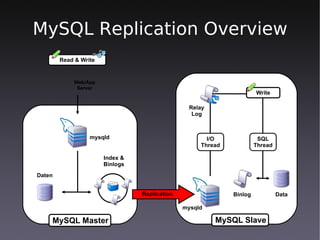
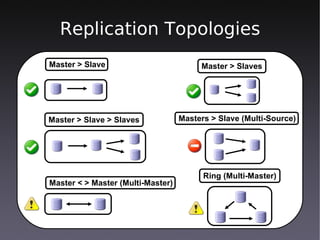
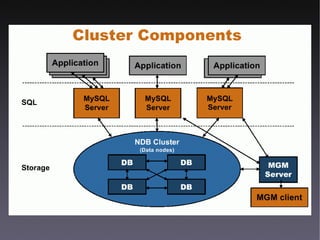
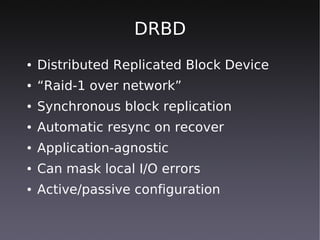
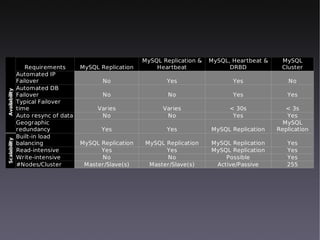
This document discusses high availability solutions for MySQL databases. It covers MySQL replication, MySQL Cluster, and DRBD. MySQL replication allows for one master and multiple slaves but has some limitations. MySQL Cluster provides automatic partitioning and failover between data nodes. DRBD can synchronize block-level replication between nodes for increased availability. The document provides an overview of each technology and their strengths for high availability use cases.