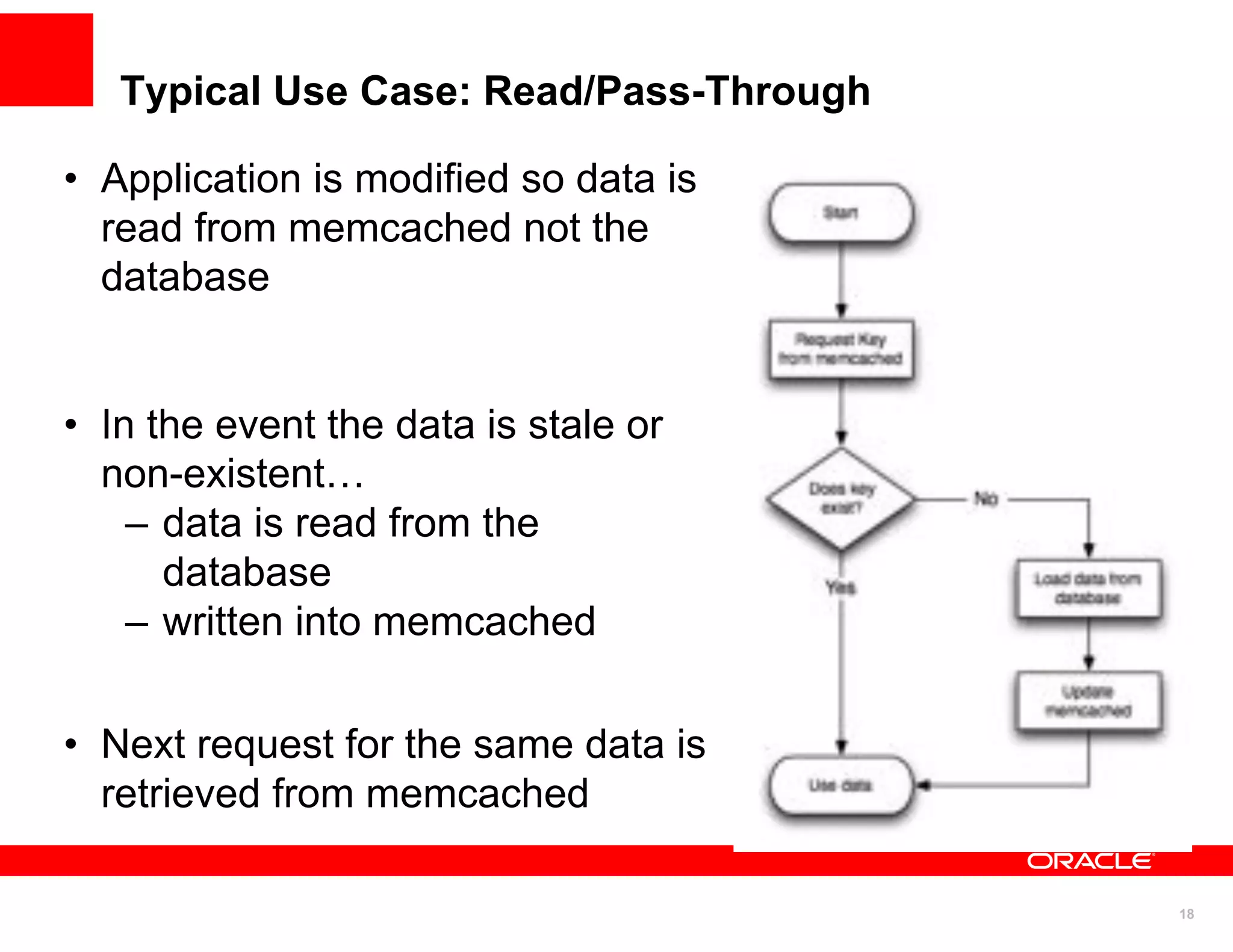
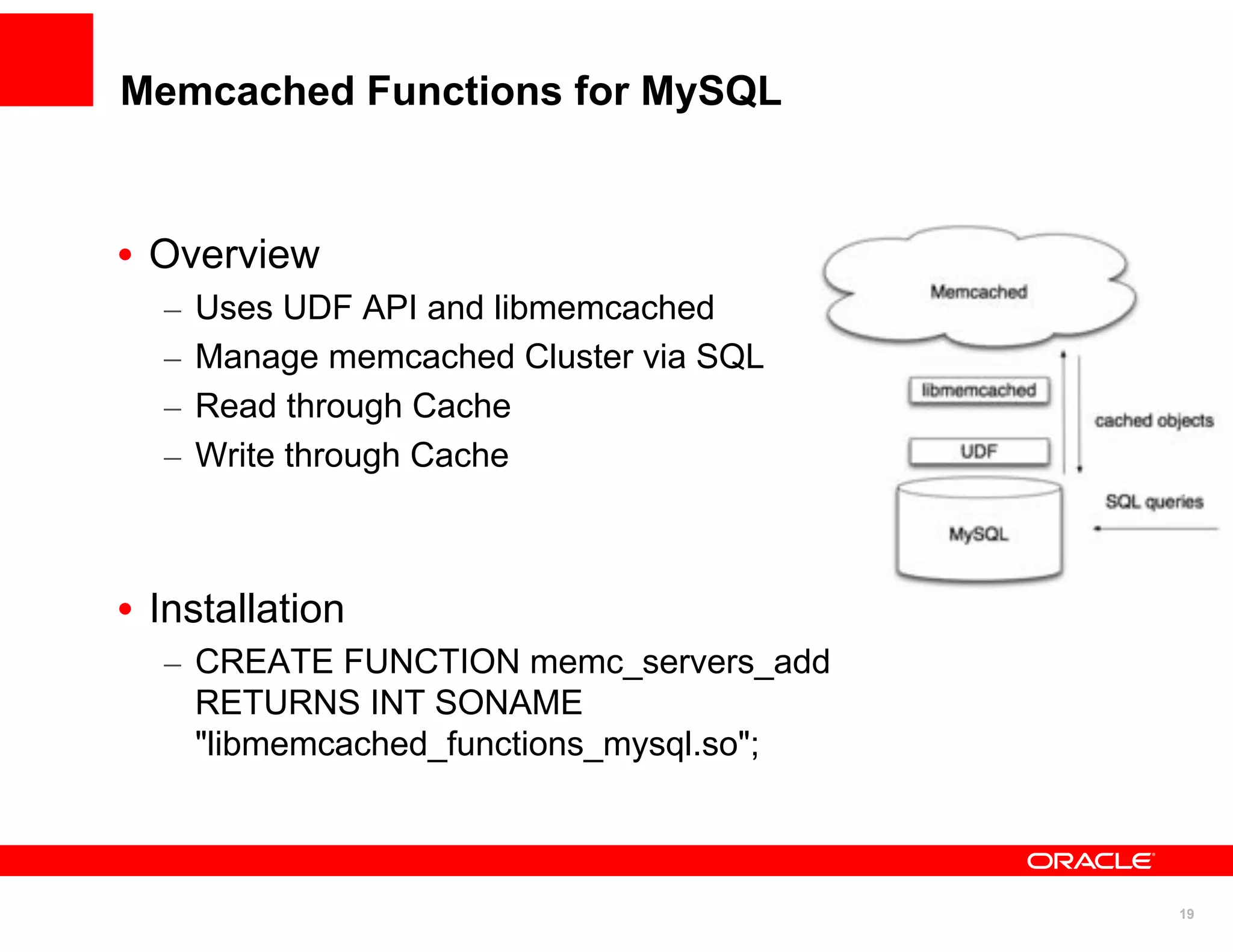
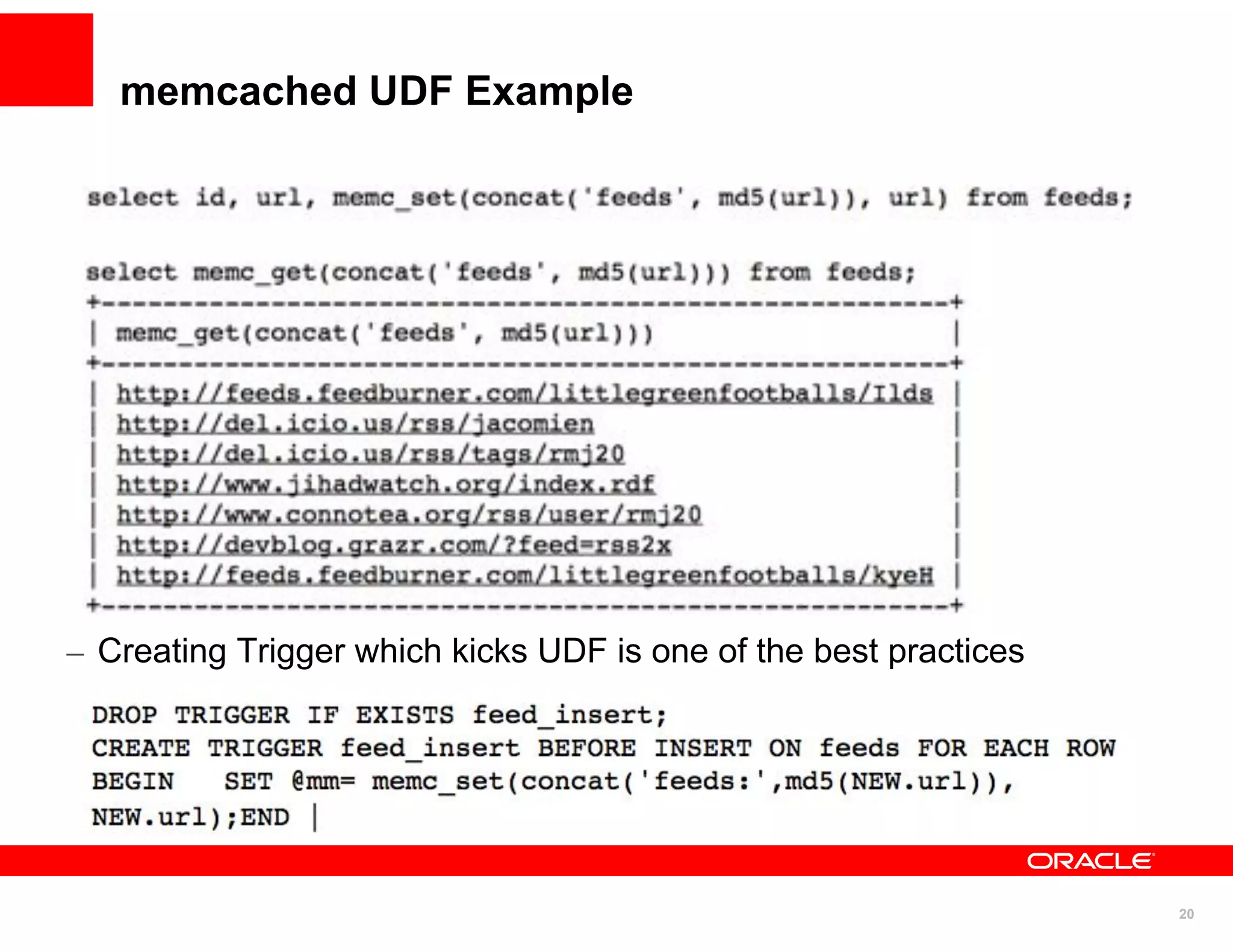
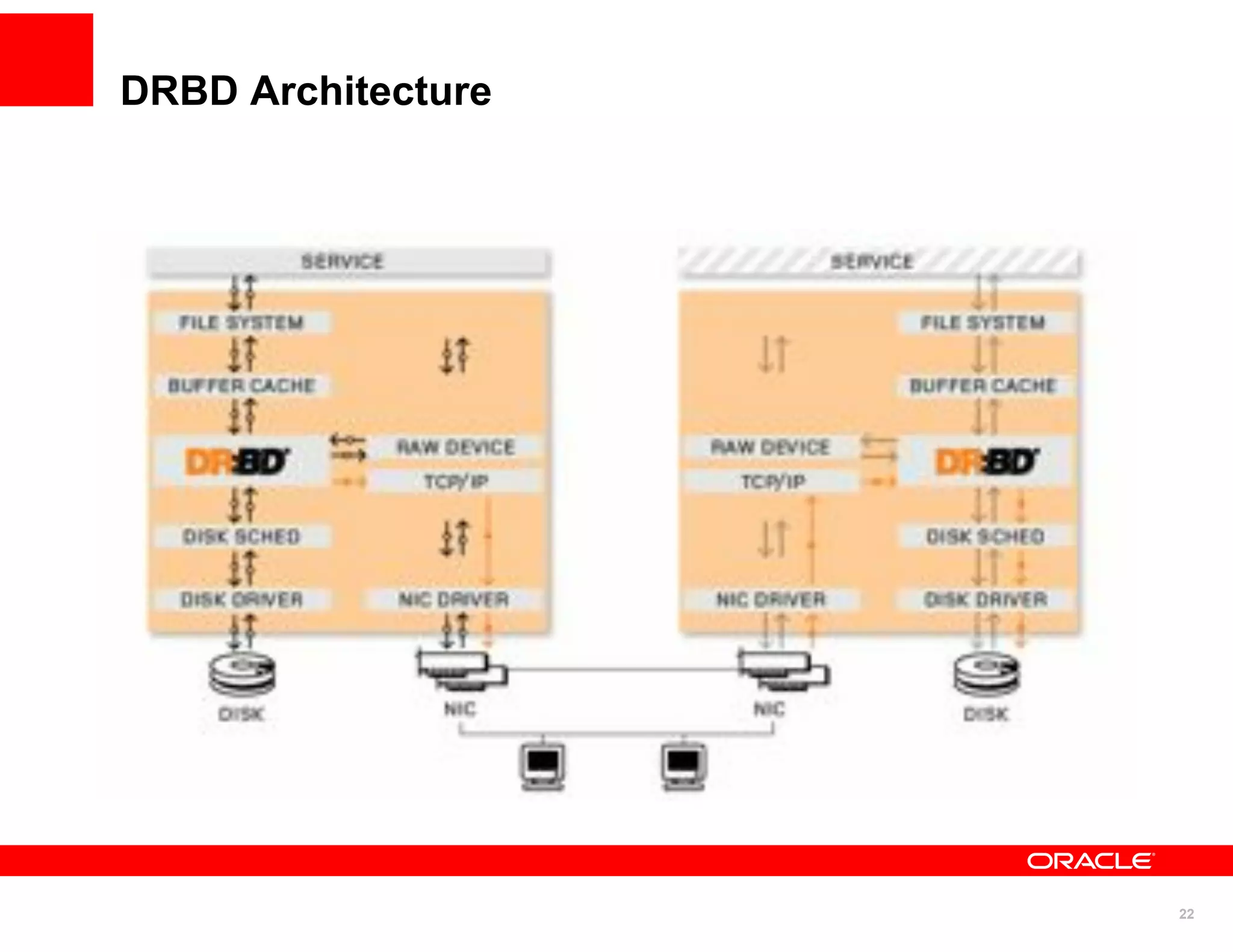
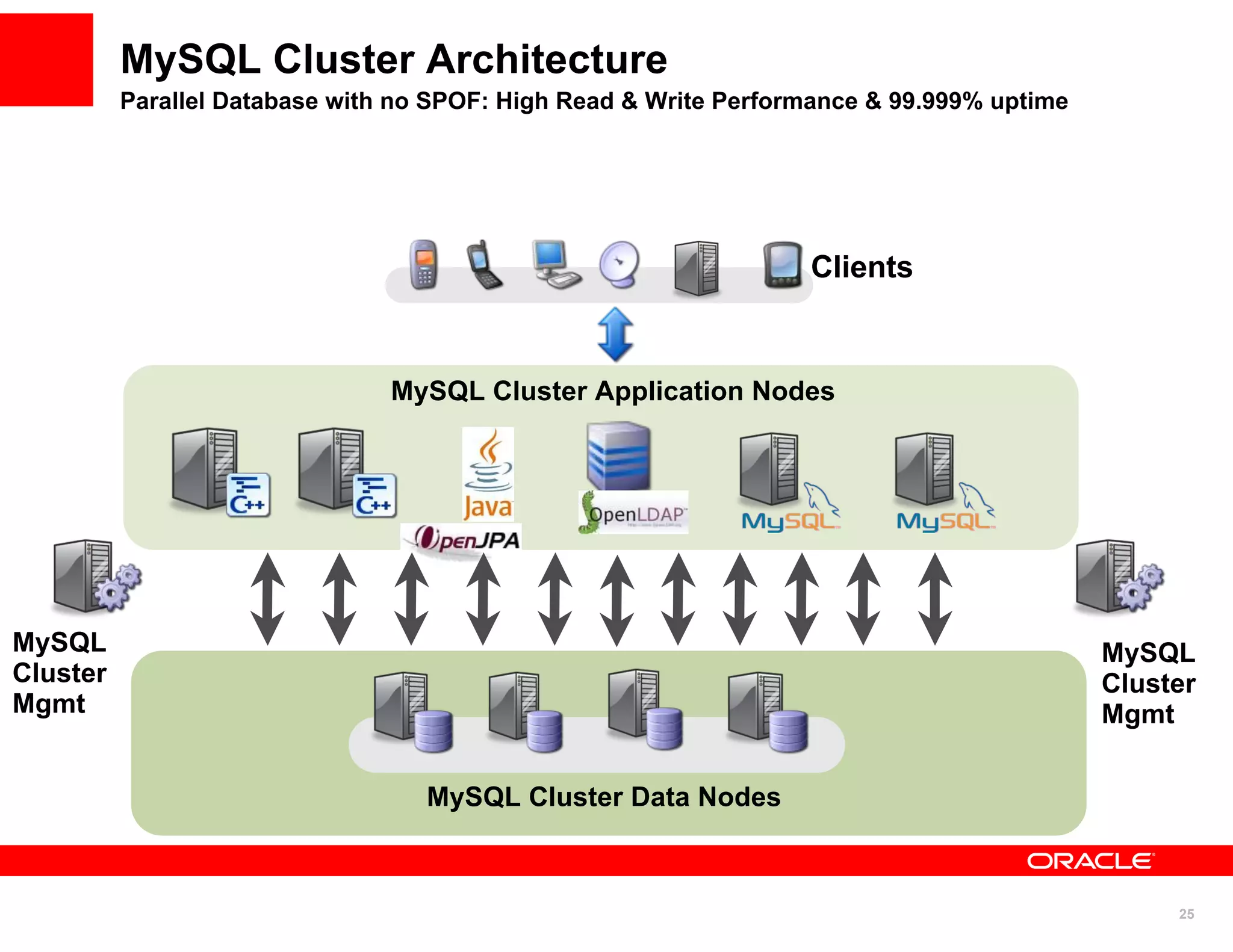
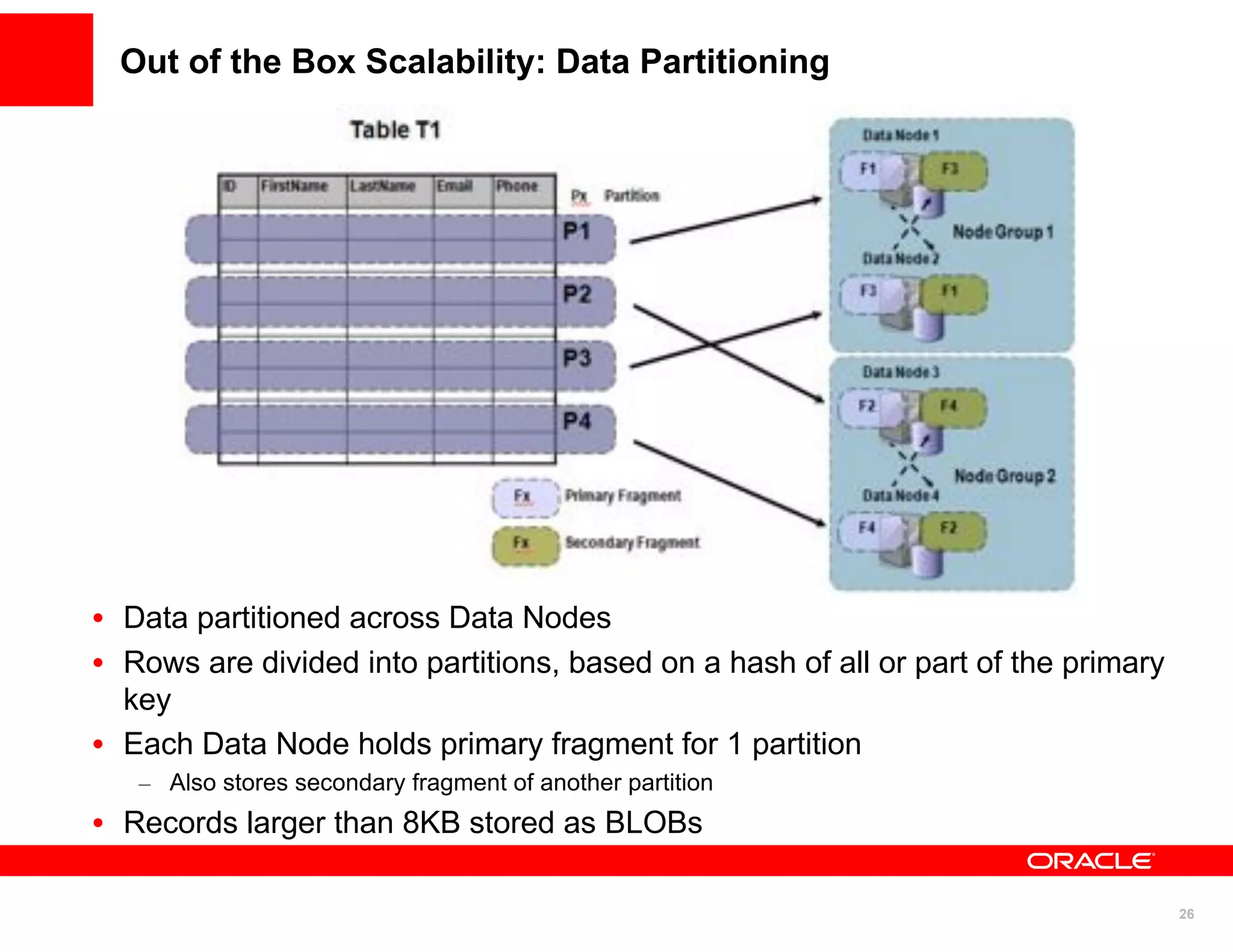
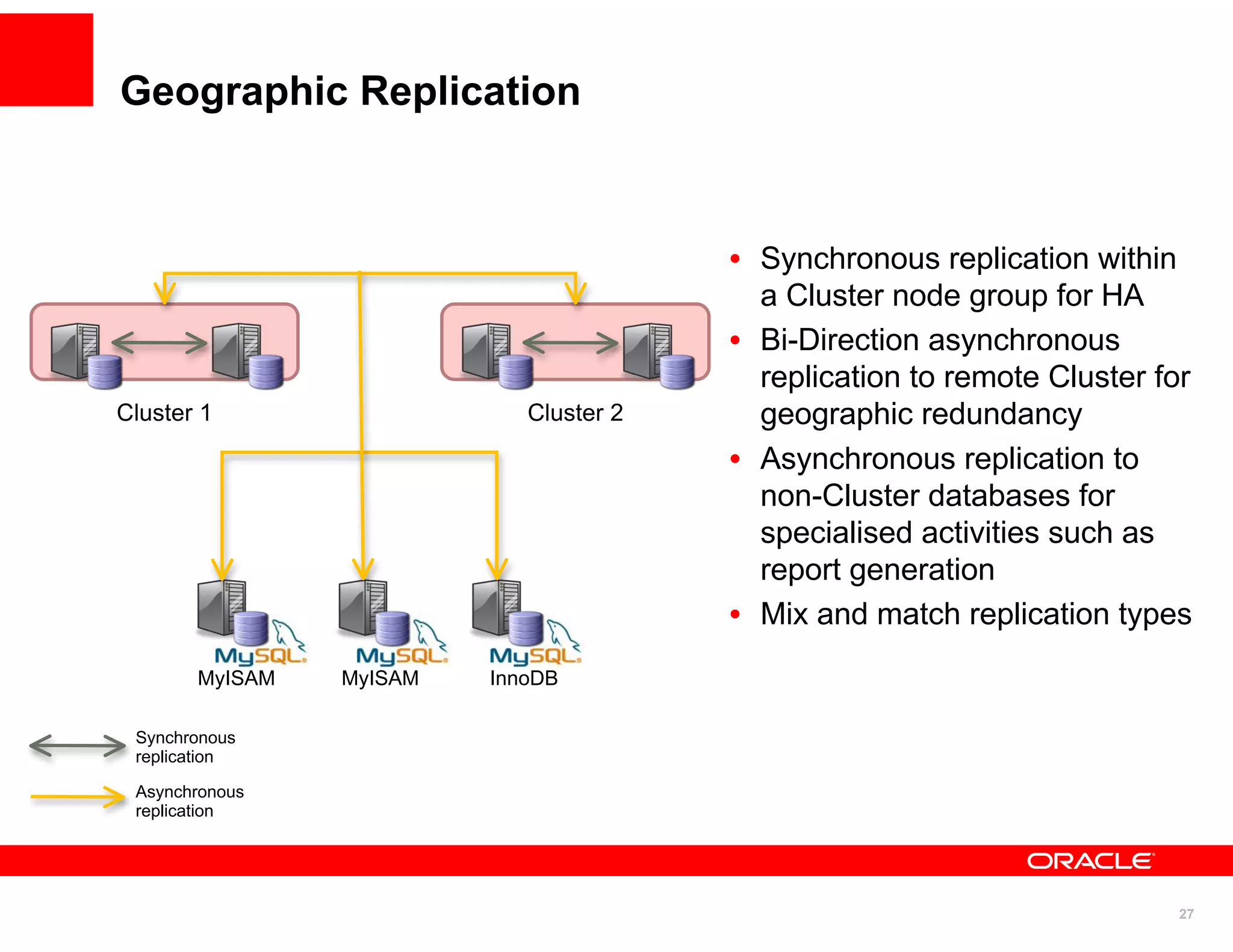
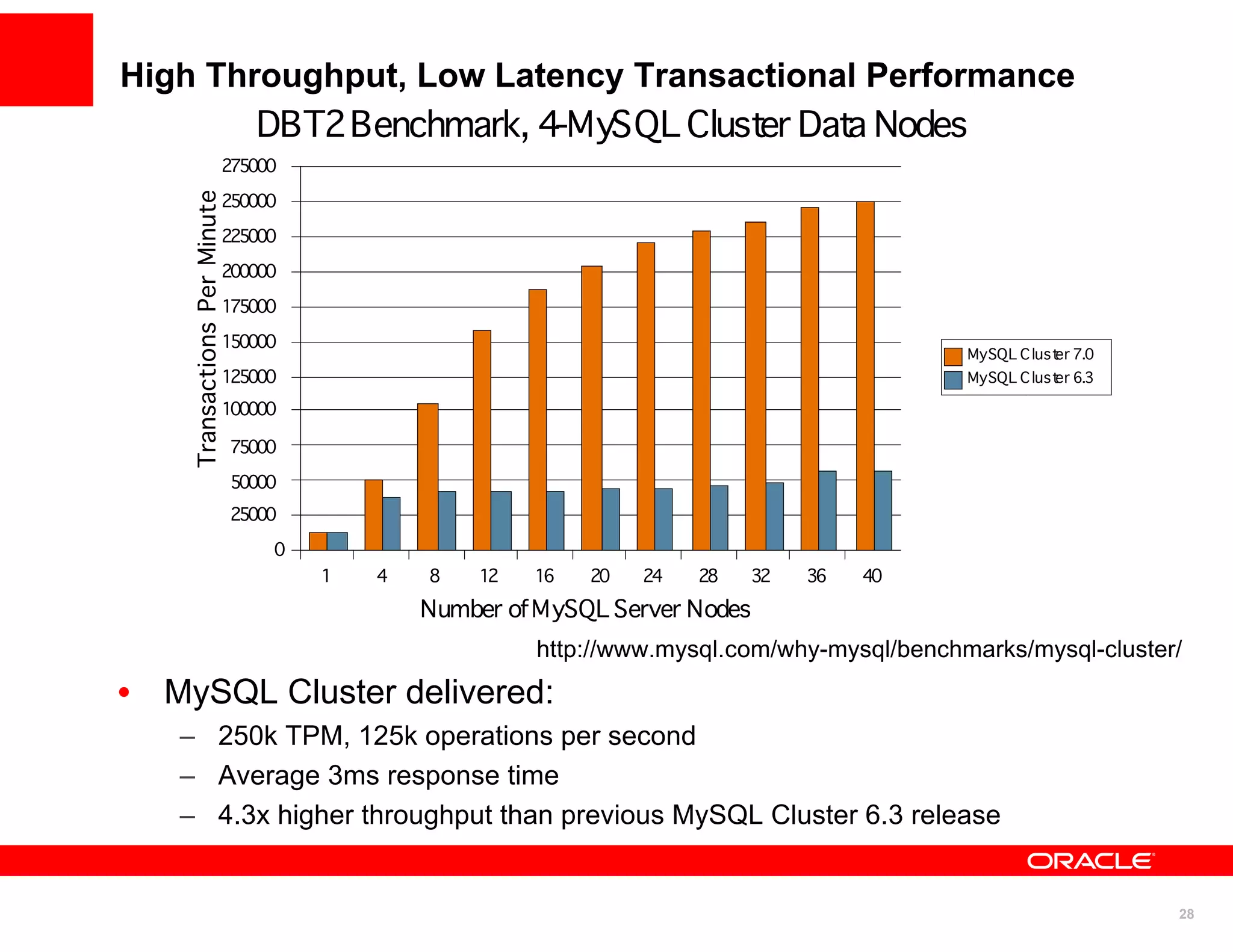
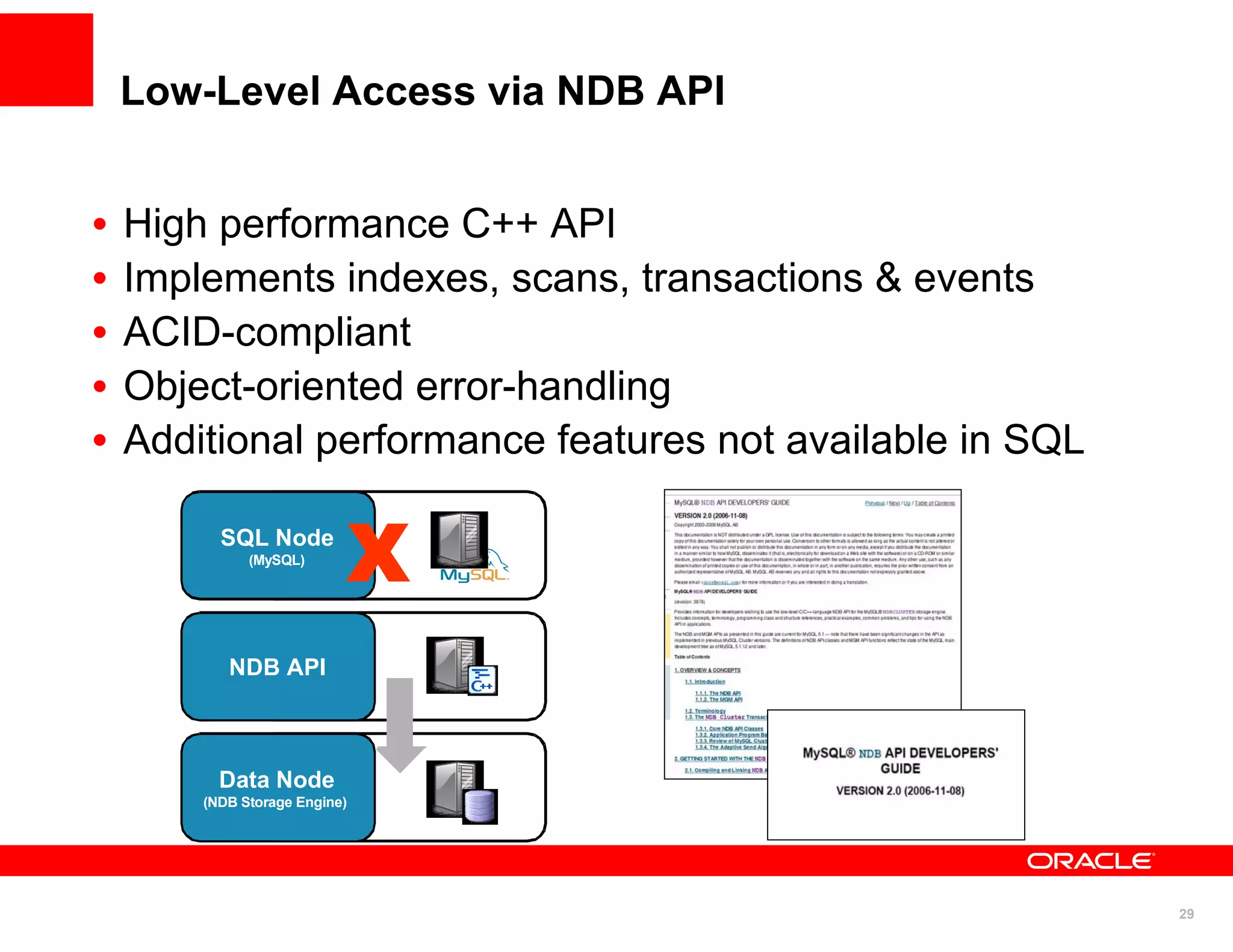
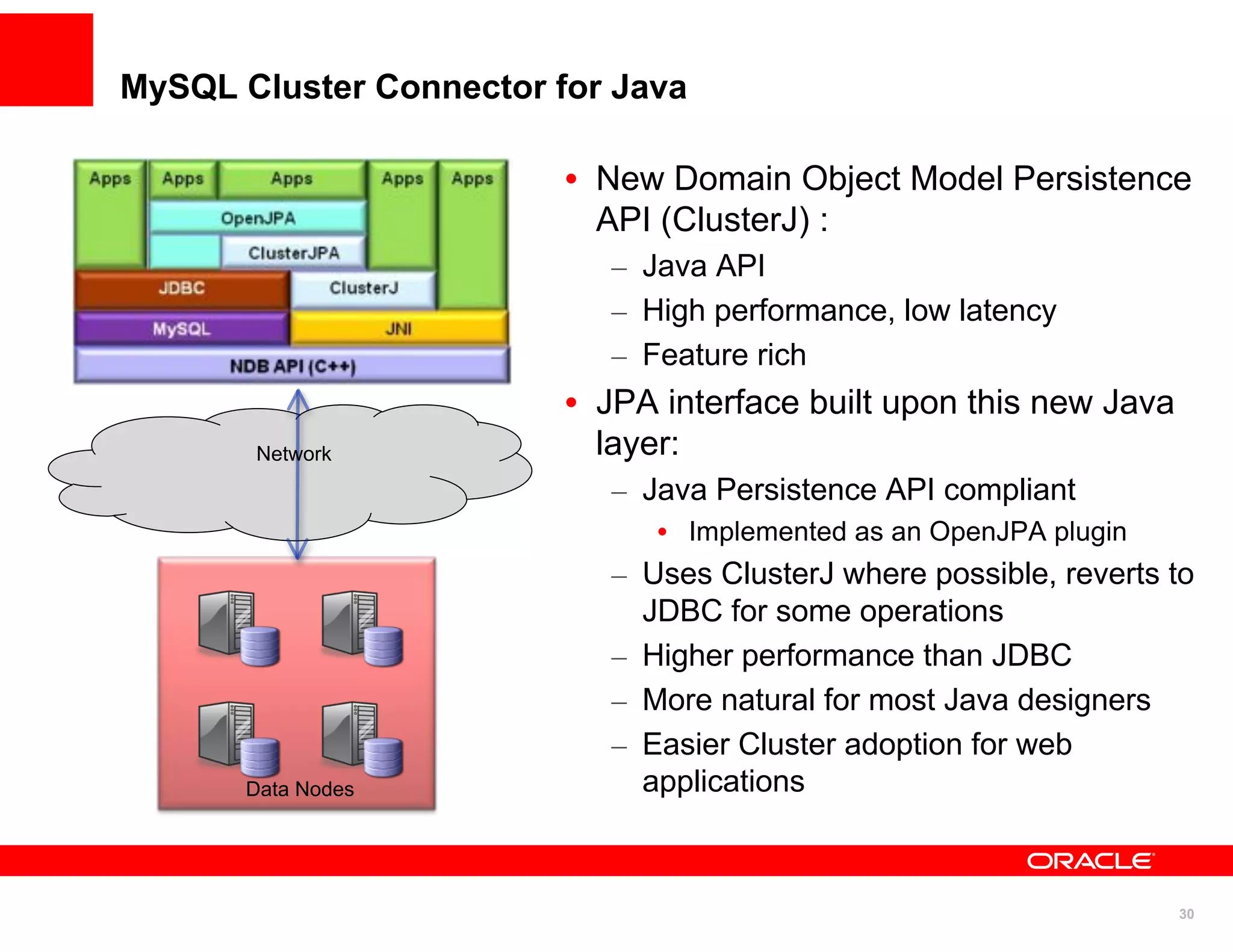
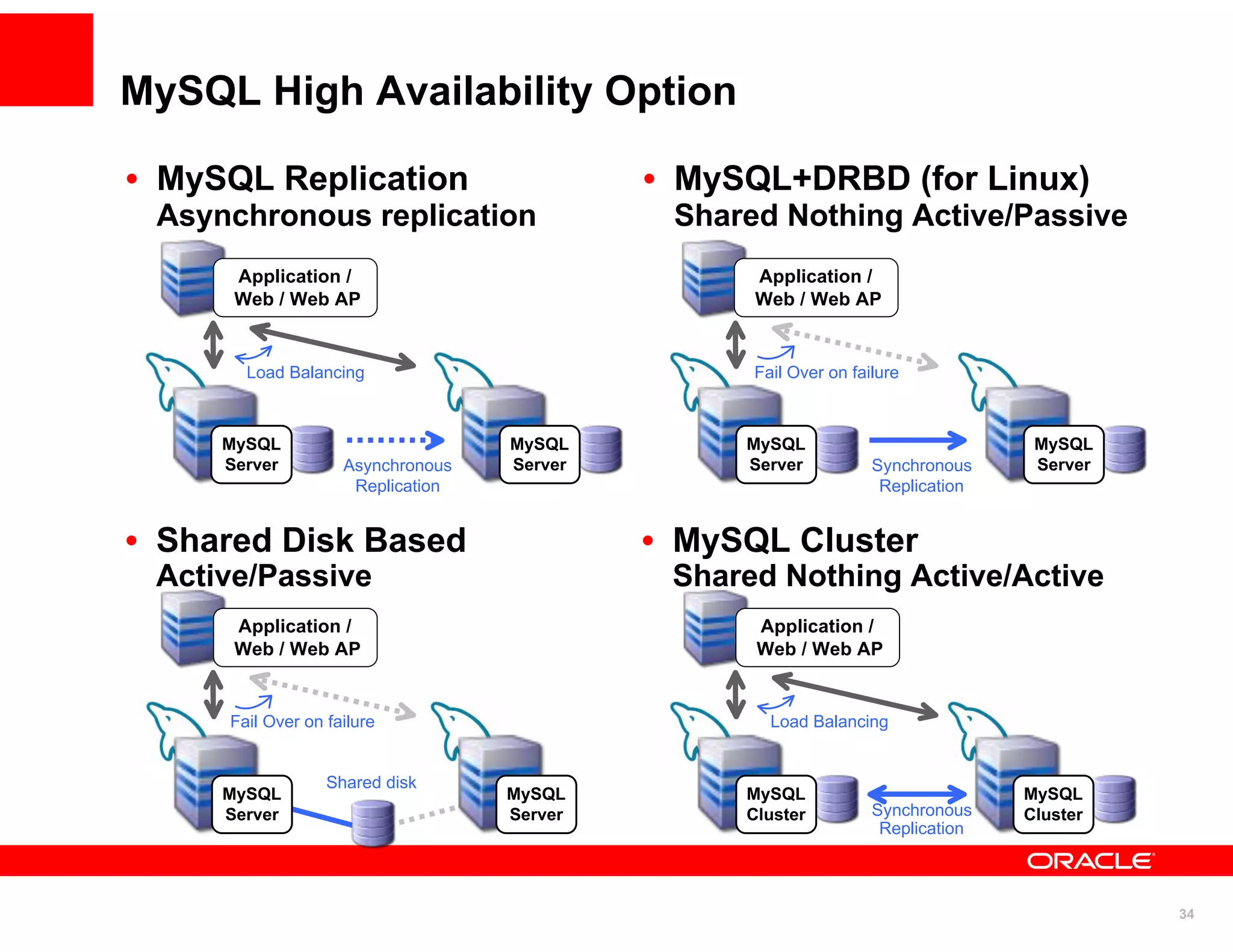
The document discusses various MySQL high availability (HA) solutions, including MySQL replication and MySQL Cluster, outlining their features, configurations, and performance characteristics. It covers different replication topologies, failover mechanisms, and the role of technologies like memcached, illustrating how they improve database performance and scalability. Key case studies highlight the practical benefits of deploying these solutions for high-traffic applications.